Permitting intra-interface traffic (hairpinning) – Cisco ASA 5505 User Manual
Page 1410
66-2
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Configuration Guide using the CLI
Chapter 66 Setting General VPN Parameters
Permitting Intra-Interface Traffic (Hairpinning)
The following example enables IPsec traffic through the ASA without checking ACLs:
hostname(config)# sysopt connection permit-vpn
Note
Decrypted through-traffic is permitted from the client despite having an access group on the outside
interface, which calls a deny ip any any access list, while no sysopt connection permit-vpn is
configured.
Users who want to control access to the protected network via site-to-site or remote access VPN using
the no sysopt permit-vpn command in conjunction with an access control list (ACL) on the outside
interface are not successful.
In this situation, when management-access inside is enabled, the ACL is not applied, and users can still
connect to the ASA using SSH. Traffic to hosts on the inside network is blocked correctly by the ACL,
but decrypted through-traffic to the inside interface is not blocked.
The ssh and http commands are of a higher priority than the ACLs. In other words, to deny SSH, Telnet,
or ICMP traffic to the box from the VPN session, use ssh, telnet and icmp commands.
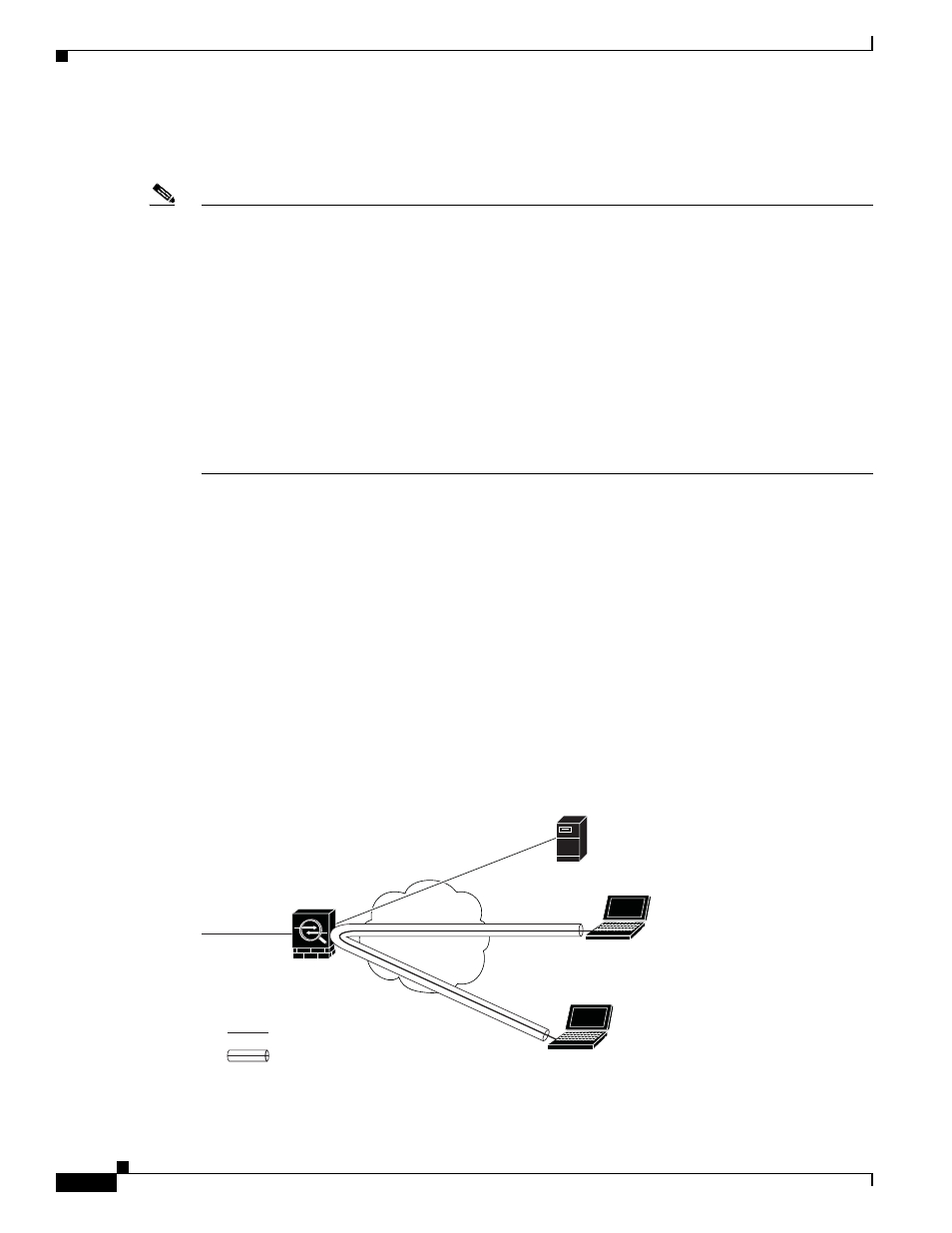
Permitting Intra-Interface Traffic (Hairpinning)
The ASA includes a feature that lets a VPN client send IPsec-protected traffic to another VPN user by
allowing such traffic in and out of the same interface. Also called “hairpinning”, this feature can be
thought of as VPN spokes (clients) connecting through a VPN hub (ASA).
In another application, hairpinning can redirect incoming VPN traffic back out through the same
interface as unencrypted traffic. This would be useful, for example, to a VPN client that does not have
split tunneling but needs to both access a VPN and browse the web.
shows VPN Client 1 sending secure IPsec traffic to VPN Client 2 while also sending
unencrypted traffic to a public web server.
Figure 66-1
VPN Client Using Intra-Interface Feature for Hairpinning
Client VPN
laptop 2
Client VPN
laptop 1
192.168.0.11
192.168.0.10
Unencrypted traffic
Ipsec/SSL encrypted traffic
192.168.0.0
Security
appliance
Public web
server
143170
