Features of the identity firewall – Cisco ASA 5505 User Manual
Page 715
36-3
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Configuration Guide using the CLI
Chapter 36 Configuring the Identity Firewall
Information About the Identity Firewall
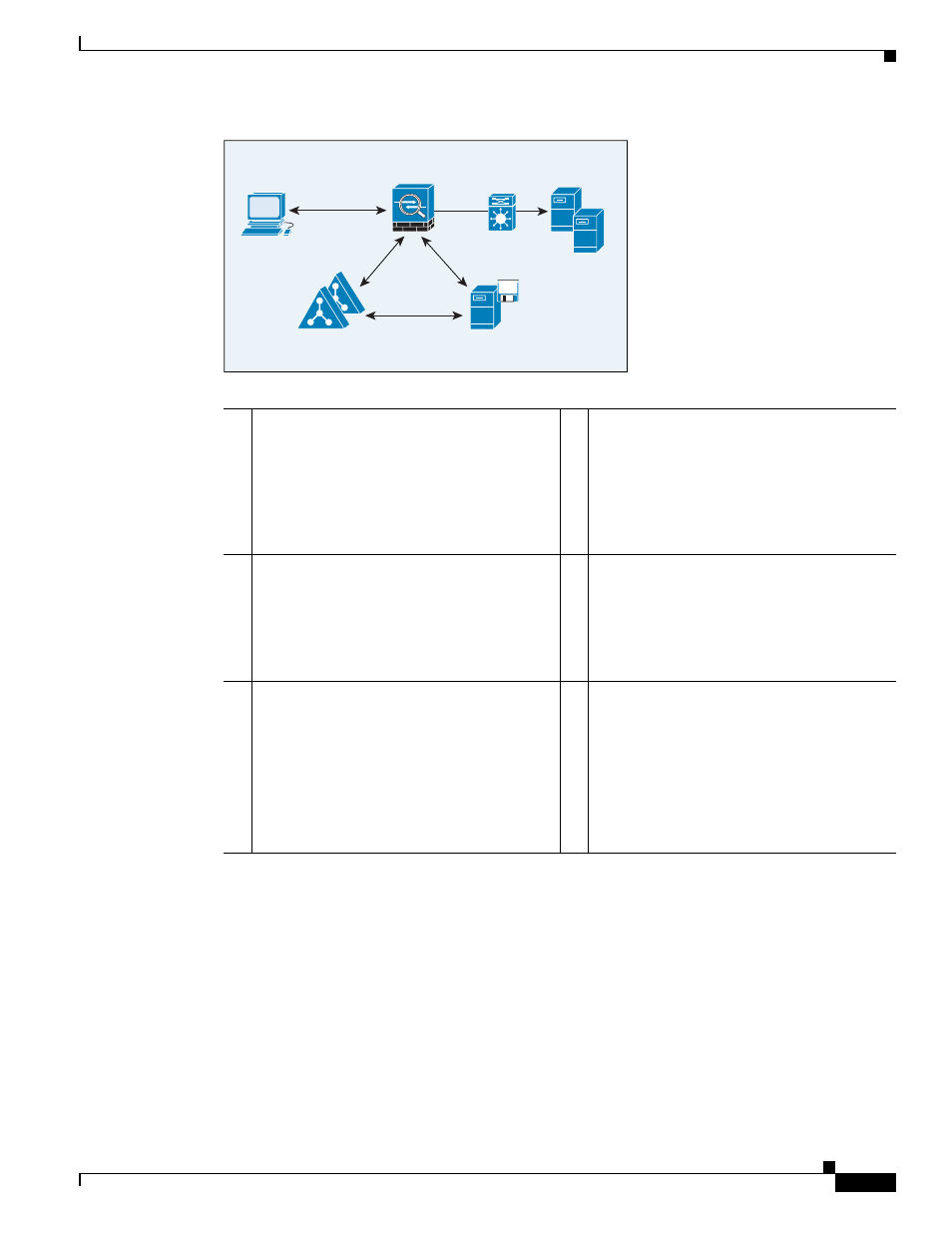
Figure 36-1
Identity Firewall Components
Features of the Identity Firewall
The Identity Firewall has the following key features.
Flexibility
•
The ASA can retrieve user identity and IP address mappings from the AD Agent by querying the
AD Agent for each new IP address or by maintaining a local copy of the entire user identity and IP
address database.
•
Supports host group, subnet, or IP address for the destination of a user identity policy.
•
Supports a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for the source and destination of a user identity
policy.
LAN
xxxxxx
Client
ASA
AD Servers
AD Agent
AD
Agent
mktg.sample.com
10.1.1.2
WMI
RADIU
S
LD
AP
NetBIOS Probe
1
On the ASA: Configure local user groups and
Identity Firewall policies.
4
Client <-> ASA: The client logs onto the
network through Microsoft Active Directory.
The AD Server authenticates users and
generates user logon security logs.
Alternatively, the client can log onto the
network through a cut-through proxy or by
using VPN.
2
ASA <-> AD Server: The ASA sends an
LDAP query for the Active Directory groups
configured on the AD Server.
The ASA consolidates local and Active
Directory groups and applies access rules and
MPF security policies based on user identity.
5
ASA <-> Client: Based on the policies
configured on the ASA, it grants or denies
access to the client.
If configured, the ASA probes the NetBIOS of
the client to pass inactive and no-response
users.
3
ASA <-> AD Agent: Depending on the
Identity Firewall configuration, the ASA
downloads the IP-user database or sends a
RADIUS request to the AD Agent querying
the user’s IP address.
The ASA forwards the new mappings learned
from web authentication and VPN sessions to
the AD Agent.
6
AD Agent <-> AD Server: Periodically or
on-demand, the AD Agent monitors the AD
Server security event log file via WMI for
client login and logoff events.
The AD Agent maintains a cache of user ID
and IP address mappings. and notifies the
ASA of changes.
The AD Agent sends logs to a syslog server.
