Brocade FastIron Ethernet Switch Administration Guide User Manual
Page 129
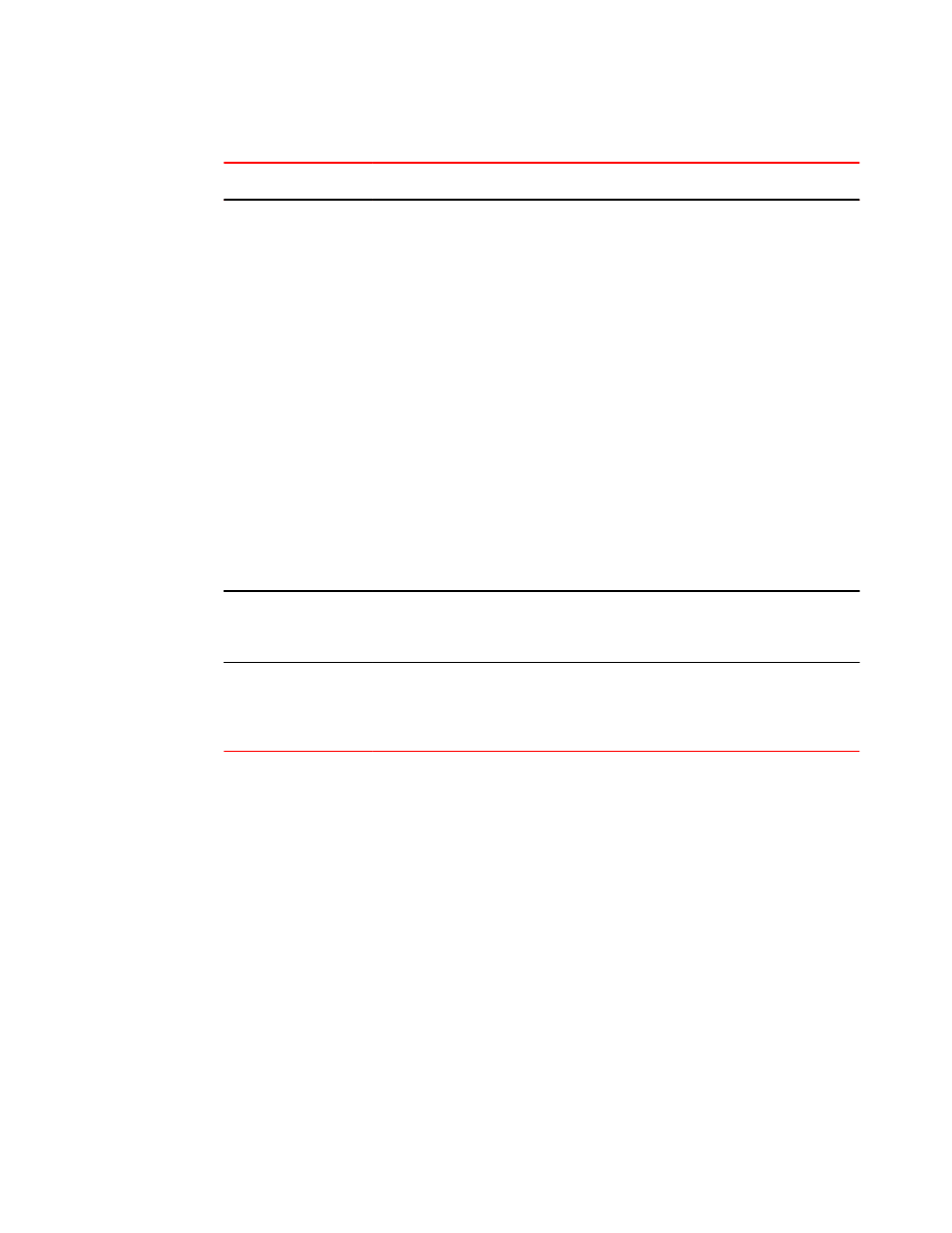
Static IPv6 route parameters (Continued)
TABLE 13
Parameter
Configuration details
Status
The route’s next-hop
gateway, which can be
one of the following:
• The IPv6 address of a
next-hop gateway.
• A tunnel interface.
You can specify the next-hop gateway as one of the
following types of IPv6 addresses:
• A global address.
• A link-local address.
If you specify a global address, you do not need to specify
any additional parameters for the next-hop gateway.
If you specify a link-local address, you must also specify the
interface through which to access the address. You can
specify one of the following interfaces:
• An Ethernet interface.
• A tunnel interface.
• A virtual interface (VE).
If you specify an Ethernet interface, also specify the port
number associated with the interface. If you specify a VE or
tunnel interface, also specify the VE or tunnel number.
You can also specify the next-hop gateway as a tunnel
interface. If you specify a tunnel interface, also specify the
tunnel number.
Mandatory for all static
IPv6 routes.
The route’s metric.
You can specify a value from 1 - 16.
Optional for all static
IPv6 routes. (The
default metric is 1.)
The route’s
administrative distance.
You must specify the distance keyword and any numerical
value.
Optional for all static
IPv6 routes. (The
default administrative
distance is 1.)
A metric is a value that the Layer 3 switch uses when comparing this route to other static routes in the
IPv6 static route table that have the same destination. The metric applies only to routes that the Layer 3
switch has already placed in the IPv6 static route table.
The administrative distance is a value that the Layer 3 switch uses to compare this route with routes
from other route sources that have the same destination. (The Layer 3 switch performs this comparison
before placing a route in the IPv6 route table.) This parameter does not apply to routes that are already
in the IPv6 route table. In general, a low administrative distance indicates a preferred route. By default,
static routes take precedence over routes learned by routing protocols. If you want a dynamic route to
be chosen over a static route, you can configure the static route with a higher administrative distance
than the dynamic route.
Configuring a static route in a non-default VRF or User VRF
To configure a static IPv6 route for a destination network with the prefix 2001:DB8::0/32, a next-hop
gateway with the global address 2001:DB8:0:ee44::1, in the non-default VRF named "blue", enter the
following at the general configuration prompt.
device(config)# ipv6 route vrf blue 2001:DB8::0/32 2001:DB8:0:ee44::1
Configuring a static route in a non-default VRF or User VRF
FastIron Ethernet Switch Administration Guide
129
53-1003075-02
