Rainbow Electronics DS3134 User Manual
Page 94
DS3134
94 of 203
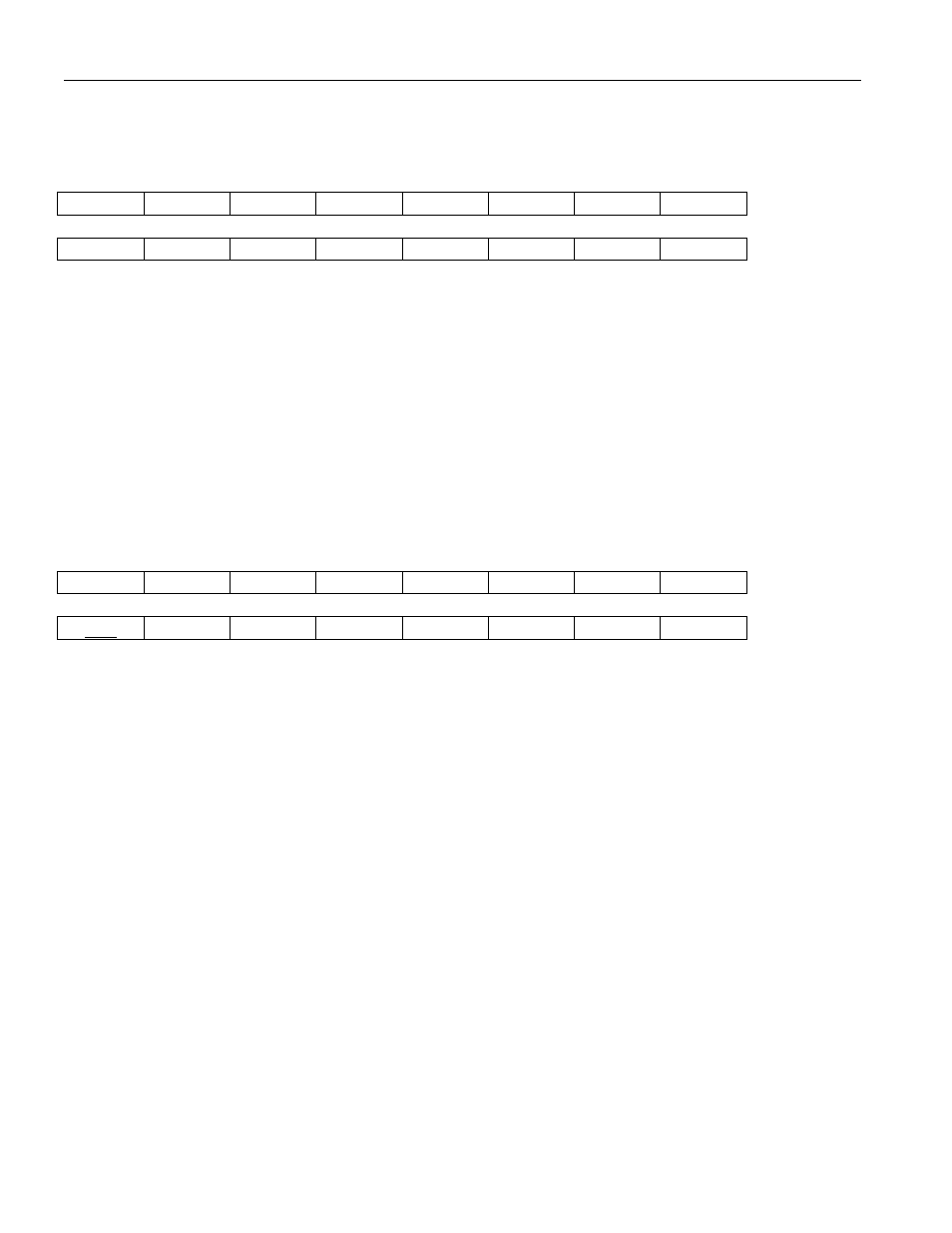
Register Name:
TFBP
Register Description: Transmit FIFO Block Pointer
Register Address:
0994h
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
TBP7
TBP6
TBP5
TBP4
TBP3
TBP2
TBP1
TBP0
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
n/a
n/a
n/a
n/a
n/a
n/a
TBP9
TBP8
Note: Bits that are underlined are read only, all other bits are read-write.
Bits 0 to 9 / Block Pointer (TBP0 to TBP9). These 10 bits indicate which of the 1024 blocks is the next
block in the link list chain. A block is not allowed to point to itself.
0000000000 (000h) = Block 0 is the Next Linked Block
0111111111 (1FFh) = Block 511 is the Next Linked Block
1111111111 (3FFh) = Block 1023 is the Next Linked Block
Register Name:
TFLWMIS
Register Description: Transmit FIFO Low Water Mark Indirect Select
Register Address:
09A0h
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
HCID7
HCID6
HCID5
HCID4
HCID3
HCID2
HCID1
HCID0
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
IAB
IARW
n/a
n/a
n/a
n/a
n/a
n/a
Note: Bits that are underlined are read only, all other bits are read-write; default value for all bits is 0.
Bits 0 to 7 / HDLC Channel ID (HCID0 to HCID7).
00000000 (00h) = HDLC Channel Number 1
11111111 (FFh) = HDLC Channel Number 256
Bit 14 / Indirect Access Read/Write (IARW). When the host wishes to read data from the internal
Transmit Low Water Mark RAM, this bit should be written to a one by the host. This causes the device
to begin obtaining the data from the channel location indicated by the HCID bits. During the read access,
the IAB bit will be set to one. Once the data is ready to be read from the TFLWM register, the IAB bit
will be set to zero. When the host wishes to write data to the internal Transmit Low Water Mark RAM,
this bit should be written to a zero by the host. This causes the device to take the data that is currently
present in the TFLWM register and write it to the channel location indicated by the HCID bits. When the
device has completed the write, the IAB will be set to zero.
Bit 15 / Indirect Access Busy (IAB). When an indirect read or write access is in progress, this read only
bit will be set to a one. During a read operation, this bit will be set to a one until the data is ready to be
read. It will be set to zero when the data is ready to be read. During a write operation, this bit will be set
to a one while the write is taking place. It will be set to zero once the write operation has completed.
