Secure shell commands, Secure shell commands -47, Table 4-15 secure shell commands -47 – SMC Networks SMC TigerStack III SMC6824MPE User Manual
Page 309
S
YSTEM
M
ANAGEMENT
C
OMMANDS
4-47
Secure Shell Commands
The Berkley-standard includes remote access tools originally designed for
Unix systems. Some of these tools have also been implemented for Microsoft
Windows and other environments. These tools, including commands such as
rlogin (remote login), rsh (remote shell), and rcp (remote copy), are not secure
from hostile attacks.
The Secure Shell (SSH) includes server/client applications intended as a
secure replacement for the older Berkley remote access tools. SSH can also
provide remote management access to this switch as a secure replacement for
Telnet. When a client contacts the switch via the SSH protocol, the switch
uses a public-key that the client must match along with a local user name and
password for access authentication.
This section describes the commands used to configure the SSH server.
However, note that you also need to install a SSH client on the management
station when using this protocol to configure the switch.
Note: The switch supports SSH version 1.5 and 2.0.
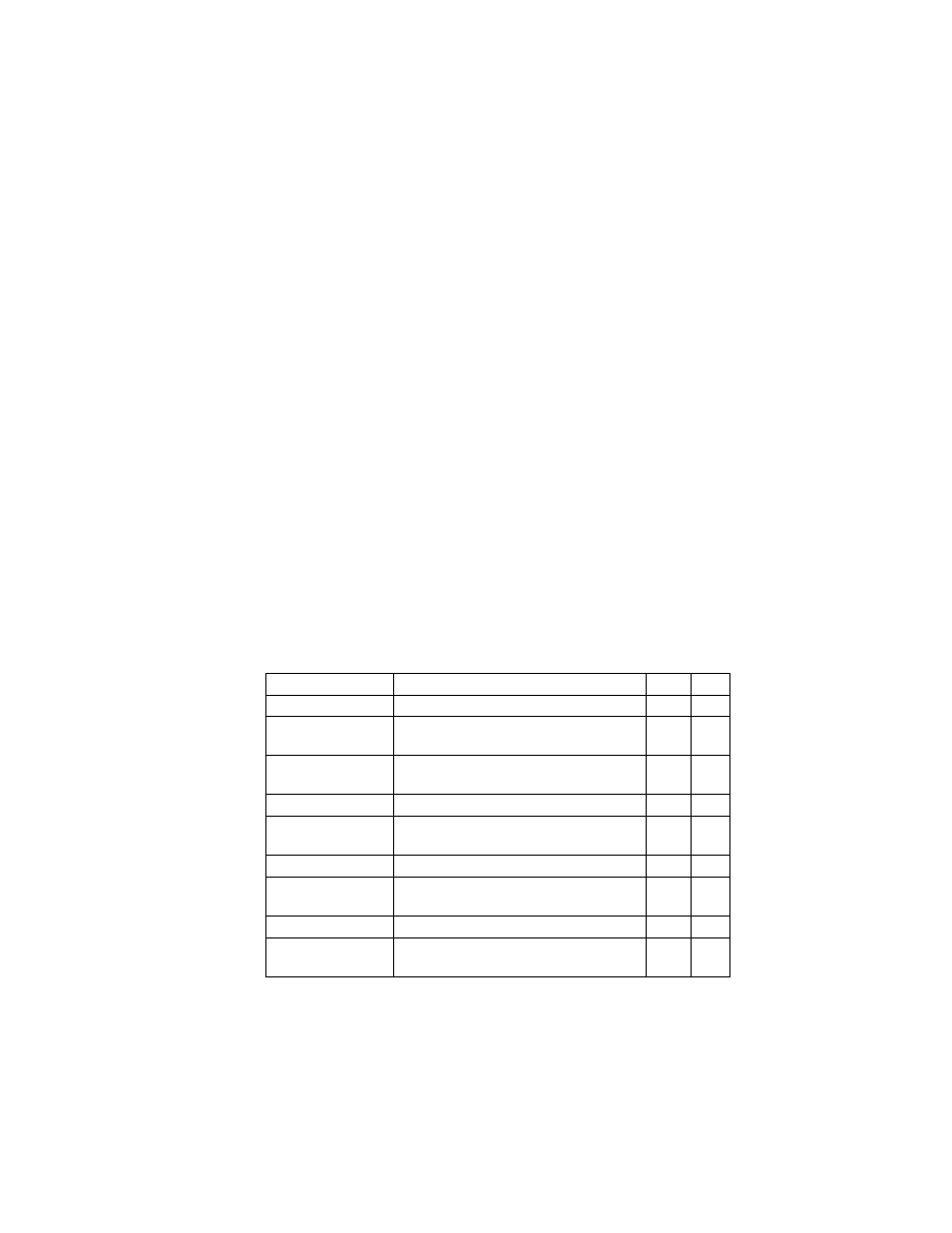
Table 4-15 Secure Shell Commands
Command
Function
Mode Page
ip ssh server
Enables the SSH server on the switch
GC
ip ssh timeout
Specifies the authentication timeout for the
SSH server
GC
ip ssh
authentication-retries
Specifies the number of retries allowed by a
client
GC
ip ssh server-key size Sets the SSH server key size
GC
copy tftp public-key
Copies the user’s public key from a TFTP
server to the switch
PE
delete public-key
Deletes the public key for the specified user PE
ip ssh crypto host-key
generate
Generates the host key
PE
ip ssh crypto zeroize Clear the host key from RAM
PE
ip ssh save host-key
Saves the host key from RAM to flash
memory
PE
