3 coordinate word – Yaskawa J50M Instructions User Manual
Page 14
2.2.3
OPTIONAL BLOCK SKIP (/1 - /9)
2.2.2
SEQUENCE NUMBER
Integers consisting of up to 4 digits may be writ-
ten following an address character
as sequence
numbers.
Sequence numbers are reference numbers for
blocks, and do not have any influence on the
meaning and sequence of machining processes.
Therefore, they may be sequential, non-sequen-
tial, and duplicated numbers, and also not using
any sequence number is also possible. Generally,
sequential numbers are convenient as sequence
numbers.
When searching for sequence numbers, be sure
to search or
numbers
hand.
Notes :
. When 5 or more digits are written as a sequence
number, only the digits up to the 4th from the
trailing end are effective.
. When two or more blocks have the same sequence
number, only one is retrieved and read, and
no more searching is performed.
Blocks without sequence numbers can also be
searched for with respect to the address data
contained in the blocks.
Those blocks
which “ /n” (n 1 - 9) is includ-
ed are neglected between In and the end of that
block, when the external optional block skip
switch for that number “n” is on.
EXAMPLE
/ 2
X 1 O O / 3
When the switch for
is on , the entire block is
neglected,
and when the switch for
is on , this
block is read as if
N 1 2 3 4
.
With “ 1“ ,
be omitted.
Notes :
The optional block skipping process is executed
while the blocks are read into the buffer
ter.
If the blocks have been read , subsequent
switching on is ineffective to skip the blocks.
While reading or punching out programs, this
function is ineffective.
The optional block skip
- /9 is an option
function.
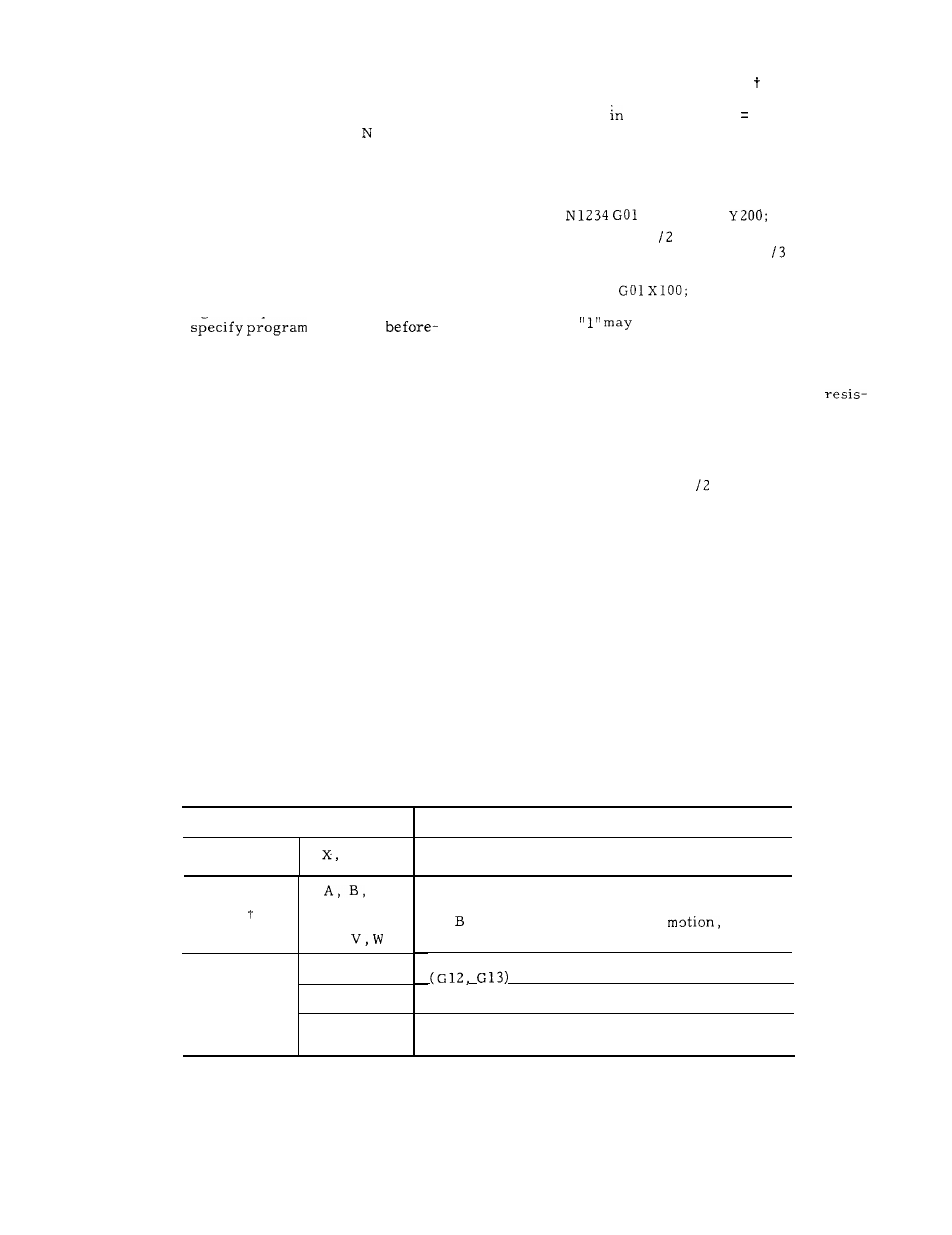
2.3 COORDINATE WORD
Generally,
commands for movements in axis direc-
tions and commands for setting coordinate sys-
tems are called coordinate words, and coordinate
words consist of address characters for desired
axes and numerals representing dimensions of
directions.
2.3.1 COORDINATE WORD
Table 2.4 Coordinate Words
A d d r e s s
Description
Main axes
Y, z
Position or distance in X, Y or Z coordinate
direction.
4th axis
Circular
interpolation
auxiliary
data
C
or
u ,
Q
R
I, J, K
These coordinate words are treated as commands
in the directions of the 4th axis.
A , and C are used for rotary
and
U , V and W are used for parallel motion
Circular arc increment in circle cutting
Generally, radius values of circles.
Generally, distances from start point to arc
center (in X , Y and Z components) .
6
