Yaskawa J50M Instructions User Manual
Page 105
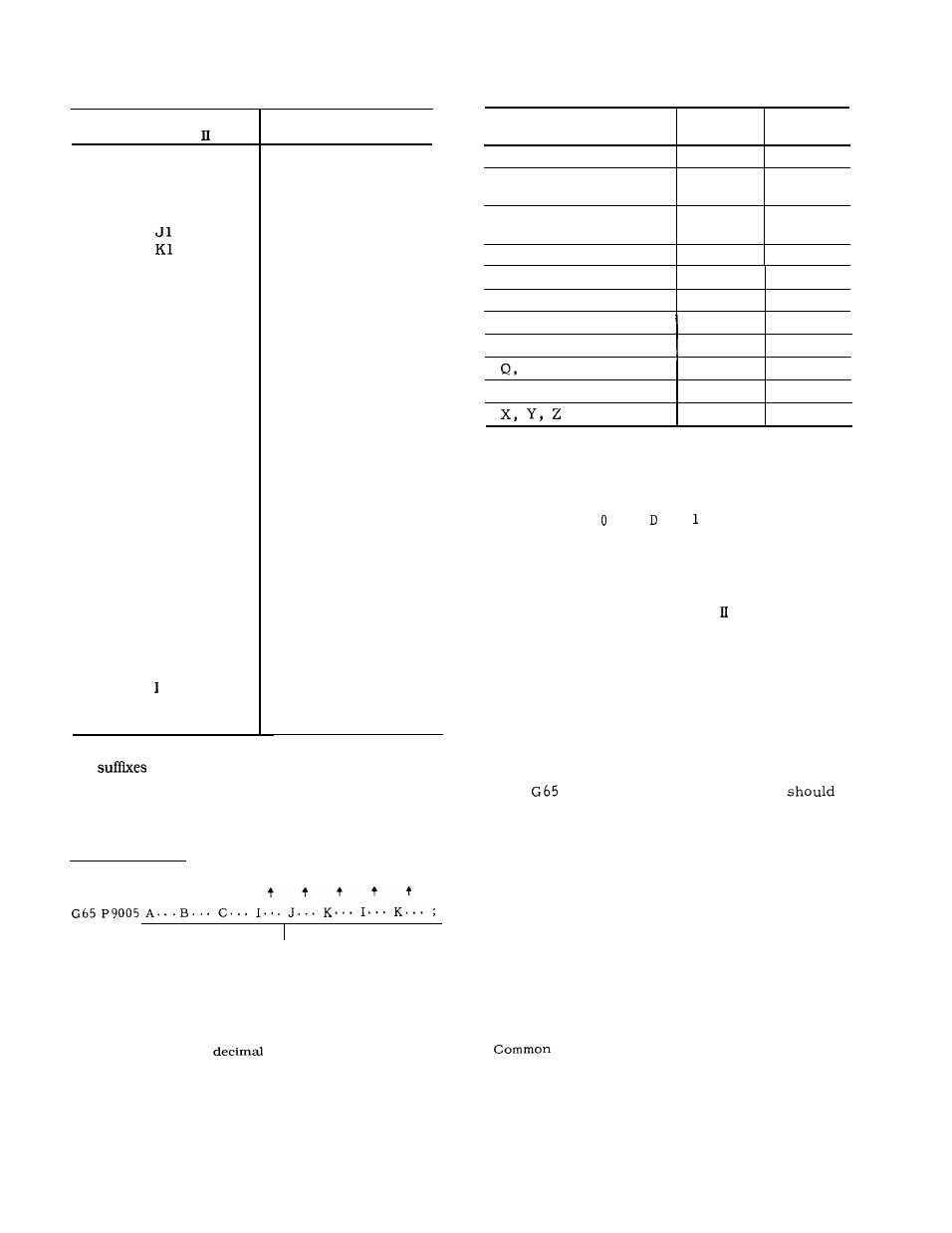
Table 2.33 Argument Designation II
Address of Argument
Designation
A
B
c
11
12
J2
K2
13
J3
K3
14
J 4
K4
15
J5
K5
16
J 6
K6
17
J 7
K7
18
J8
K8
19
J 9
K9
10
J1O
K1O
Variables in
User Macro Body
#1
#2
#3
#4
#5
#6
#7
#8
#9
# l o
#11
#12
#13
#14
#15
#16
#17
#18
#19
#20
#21
#22
#23
#24
#25
#26
#27
#28
#29
#30
#31
#32
#33
The
1 through 10 to 1, J and K are determined by
the order of the designated I, J and K combination.
For the address in which no argument need be desig-
nated, the command can be omitted.
Sample Program
#4
#5 #6
#7 #9
Argument Designation Part
(3)
Position of Decimal Point Argument
An
argument may generally be designated with a sign
and decimal point. For the designation without decimal
point, the position of
point is as shown in Table
2.34.
Table 2.34 Position of Decimal Point Argument
Address in
Metric
Inch
Argument Designation
Input
Input
A , C
3 (2)
3 (2)
B (Without B 3-digit
3 (2)
3 (2)
option )
B (With B 3-digit
o
0
option )
D, H
o
0
E, F
o (1)
1 (2)
I, J, K
3 (2)
4 (3)
M
o
4
S , T
o
0
R
3 (2)
4 (3)
u, v, w
3 (2)
4 (3)
3 (2)
4 (3)
The value shows the position of decimal point
as counted from the least significant digit. The
value in parentheses indicates the number of
digits that follows decimal point as designated by
parameter #6020D = 1, 2 = for addresses E
and F, and parameter #6006D 5 = 1 for the other
addresses.
(4) Considerations
in Argument Designation
A. Argument designation types I and can be used con-
currently. If the same variable has been duplicated, the
last one is validated.
B. For both types I and II, addresses 1, J, and K should
be designated in this order. The other addresses can be
designated in any order.
C. In the argument designation part, negative sign and
decimal point can be used regardless of the address.
D.
In
and G66 blocks, G65 and G66
always be specified before each argument desig-
nation.
This holds true with the macro call by
G code.
(e) M cannot be used for the argument designation
address when using 24 pairs, or alarm will occur.
2.11.4 OVERVIEW OF USER MACRO BODY
A user macro body is programmed using the com-
bination of the following commands.
( 1 ) V a r i a b l e s
A. Local variable (#1 through #33)
B
.
variable (#100 through #559)
C. System variable ( #1000 through #5104)
97
