3 multiple interrupt servicing – NEC PD78F9488 User Manual
Page 304
CHAPTER 16 INTERRUPT FUNCTIONS
304
User’s Manual U15331EJ4V1UD
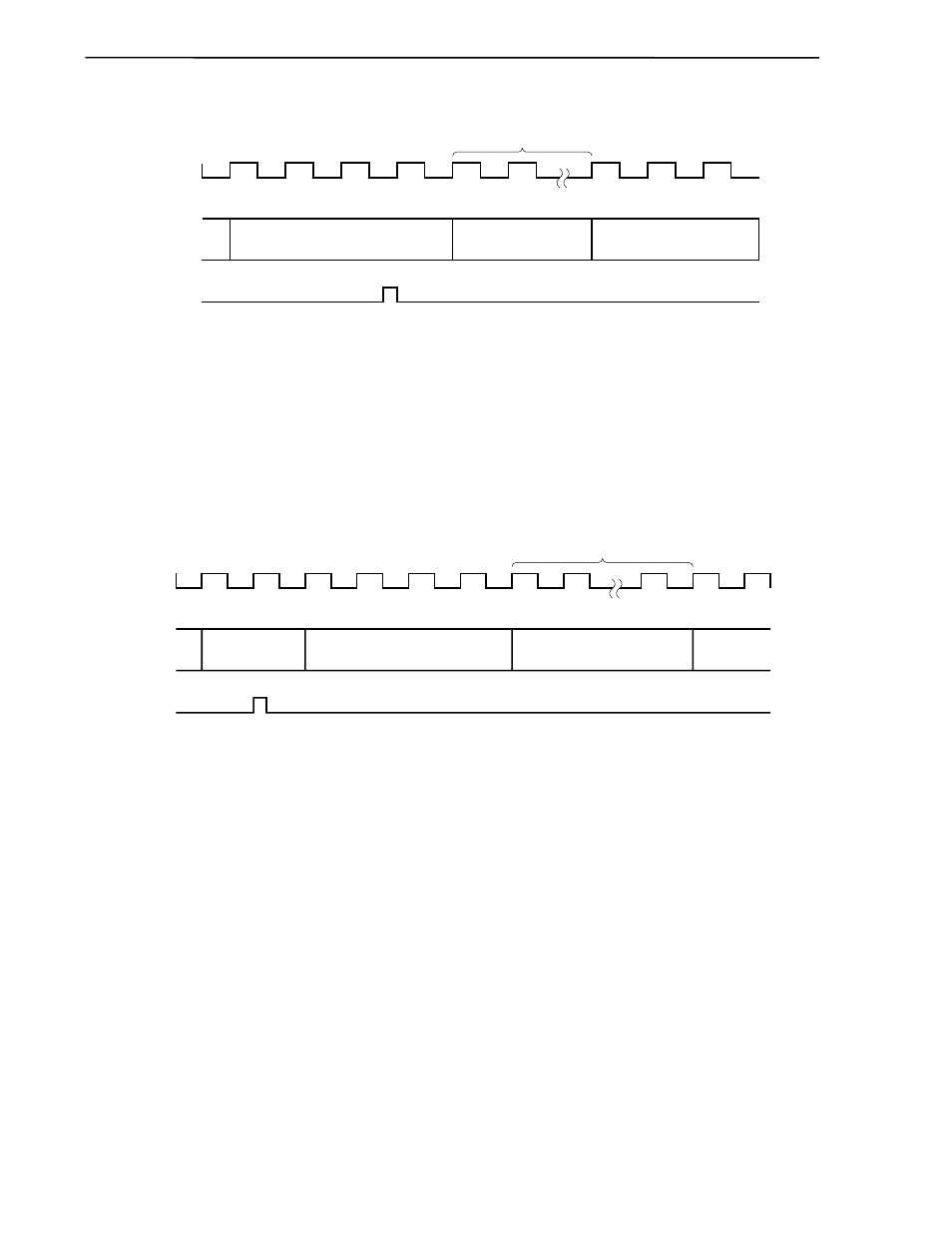
Figure 16-14. Interrupt Request Acknowledgment Timing (Example: MOV A, r)
Clock
CPU
MOV A, r
Saving PSW and PC, and
jump to interrupt servicing
8 clocks
Interrupt servicing program
Interrupt
If the interrupt request has generated an interrupt request flag (xxIFx) by the time the instruction clocks under
execution, n clocks (n = 4 to 10), are n
− 1, interrupt request acknowledgment processing will start following the
completion of the instruction under execution. Figure 16-14 shows an example using the 8-bit data transfer instruction
MOV A, r. Because this instruction is executed in 4 clocks, if an interrupt request is generated between the start of
execution and the 3rd clock, interrupt request acknowledgment processing will take place following the completion of
MOV A, r.
Figure 16-15. Interrupt Request Acknowledgment Timing
(When Interrupt Request Flag Is Generated in Final Clock Under Execution)
Clock
CPU
NOP
MOV A, r
Saving PSW and PC, and
jump to interrupt servicing
Interrupt servicing
program
Interrupt
8 clocks
If the interrupt request flag (xxIFx) is generated in the final clock of the instruction, interrupt request
acknowledgment processing will begin after execution of the next instruction is complete.
Figure 16-15 shows an example whereby an interrupt request was generated in the 2nd clock of NOP (a 2-clock
instruction). In this case, the interrupt request will be processed after execution of MOV A, r, which follows NOP, is
complete.
Caution When interrupt request flag registers (IF0 to IF2), or interrupt mask flag registers (MK0 to MK2)
are being accessed, interrupt requests will be held pending.
16.4.3 Multiple interrupt servicing
Multiple interrupt servicing, in which an interrupt request is acknowledged while another interrupt request being
serviced, can be executed using the priority order. If multiple interrupts are generated at the same time, they are
serviced in the order according to the priority assigned to each interrupt request in advance (refer to Tables 16-1 and
16-2).
