2 starting and stopping time – Yaskawa Sigma II Series SGMVH User Manual
Page 73
4.5 SERVOPACK Overload Characteristics and Allowable Load Moment of Inertia
4
SER
VOP
ACK Specifications and Dimensional Drawings
4-13
4.5.2 Starting and Stopping Time
The motor starting time (tr) and stopping time (tf) under a constant load are calculated using the following for-
mulas. Motor viscous torque and friction torque are ignored.
Calculate the torque from the motor current using servomotor torque constant
× motor current (effective value).
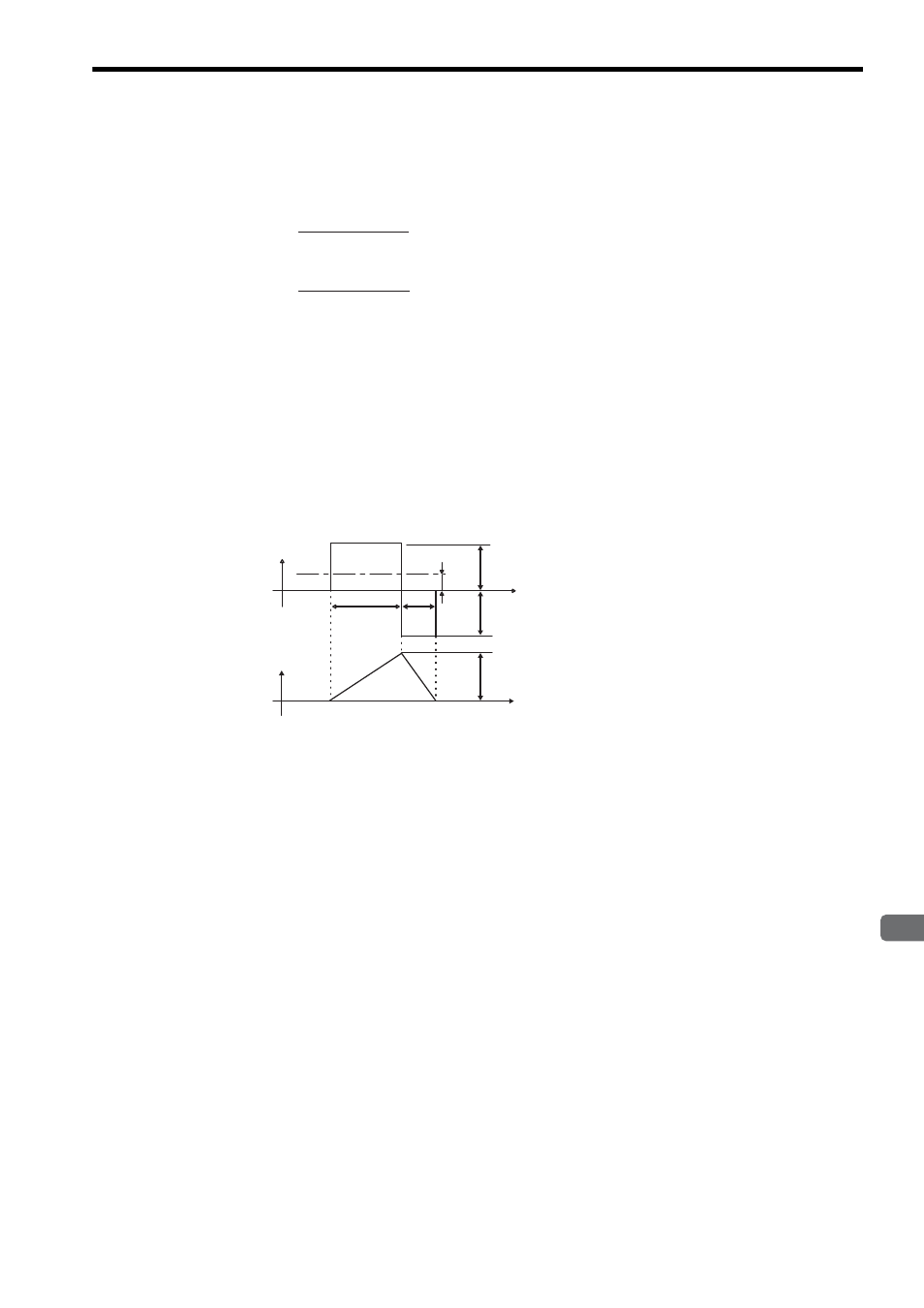
The following figure shows the motor torque and motor speed timing chart.
n
M
:
Motor speed (min
-1
)
J
M
:
Motor rotor moment of inertia (kgxm
2
)
J
L
:
Load converted to shaft moment of inertia (kgxm
2
)
T
PM
:
Instantaneous peak motor torque when combined with a SERVOPACK (Nxm)
T
L
:
Load torque (Nxm)
tr =
tf =
Starting time:
Stopping time:
2
π n
M
(J
M
+ J
L
)
(T
PM
- T
L
)
60
[s]
[s]
2
π n
M
(J
M
+ J
L
)
(T
PM
+ T
L
)
60
Motor torque
(current amplitude)
Motor speed
tr
tf
n
M
T
PM
T
L
Time
Time
T
PM
- Tag Generator (30 pages)
- MP3300iec (82 pages)
- 1000 Hz High Frequency (18 pages)
- 1000 Series (7 pages)
- PS-A10LB (39 pages)
- iQpump Micro User Manual (300 pages)
- 1000 Series Drive Option - Digital Input (30 pages)
- 1000 Series Drive Option - CANopen (39 pages)
- 1000 Series Drive Option - Analog Monitor (27 pages)
- 1000 Series Drive Option - CANopen Technical Manual (37 pages)
- 1000 Series Drive Option - CC-Link (38 pages)
- 1000 Series Drive Option - CC-Link Technical Manual (36 pages)
- 1000 Series Drive Option - DeviceNet (37 pages)
- 1000 Series Drive Option - DeviceNet Technical Manual (81 pages)
- 1000 Series Drive Option - MECHATROLINK-II (32 pages)
- 1000 Series Drive Option - Digital Output (31 pages)
- 1000 Series Drive Option - MECHATROLINK-II Technical Manual (41 pages)
- 1000 Series Drive Option - Profibus-DP (35 pages)
- AC Drive 1000-Series Option PG-RT3 Motor (36 pages)
- Z1000U HVAC MATRIX Drive Quick Start (378 pages)
- 1000 Series Operator Mounting Kit NEMA Type 4X (20 pages)
- 1000 Series Drive Option - Profibus-DP Technical Manual (44 pages)
- CopyUnitManager (38 pages)
- 1000 Series Option - JVOP-182 Remote LED (58 pages)
- 1000 Series Option - PG-X3 Line Driver (31 pages)
- SI-EN3 Technical Manual (68 pages)
- JVOP-181 (22 pages)
- JVOP-181 USB Copy Unit (2 pages)
- SI-EN3 (54 pages)
- MECHATROLINK-III (35 pages)
- SI-ET3 (49 pages)
- EtherNet/IP (50 pages)
- SI-EM3 (51 pages)
- 1000-Series Option PG-E3 Motor Encoder Feedback (33 pages)
- 1000-Series Option SI-EP3 PROFINET (56 pages)
- PROFINET (62 pages)
- AC Drive 1000-Series Option PG-RT3 Motor (45 pages)
- SI-EP3 PROFINET Technical Manual (53 pages)
- A1000 Drive Option - BACnet MS/TP (48 pages)
- 120 Series I/O Modules (308 pages)
- A1000 12-Pulse (92 pages)
- A1000 Drive Software Technical Manual (16 pages)
- A1000 Quick Start (2 pages)
- JUNMA Series AC SERVOMOTOR (1 page)
- A1000 Option DI-101 120 Vac Digital Input Option (24 pages)
