Taking down a path to a mirrored disk, Example – HP NonStop G-Series User Manual
Page 154
Performing Routine Disk Operations
Guardian User’s Guide — 425266-001
9 -8
Taking Down a Path To a Mirrored Disk
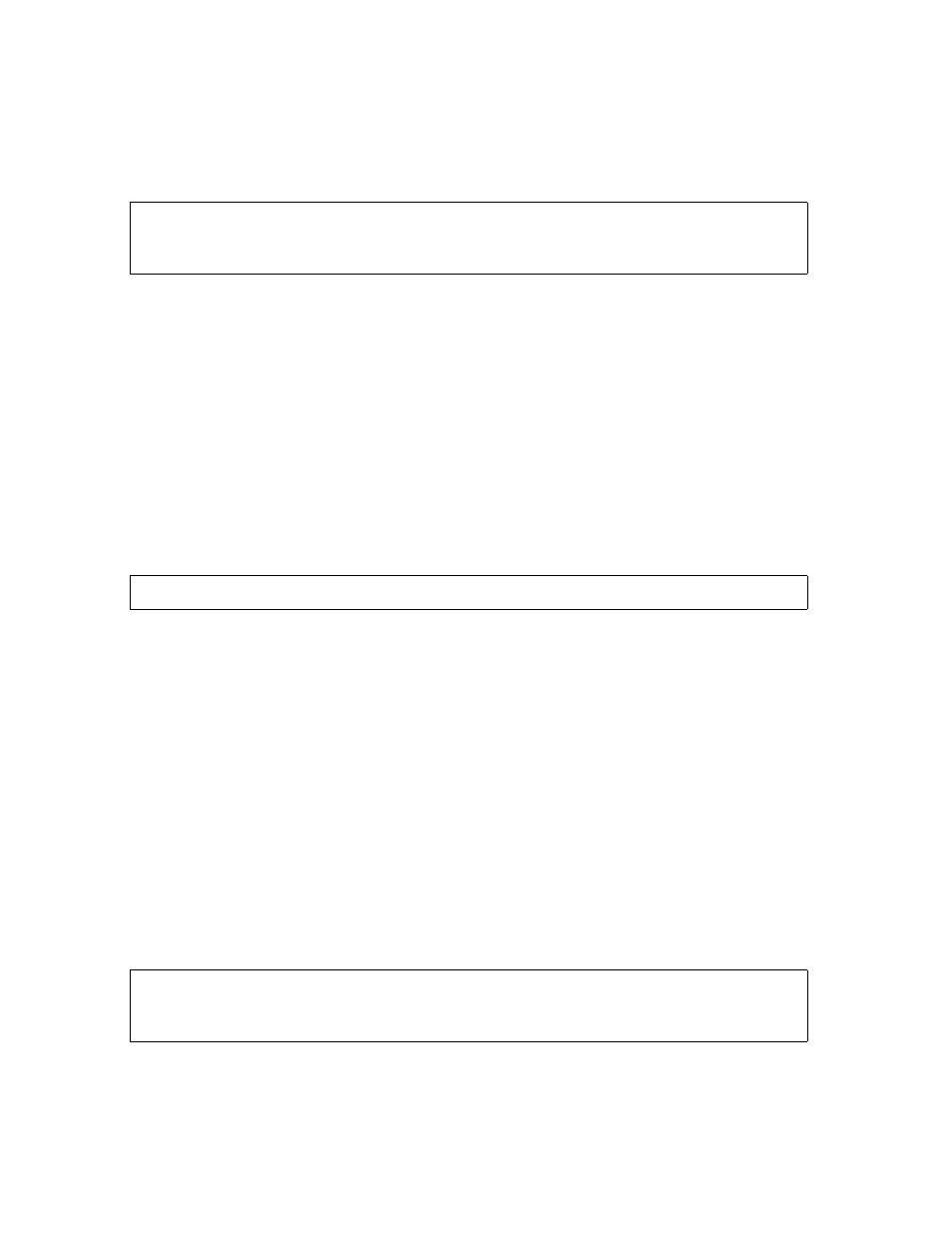
3. Check the disk status to confirm it is down:
> SCF STATUS DISK $AMBER
A listing similar to this is displayed on your home terminal:
Taking Down a Path To a Mirrored Disk
1. Make sure you are logged on as a super-group user (255,
n
).
2. Stop the path:
> SCF
-> STOP DISK $disk { -P | -B | -M | -MB }
You must specify one of the following parameters for mirrored disks: -P (for
primary path); -B (for backup path); -M (for mirror path); or -MB (for mirror
backup path).
If you do not specify a path, the following message is displayed:
3. Check the path status to confirm it is down:
> SCF STATUS DISK $disk
Example
To make the primary path to the mirror disk $DATA inaccessible:
1. Make sure you are logged on as a super-group user (255,
n
).
2. Stop the path:
> SCF STOP DISK $DATA-M
3. Check the path status to confirm it is down:
> SCF STATUS DISK $DATA
A listing similar to this is displayed on your home terminal:
STORAGE - Status DISK \SHARK.$AMBER
LDev Primary Backup Mirror MirrorBackup Primary Backup
PID PID
61 STOPPED STOPPED STOPPED STOPPED 0,269 1,264
STORAGE W01007 The STOP command will make all paths to $disk inaccessible.
STORAGE - Status DISK \SHARK.$DATA
LDev Primary Backup Mirror MirrorBackup Primary Backup
PID PID
50 STARTED STARTED STOPPED STOPPED 3,260 2,265
