Figure 8-3, Structure of a relative file, Creating a key-sequenced file – HP NonStop G-Series User Manual
Page 131: Figure 8-3. structure of a relative file
Using FUP for Advanced File Management
Guardian User’s Guide — 425266-001
8 -9
File-Creation Examples
To create a relative file named $USERS.JOHN.RELATIVE whose primary extent size
is 5 pages, whose secondary extent size is 2 pages, and whose record length is 120 bytes,
enter:
Creating a Key-Sequenced File
In a key-sequenced file, records are stored by the values of their primary keys. A
primary key is a field within a record that uniquely identifies the record.
shows a possible format for a record in a key-sequenced file.
-SET TYPE R --Set the file type to relative.
-SET EXT (5,2) --You can specify extent sizes in
--pages, bytes, records, and megabytes
. --If you do not give a unit, FUP
--assumes pages.
-SET REC 120 --Set the record length to 120 bytes.
-SHOW --Show the current parameter values.
TYPE R
EXT ( 5 PAGES, 2 PAGES )
REC 120
BLOCK 4096
MAXEXTENTS 16
-CREATE RELATIVE --Create the file.
CREATED - $USERS.JOHN.RELATIVE
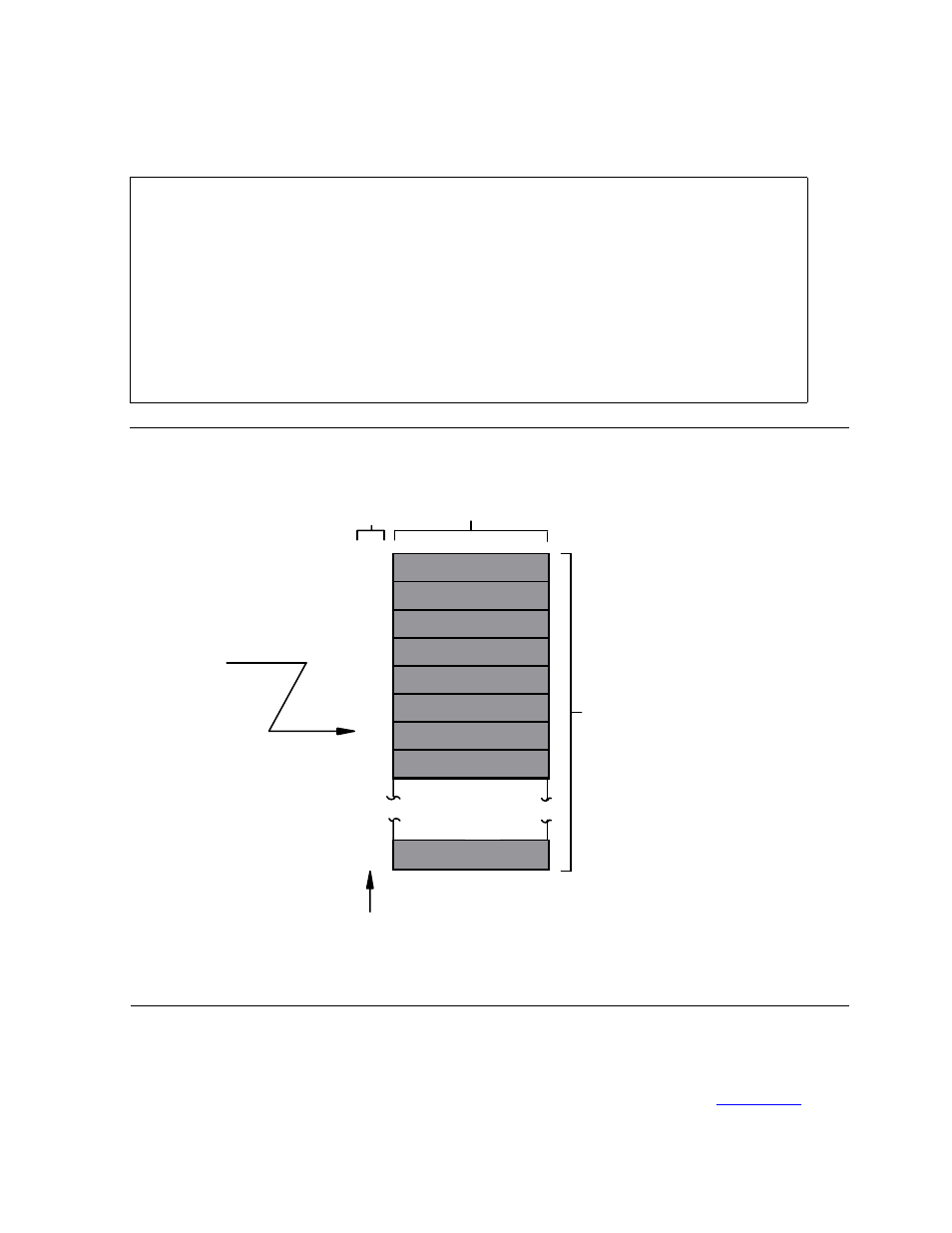
Figure 8-3. Structure of a Relative File
003
CDT
.CDD
Relative
File:
Primary access is via
record number.
Example:
FIND 6th
nth
Record
Number
Records are stored according to a record number
supplied by the application program.
Record
Relative
File
.
.
.
.
0th
1st
2nd
3rd
4th
5th
6th
7th
