Multichannel Systems MC_Rack Manual User Manual
Page 145
MC_Rack Features
139
Example:
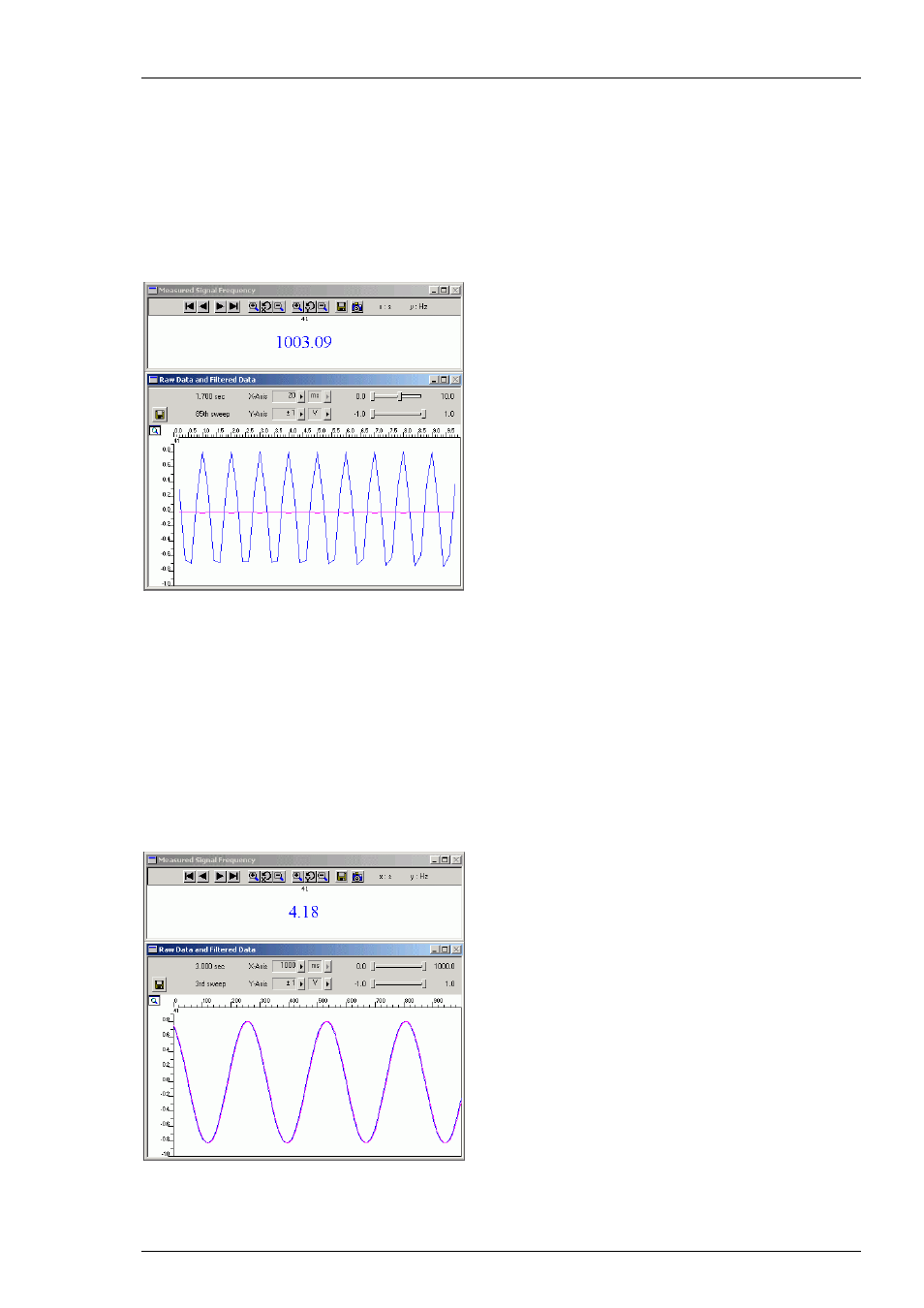
This can be demonstrated by the following experiment. A regular 1000 Hz signal (from a pulse
generator) is applied to electrode input channels of the MC_Card. In this experiment, this signal
represents the high frequency noise that should be removed. A 100 Hz Low Pass filter is used to
remove this high frequency "noise" signal.
At a sampling rate of 5 kHz, signals up to 2.5 kHz are safe from aliasing, resulting in a good
sampling and filtering result. The screen shot shows the raw data (blue trace) and filtered data
(magenta).
The high frequency "noise" signal has been removed by the filter. The signal frequency of the
digitized data (measured with a Spike Detector and Analyzer) matches the frequency of the
analog input signal.
At a sampling rate of 1 kHz, aliasing occurs to frequencies above 1/2 sampling rate, that is, above
500 Hz. Thus, the 1000 Hz signal is digitized to a low frequency signal of about 4 Hz (see time
scale of display). Please note that the only difference between the two screen shots is the altered
sampling rate. The input signal is exactly the same.
Of course, the low frequency noise signal passes the digital low pass filter. The raw data and the
filtered data traces match perfectly.
