Free queue, Figure 9-5. receive free-queue descriptor, 3 free queue – Rainbow Electronics DS31256 User Manual
Page 92
DS31256
92 of 181
9.2.3 Free Queue
The host writes the 32-bit addresses of the available (free) data buffers and their associated packet
descriptors to the receive free queue. The descriptor space is indicated through a 16-bit pointer, which
the DMA uses along with the receive packet descriptor base address to find the exact 32-bit address of
the associated receive packet descriptor.
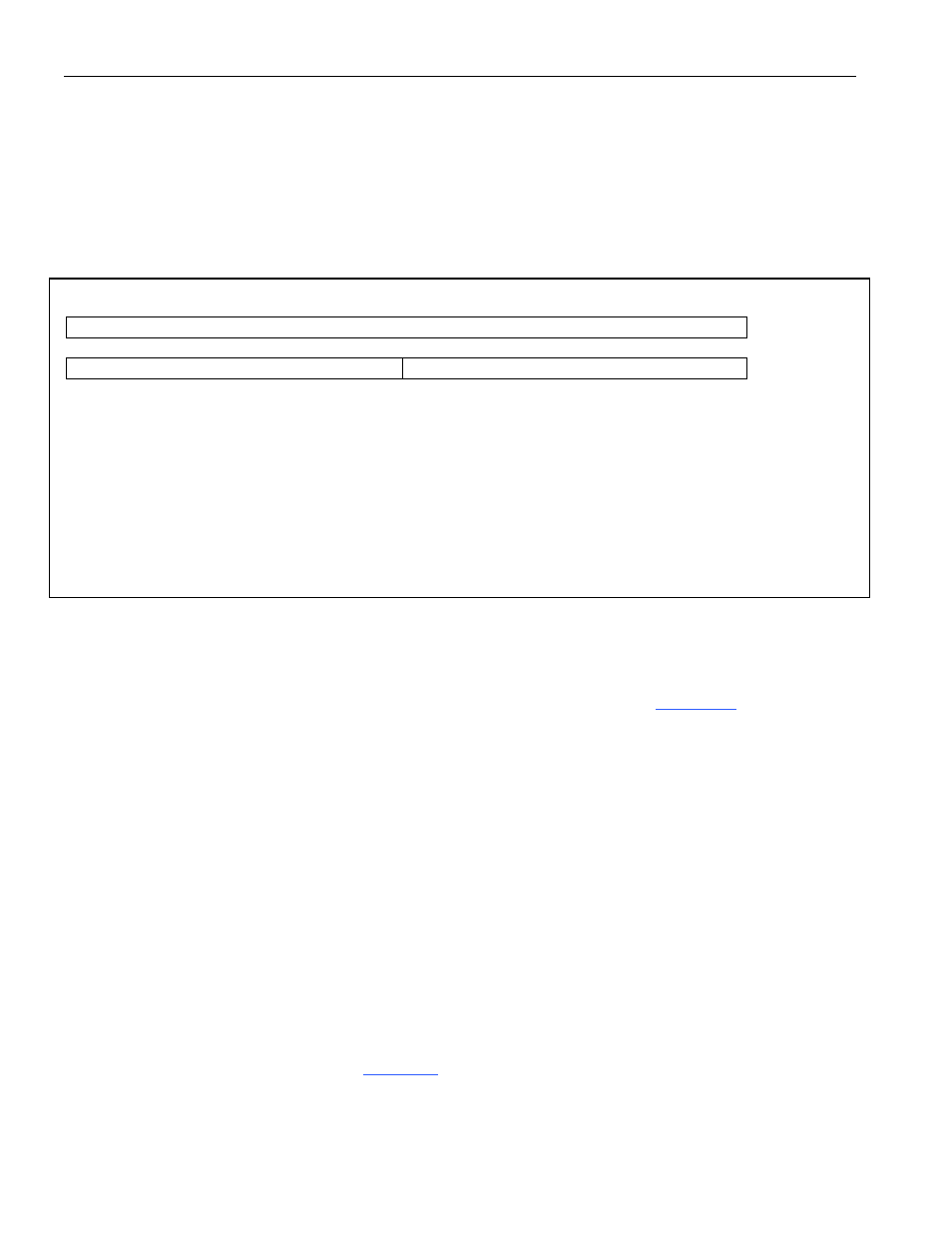
Figure 9-5. Receive Free-Queue Descriptor
dword 0
Free Data Buffer Address (32)
dword 1
Unused (16)
Free Packet Descriptor Pointer (16)
Note: The organization of the free queue is not affected by the enabling of Big Endian.
dword 0; Bits 0 to 31/Data Buffer Address. Direct 32-bit starting address of a free data buffer.
dword 1; Bits 0 to 15/Free Packet Descriptor Pointer. This 16-bit value is the offset from the receive descriptor
base address of the free descriptor space associated with the free data buffer in dword 0. Note: This is an index,
not an absolute address.
dword 1; Bits 16 to 31/Unused. Not used by the DMA. Can be set to any value by the host and is ignored by the
receive DMA.
The receive DMA reads from the receive free-queue descriptor circular queue which data buffers and
their associated descriptors are available for use by the DMA.
The receive free-queue descriptor is actually a set of two circular queues (
). There is one
circular queue that indicates where free large buffers and their associated free descriptors exist. There is
another circular queue that indicates where free small buffers and their associated free descriptors exist.
Large and Small Buffer Size Handling
Through the receive configuration-RAM buffer-size field, the DMA knows for a particular HDLC
channel whether the incoming packets should be stored in the large or the small free data buffers. The
host informs the DMA of the size of both the large and small buffers through the receive large and small
buffer size (RLBS/RSBS) registers. For example, when the DMA knows that data is ready to be written
onto the PCI bus, it checks to see if the data is to be sent to a large buffer or a small buffer, and then it
goes to the appropriate free-queue descriptor and pulls the next available free buffer address and free
descriptor pointer. If the host wishes to have only one buffer size, then the receive free queue small-
buffer start address is set equal to the receive free-queue end address. In the receive configuration RAM,
none of the active HDLC channels are configured for the small buffer size.
There are a set of internal addresses within the device to keep track of the addresses of the dual circular
queues in the receive free queue. These are accessed by the host and the DMA. On initialization, the host
configures all of the registers shown in
. After initialization, the DMA only writes to (changes)
the read pointers and the host only writes to the write pointers.
