Pci bus arbitration, Pci initiator abort, 3 pci bus arbitration – Rainbow Electronics DS31256 User Manual
Page 133: 4 pci initiator abort, Figure 10-5. pci initiator abort
DS31256
133 of 181
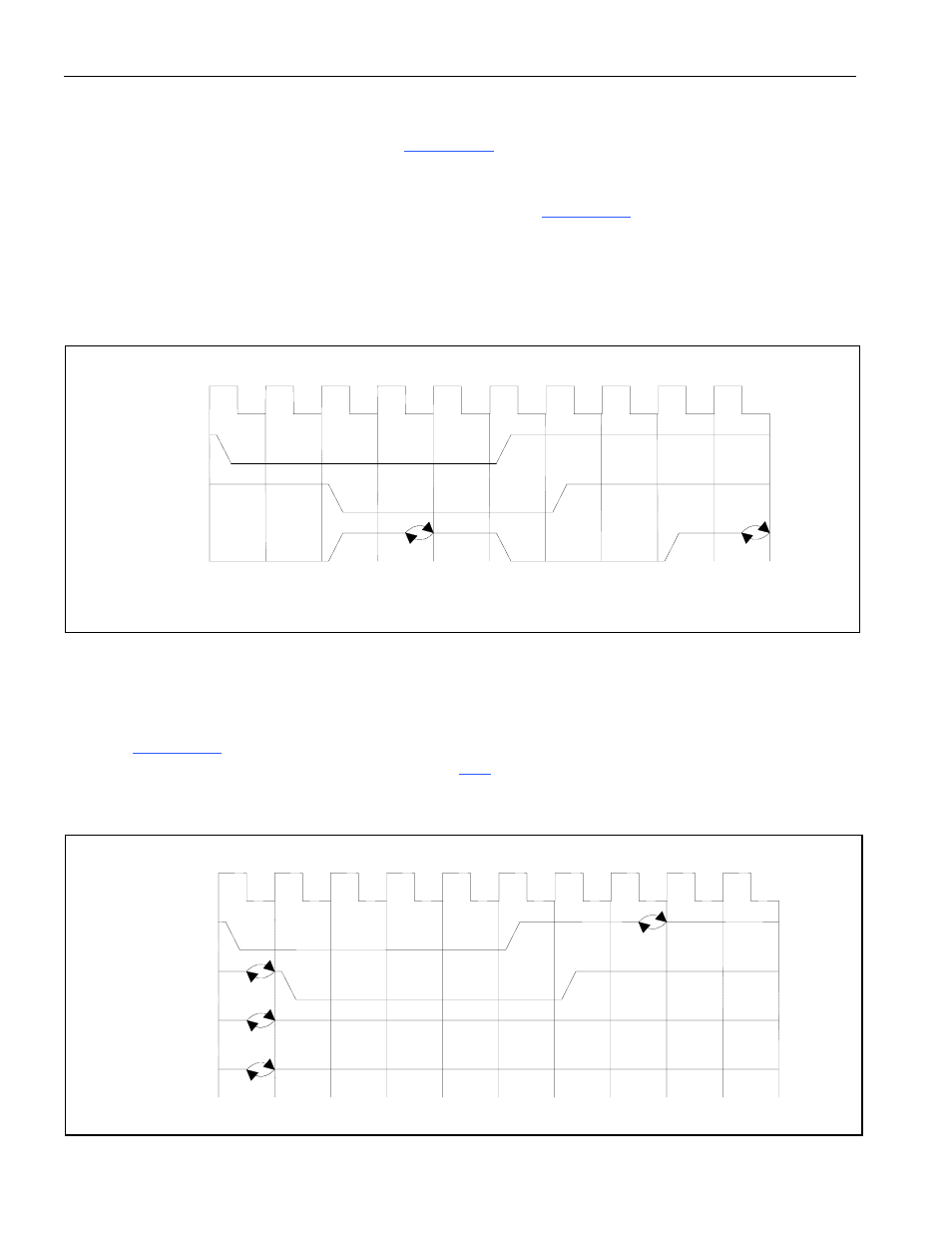
10.1.3 PCI Bus Arbitration
The PCI bus can be arbitrated as shown in
. The initiator requests bus access by asserting
PREQ. A central arbiter grants the access some time later by asserting PGNT. Once the bus has been
granted, the initiator waits until both PIRDY and PFRAME are deasserted (i.e., an idle cycle) before
acquiring the bus and beginning the transaction. As shown in
, the bus was still being used
when it was granted and the device had to wait until clock cycle #6 before it acquired the bus and began
the transaction. The arbiter can deassert PGNT at any time and the initiator must relinquish the bus after
the current transfer is complete, which can be limited by the latency timer.
Figure 10-4. PCI Bus Arbitration Signaling Protocol
10.1.4 PCI
Initiator
Abort
If a target fails to respond to an initiator by asserting PDEVSEL and PTRDY within 5 clock cycles, then
the initiator aborts the transaction by deasserting PFRAME and then, one clock later, by deasserting
PIDRY (
). If such a scenario occurs, it is reported through the master abort status bit in the
PCI command/status configuration register (Section
Figure 10-5. PCI Initiator Abort
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
PCLK
PREQ
PGNT
PFRAME
Bus is Relinquished
Bus is Acquired
Wait for
PGNT Asserted
and then
PFRAME and
PIRDY Deasserted
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
PCLK
PFRAME
PIRDY
PTRDY
PDEVSEL
