Figure 9-20. transmit done-queue structure – Rainbow Electronics DS31256 User Manual
Page 122
DS31256
122 of 181
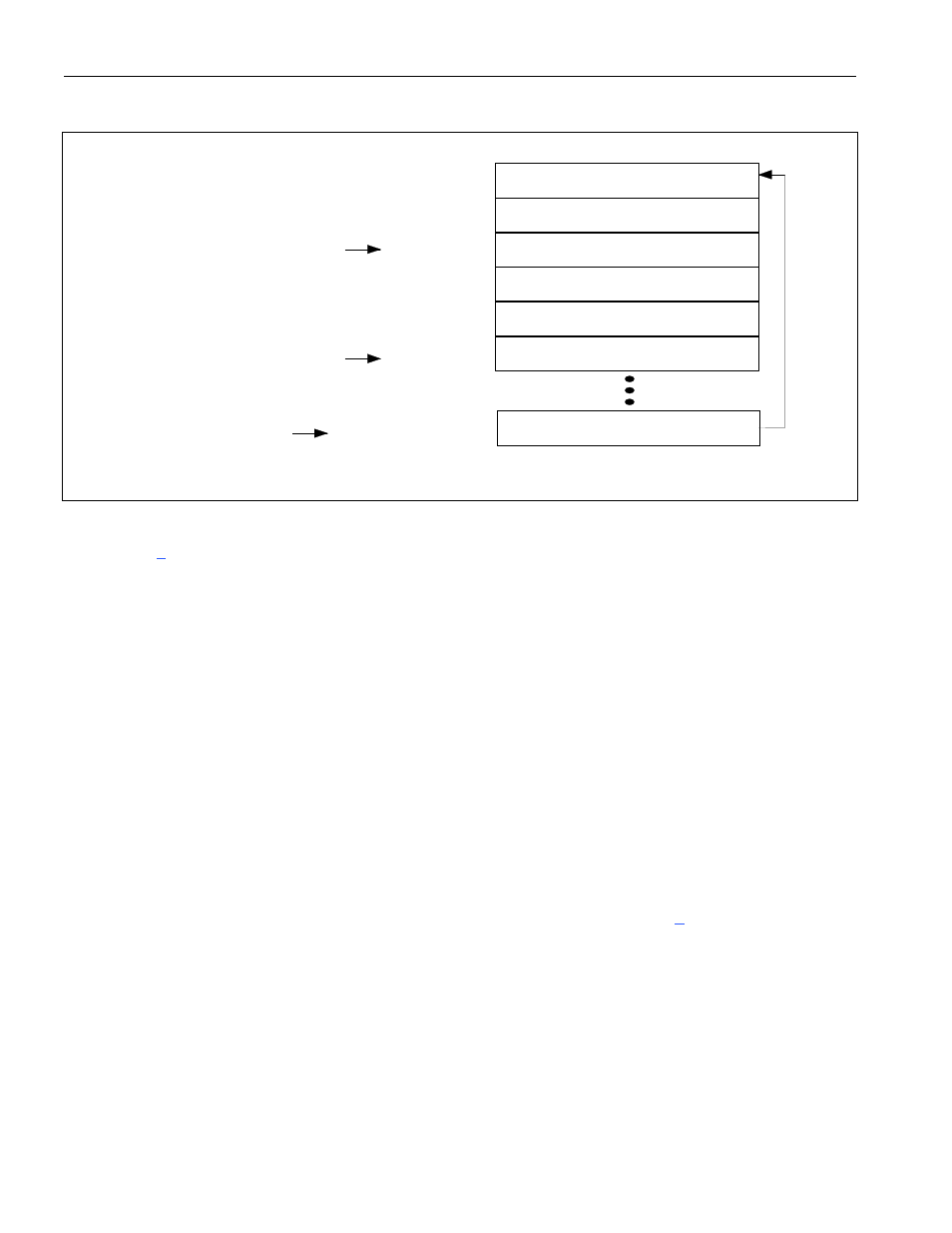
Figure 9-20. Transmit Done-Queue Structure
Once the transmit DMA is activated (through the TDE control bit in the master configuration register;
see Section
for more details), it can begin writing data to the done queue. It knows where to write data
into the done queue by reading the write pointer and adding it to the base address to obtain the actual 32-
bit address. Once the DMA writes to the done queue, it increments the write pointer by one dword. A
check must be made to ensure the incremented address does not exceed the transmit done-queue end
address. If the incremented address does exceed this address, the incremented write pointer is set equal to
0000h (i.e., the base address).
Status Bits/Interrupts
On writes to the done queue by the DMA, the DMA sets the status bit for the transmit DMA done-queue
write (TDQW) in the status register for DMA (SDMA). The host can configure the DMA to either set
this status bit on each write to the done queue or only after multiple (from 2 to 128) writes. The host
controls this by setting the TDQT0 to TDQT2 bits in the transmit DMA queues-control (TDMAQ)
register. See the description of the TDMAQ register at the end of this section for more details. The DMA
also checks the transmit done-queue host read pointer to ensure that an overflow does not occur. If this
does occur, the DMA sets the status bit for transmit DMA done-queue write error (TDQWE) in the status
register for DMA (SDMA), and it does not write to the done queue nor does it increment the write
pointer. In such a scenario, information on transmitted packets is lost and unrecoverable. Each of the
status bits can also (if enabled) cause an hardware interrupt to occur. See Section
for more details.
Done-Queue Burst Writing
The DMA can write to the done queue in bursts. This allows for a more efficient use of the PCI bus. The
DMA can hand off descriptors to the done queue in groups rather than one at a time, freeing up the PCI
bus for more time-critical functions.
An internal FIFO can store up to 8 done-queue descriptors (8 dwords, since each descriptor occupies one
dword). The host must configure the FIFO for proper operation through the transmit DMA queues
control (TDMAQ) register (see the following).
Base + 00h
Base + 04h
Base + 08h
Base + 0Ch
Base + 10h
Base + 14h
Base + End Address
Pending-Queue Host Write Pointer
Pending-Queue DMA Read Pointer
Maximum of 65,536
Pending-Queue Descriptors
DMA Acquired
Pending-Queue Descriptor
Host Readied
Pending-Queue Descriptor
Host Readied
Pending-Queue Descriptor
Host Readied
Pending-Queue Descriptor
DMA Acquired
Pending-Queue Descriptor
DMA Acquired
Pending-Queue Descriptor
Host Readied
Pending-Queue Descriptor
