Table 3.1 opcode bit options, 2 memory move instructions, 3 transfer control instructions – Avago Technologies LSI53C1010 User Manual
Page 42: Memory move instructions, Transfer control instructions, Opcode bit options, Table 3.1
3-2
The SCSI SCRIPTS Processor Instruction Set
3.1.2 Memory Move Instructions
The Memory Move Instruction type is selected when the two high order
bits of the DCMD register are 0b11. Memory Moves allow data transfer
from one 32
-
bit memory location to another. The source or the
destination may be a chip register. A 24-bit byte counter allows large
moves to occur with no intervention from the host processor. If both
addresses are in system memory, the device functions as a high speed
DMA controller, able to move data at sustained speeds up to 40 Mbytes/s
without using the host processor or its cache memory. Data is moved
from the source address into the chip's DMA FIFO and then out to the
destination address. This instruction type does not allow indirect
addressing, so the physical 32-bit address must be in the SCRIPTS
instruction.
In chips supporting instruction prefetching, the NOFLUSH qualifier
prevents flushing the prefetch buffer when the chip performs a
Memory-to-Memory Move instruction.
3.1.3 Transfer Control Instructions
The Transfer Control instruction type is selected when the two high order
bits of the DCMD register are 0b10. Transfer Controls perform SCRIPTS
operations such as JUMP, CALL, RETURN, and INTERRUPT. These
instructions allow comparisons of current phase values on the SCSI bus
or the first byte of data on any asynchronous incoming bytes, and
transfer control to another address depending on the results of the
comparison test. These operations may conduct a test of the ALU carry
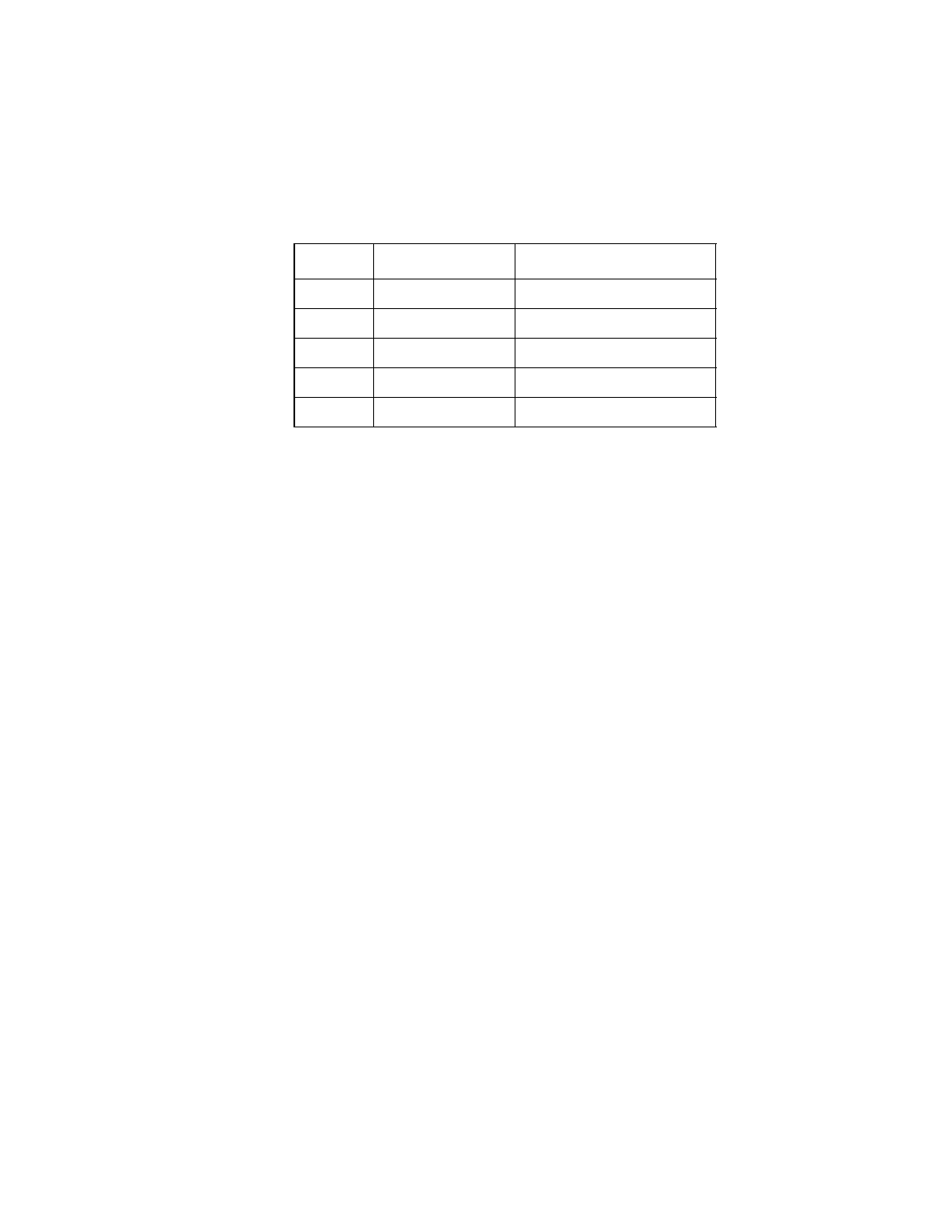
Table 3.1
Opcode Bit Options
Opcode
Target
Initiator
0b000
RESELECT
SELECT, SELECT with ATN
0b001
DISCONNECT
WAIT for DISCONNECT
0b010
WAIT for SELECT
WAIT for RESELECT
0b011
SET
SET
0b100
CLEAR
CLEAR
