2 registers used for target operation, Table 11.2 register bits used for target operation, 3 using scripts for target operation – Avago Technologies LSI53C1010 User Manual
Page 253: Registers used for target operation, Using scripts for target operation, Register bits used for target operation
Registers Used for Target Operation
11-3
11.2 Registers Used for Target Operation
Only a few of the operating register values are different for target
operation when compared to initiator operation.
summarizes
the register bit operations specific to target operation.
11.3 Using SCRIPTS for Target Operation
SCRIPTS instructions operate identically in target or initiator mode,
except for certain forms that are valid in only one mode. These
exceptions are all noted in the individual instruction descriptions in
Chapter 3, “The SCSI SCRIPTS Processor Instruction Set.”
When the
target device is moving data to the SCSI bus and is halted for any
reason, the residual data in the FIFO must be cleared before resuming
the transfer. It is most common to empty the FIFOs, send a Restore
Pointers message and start the transfer again.
Most interrupts to target operation are expected. The floppy disk provided
with this programming guide contains a sample interrupt service routine
for a target device.
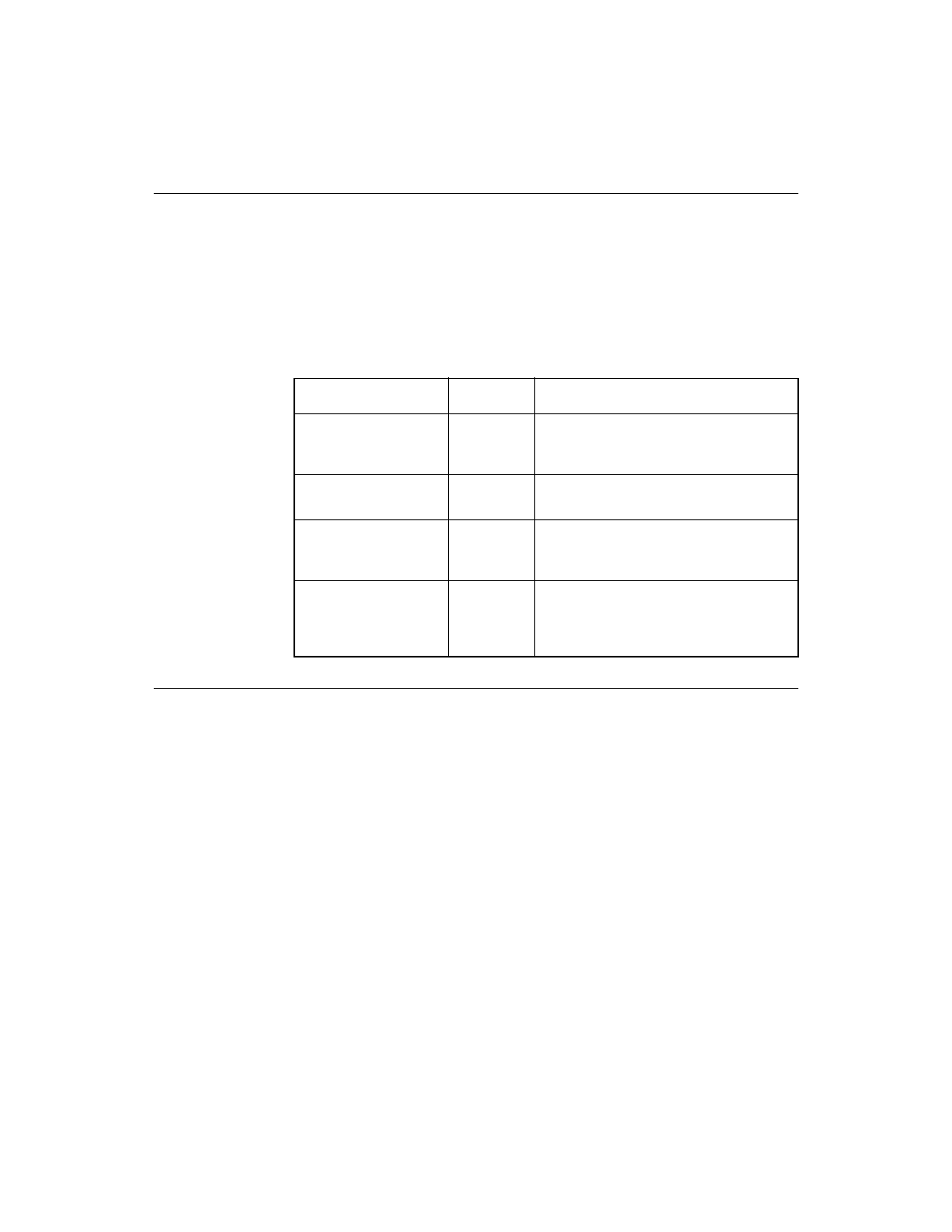
Table 11.2
Register Bits Used for Target Operation
Register Name
Bits
Description
RESPID1, RESPID0
all
Setting multiple bits in these registers
allows the processor to respond to
multiple SCSI IDs.
SCNTL0
0
Set this bit to make the chip a target
device by default.
SCID
5
Set this bit to allow the processor to
respond to bus initiated selection at the
chip ID in the RESPID1–0 registers.
SCNTL1
5
When this bit is cleared, the processor
halts the data transfer when a parity
error is detected or when the SATN/
signal is asserted.
