2 allocating and unallocating volumes, 2-1 allocating a volume to a host, 2-1-1 operating with the device manager agent – HP StorageWorks XP48 Disk Array User Manual
Page 44: 2-1-2 operating without the device manager agent, Unallocating a volume, Managing hosts, Viewing host information, Updating host information, Creating, expanding, and deleting file systems, Creating a file system
Using Provisioning Manager 44
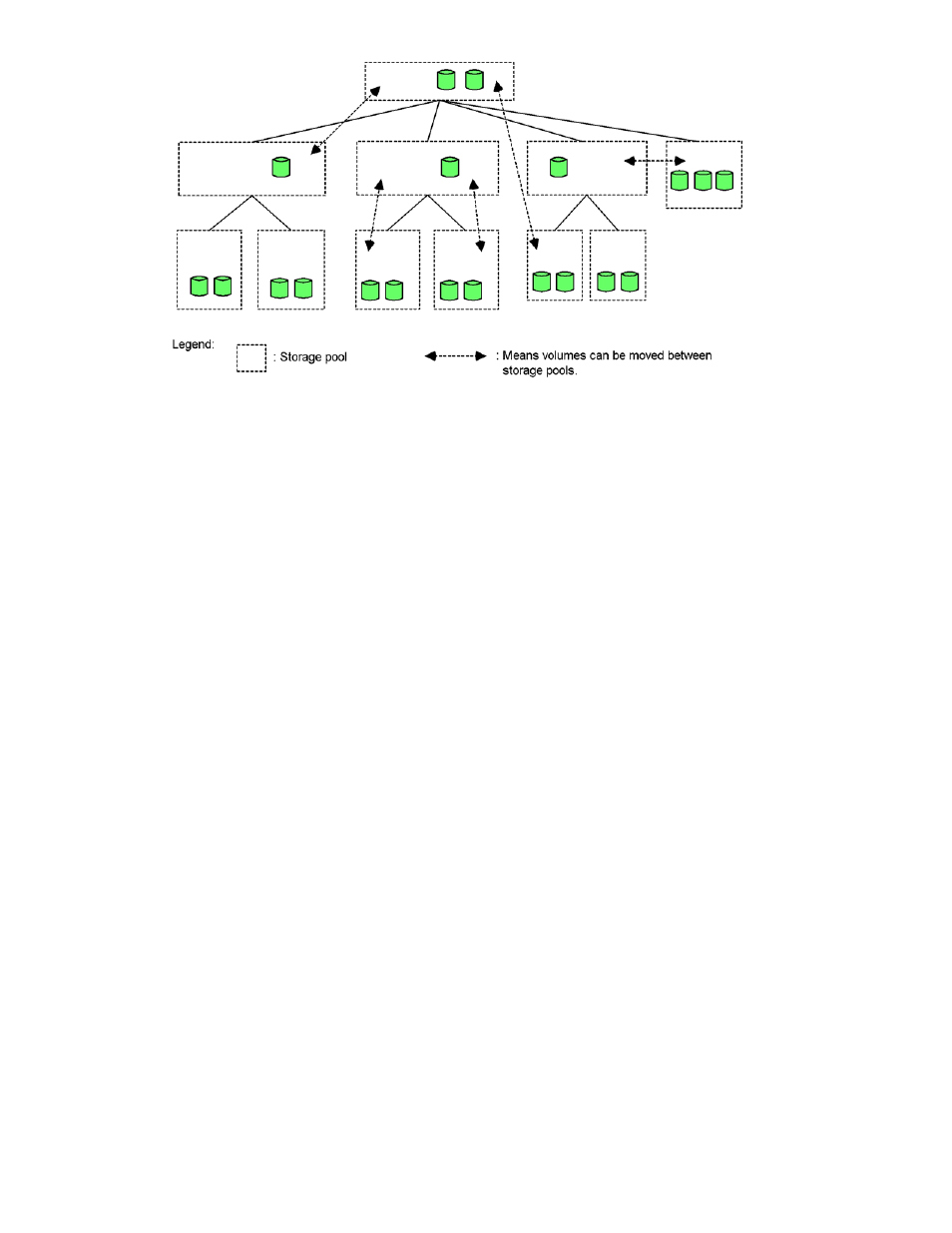
Figure 3-7
Example of Moving Volumes between Storage Pools
3-2 Allocating and Unallocating Volumes
You can allocate a storage volume included in a storage pool to any host managed by a user group, and you
can unallocate a storage volume from a host. You can also use a filtering facility defined in a provisioning plan
to easily manipulate massive storage volumes that are displayed in a list of unallocated volumes or in a list of
allocated volumes.
This facility provides settings for storage subsystems only; host settings are performed using functionality,
described later, for managing hosts, and for creating file systems and device files.
3-2-1 Allocating a Volume to a Host
You can select one or more unallocated volumes that are listed and allocate them to a host. Allocating a
volume means to set a path between the host and the volume that is routed via a subsystem port.
When you allocate a volume to a host, configure all the settings for the storage subsystem from the list of
allocated volumes or the list of unallocated volumes displayed in Provisioning Manager.
Using Device Manager to allocate the volume to a host allows you to view host information in the Provisioning
Manager Show Hosts window.
Before allocating a volume to a host, however, the host must be set up as part of the system. The procedure
for setting up a host in a system differs depending on whether you plan to operate the host with or without a
Device Manager agent. Both of these cases are explained in the following sections.
3-2-1-1 Operating With the Device Manager Agent
To set up a host in a system:
1.
Add the application server (host) to a network connected to a management server.
2.
Install a Device Manager agent onto the host or restart the host if one is already installed. This step
registers the host in the system.
3.
Use the Provisioning Manager update (refresh) function to register the host (the WWN of the host port) to
the system.
4.
Use Device Manager to place the host under the management of the user group that manages the
storage pool.
Whether you operate with or without the Device Manager agent, registering a host to a system can be
performed by users with system administrator or storage administrator permissions. Placing a host under the
management of a user group can be performed by users with system administrator or local system
administrator permissions. However, users with local system administrator permissions can place hosts only
under the management of groups positioned below the user group to which they belong.
3-2-1-2 Operating Without the Device Manager Agent
To set up a host in a system:
