7-2-1 types of volume managers, 7-2-2 setting up for volume managers, 7-2-3 specifying use of the volume manager – HP StorageWorks XP48 Disk Array User Manual
Page 25: 7-2-4 using the volume manager directly, About single sign-on functionality, Figure 1-8
Overview of HP StorageWorks XP Provisioning Manager 25
Figure 1-8
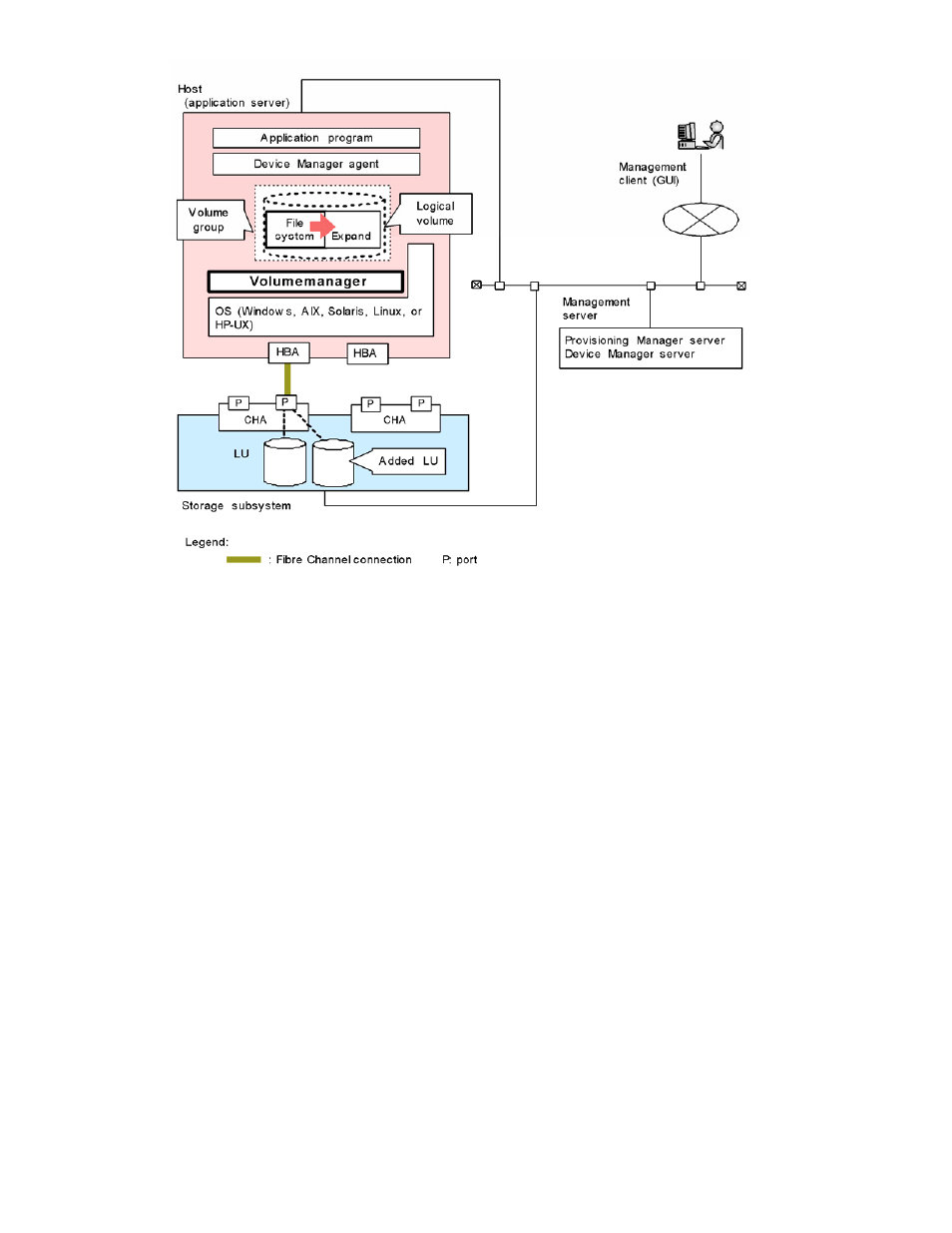
Linking with a Volume Manager (Expanding a File System)
1-7-2-1 Types of Volume Managers
A Volume Manager must be installed on the host. Some volume managers are provided by default with the
host OS. Other volume managers might be available even if they are not provided by default.
1-7-2-2 Setting Up for Volume Managers
You can link the volume managers of other manufacturers with Provisioning Manager. Some volume managers
are provided by default with the host OS. Other volume managers might be available on some OSs even if they
are not provided by default. You do not need to perform setup, other than installation of a volume manager that
is not provided by default with the host OS on the host, in order to link a volume manager with Provisioning
Manager. Even if a volume manager is installed on the host, each time you create a device file or file system,
you must specify on the GUI window whether that volume manager is to be used. As a result, the storage
subsystem might contain some device files and file systems created by using the volume manager, and some
that were created without using the volume manager. Even if a volume manager is installed on the host and set
up to link with Provisioning Manager, the user can use the volume manager directly to create, expand, and
delete volume (disk) groups and logical volumes. If Provisioning Manager used the volume manager to create
a file system or device file, the user can use the volume manager directly to expand or delete a target volume
group or logical volume.
1-7-2-3 Specifying Use of the Volume Manager
Even if a volume manager is installed on the host, you must specify through the interface whether that volume
manager is to be used each time you create a device file or file system. As a result, the storage subsystem
might contain a mix of device files and file systems: some created by using the volume manager, and some
created without using the volume manager.
1-7-2-4 Using the Volume Manager Directly
You can use the volume manager directly to create, expand, and delete volume (disk) groups and logical
volumes even if a volume manager is installed on the host and set up to link with Provisioning Manager.
If Provisioning Manager used the volume manager to create a file system or device file, you can use the
volume manager directly to expand or delete a target volume group or logical volume.
