Integrity mechanisms, Processor integrity, System firmware image – Echelon Series 6000 Chip databook User Manual
Page 82: Application integrity using checksums, Ee processor integrity
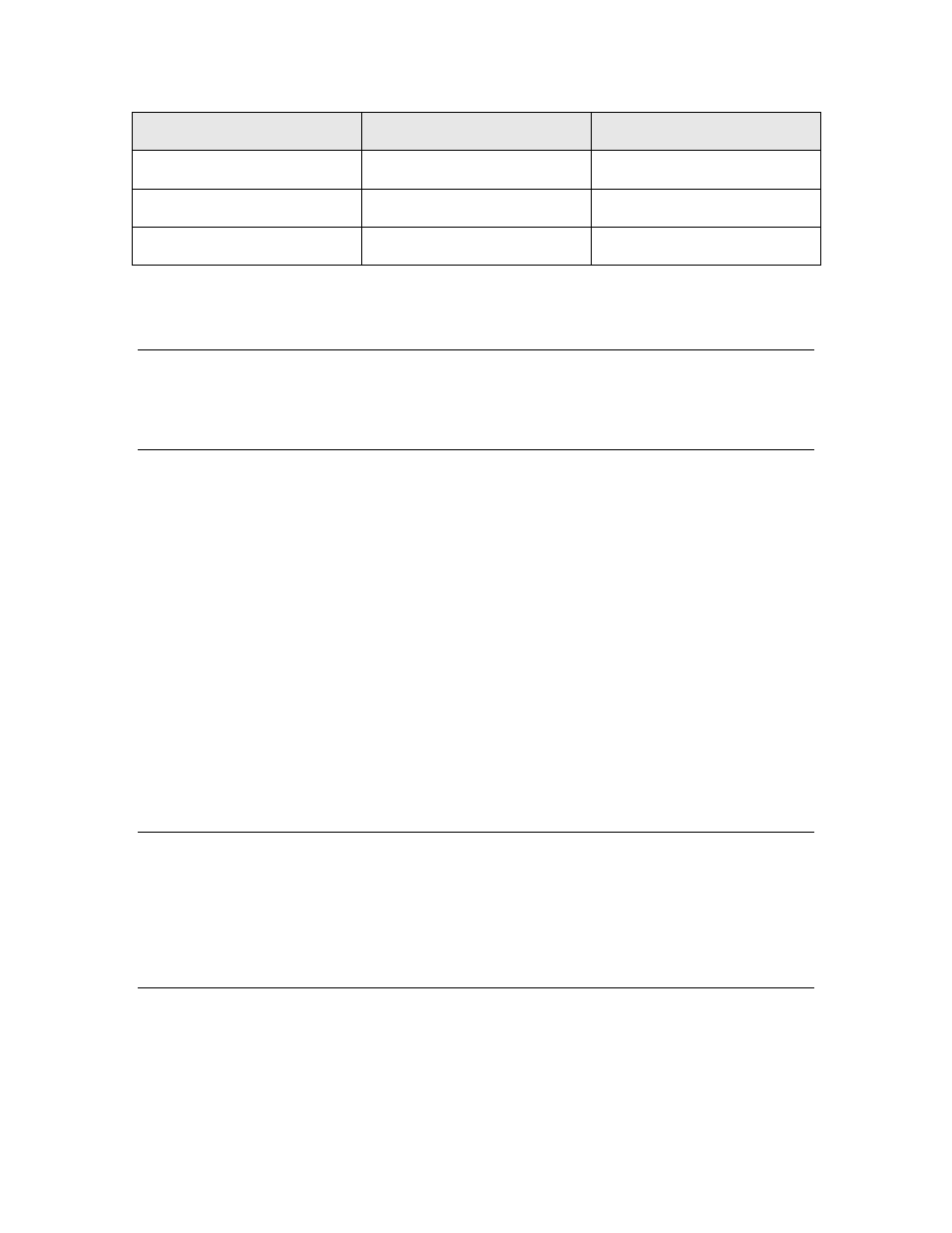
Device State
State Code
Service LED
Configured, Hard Offline
6
Off
Configured
4
Off
Defective External Memory
—
On
The SVC~ pin is active low, and the service pin message is sent once per SVC~ pin
transition. The service pin message goes into the next available non-priority output network
buffer.
Integrity Mechanisms
The Neuron architecture for a Series 6000 chip includes mechanisms for maintaining system
integrity by ensuring processor integrity and application integrity.
Processor Integrity
To maintain processor integrity while an application is running, the Neuron architecture
provides a set of interrupts for various error conditions that allow the application or
firmware to continue to run. There are certain error conditions that, without interrupt
support, would cause the processor to stop execution and possibly cause a reset of the device.
A Series 6000 chip handles the following error conditions with system-level traps:
•
Watchdog timer timeout
•
Memory-protection violations for writing to system image
•
Stack exceptions, including underflow, overflow, and collision conditions for the data
stack, return stack, and ISR stack
•
Execution of an illegal Neuron assembly language opcode
•
Execution of the Neuron assembly language HALT instruction
A system-level trap is highest level of interrupt and is non-maskable, that is, it cannot be
disabled. For each of these traps, the system firmware handles the interrupt, initiates a
reset if necessary, and updates the error log for the chip.
System Firmware Image
The 16 KB of RAM from memory address 0x0000 to address 0x3FFF holds the executing copy
of the Neuron firmware that is copied from external flash memoryThis memory area is write
protected so that an application program cannot alter the system firmware. Attempted
writes to this memory area trigger a memory-protection violation trap, which causes the chip
to reset.
Application Integrity Using Checksums
To ensure application integrity, the Neuron firmware maintains a checksum of the
application image. The checksum is a single byte, and is the two’s complement of the sum of
all bytes that it covers. The checksums is verified during reset processing, and also on a
continual basis through a background diagnostic process.
70
Hardware Resources
