Soldering surface mount (smt) parts, General esd handling guidelines – Echelon Series 6000 Chip databook User Manual
Page 159
Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive (2002/95/EC), thus their profiles use the lead-free
assembly, with a peak temperature T
p
of 260 ºC.
Soldering Surface Mount (SMT) Parts
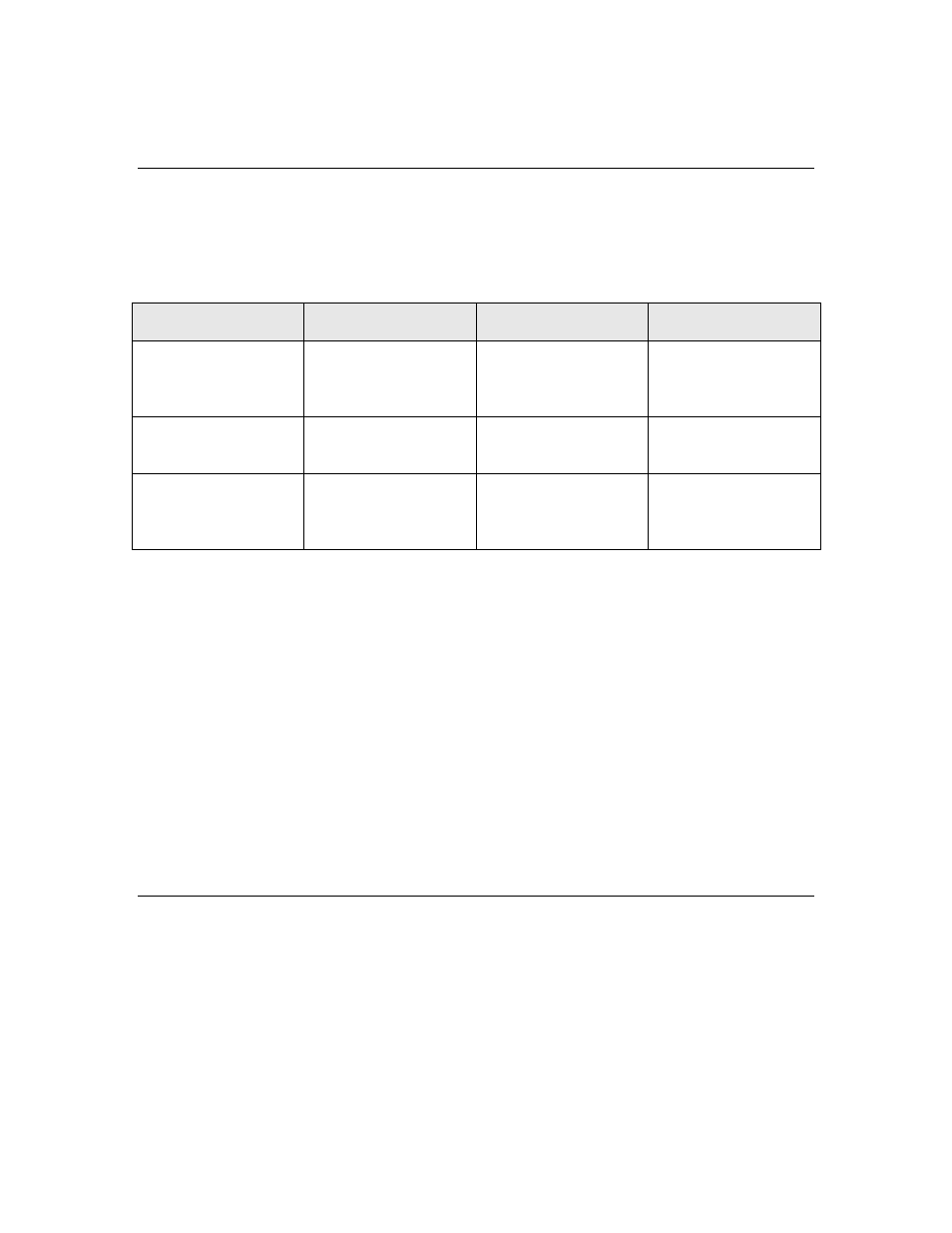
Table 43 lists the maximum reflow temperature for surface mount (SMT) parts. In all cases,
consult the solder manufacturer’s data sheet for recommendations on optimum reflow profile.
The actual reflow profile chosen should consider the peak temperature limitations.
Table 43. Peak Temperatures for Surface Mount Parts
Product
RoHS Compliant
Model Number
Peak Temperature
FT 6000 Free
Topology Smart
Transceiver
Yes
14235R
260 ºC
Neuron 6000
Processor
Yes
14305R
260 ºC
FT-X3
Communications
Transformer
Yes
14255R
245 ºC
As measured according to the IPC/JEDEC Standard J-STD-020D.1, Series 6000 chips have a
Level 3 Classification. The recommended soldering technique for Series 6000 chips is surface
mount reflow. Soldering techniques that involve immersing the entire part are not
recommended. Consult the solder manufacturer’s datasheet for recommendations on
optimum reflow profile.
Dry pack is a process that slowly bakes moisture from the surface mount technology package
and seals it into a dry pack bag to shield the unit from moisture in the atmosphere. The
exterior of the bag is marked with a label that indicates that the devices are moisture
sensitive and is marked with the date that the bag was sealed (there is a one year shelf life
for such devices).
There is a limited amount of time to use surface-mount devices after they are removed from
the dry pack. Before surface mounting, packages should not be out of the dry pack longer
than 168 hours at ≤ 60% relative humidity and ≤ 30 °C. If the units have not been shipped
dry pack or have been unpacked for too long, then units must be baked at 125 °C for 12 hours
prior to board soldering. If this is not done, some percentage of the units can exhibit
destructive failures or latent failures after the soldering process.
General ESD Handling Guidelines
All complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) devices have an insulated gate that is
subject to voltage breakdown. The high-impedance gates on the devices are protected by on-
chip networks. However, these on-chip networks do not make the chip immune to ESD.
Laboratory tests show that devices can fail after one very high voltage discharge. They can
also fail due to the cumulative effect of several discharges of lower potential.
Static-damaged devices behave in various ways, depending on the severity of the damage.
The most severely damaged are the easiest to detect because the input or output has been
completely destroyed and is shorted to V
DD
, shorted to GND, or is open-circuited. As a result
of this damage, the device no longer functions. Less severe cases are more difficult to detect
Series 6000 Chip Data Book
147
