Application considerations, Termination of unused pins – Echelon Series 6000 Chip databook User Manual
Page 154
Application Considerations
This section describes application considerations for design and manufacturing of L
ON
W
ORKS
devices.
Termination of Unused Pins
Because Series 6000 devices are CMOS devices, you must terminate all unused input pins,
including undeclared or unconnected I/O pins that are configured as inputs and including
three-state pins, to assure proper operation and reliability.
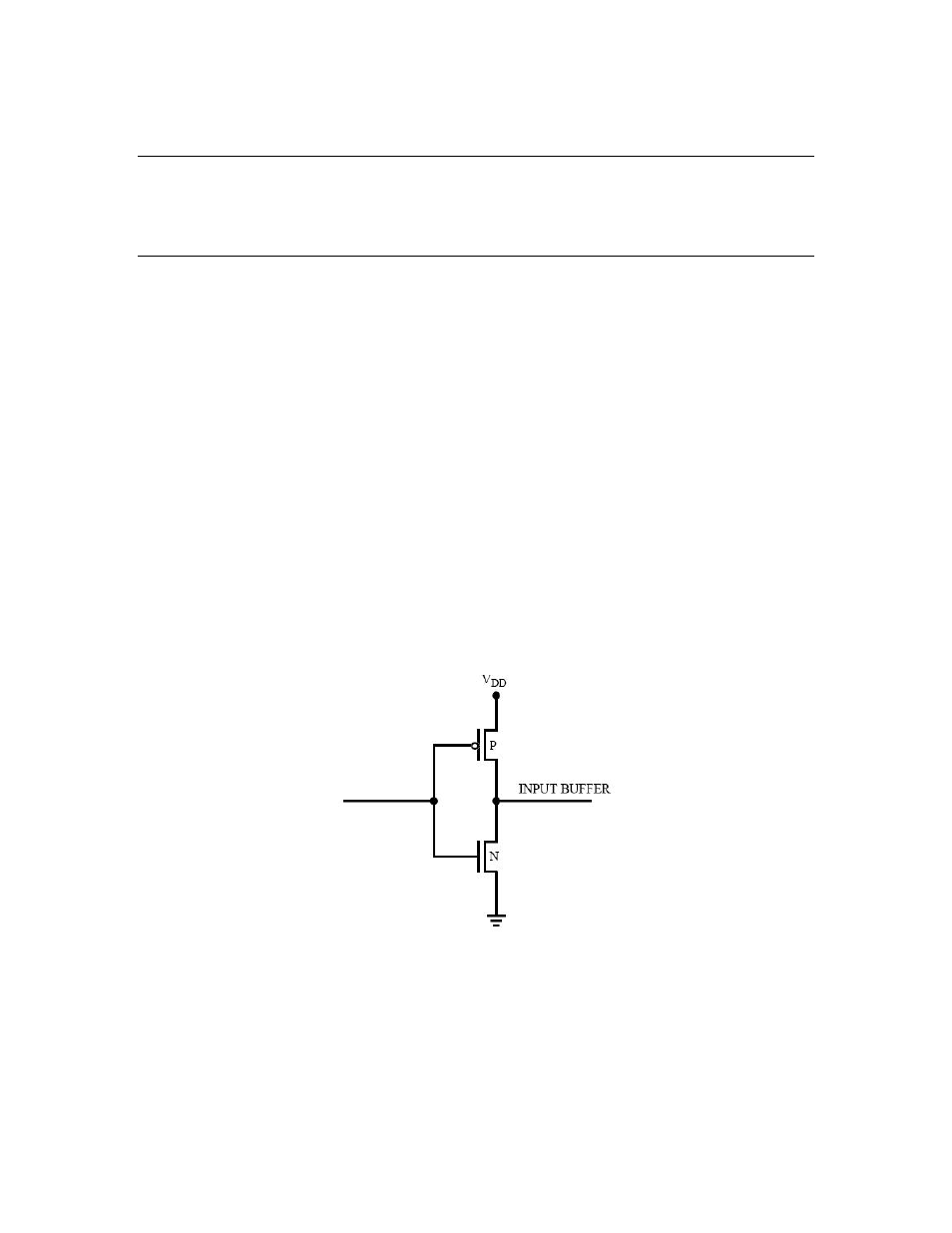
Figure 52 shows a CMOS inverter representative of circuitry found on CMOS input pins.
When the input is logic zero, the P-channel transistor is on (conducts), and the N-channel
transistor is off. When the input is a logic one, the P-channel transistor is off, and the N-
channel transistor is on. These transistors are linear devices with relatively broad switch
points. As the input transitions through the mid-supply region, there is a period of time
when both transistors are conducting. With fast rise-time digital signals at the input, this
period is very short. When the inverter is out of the linear region, there is very little current
flow. This effect is the reason that the overall current drain of a CMOS device is directly
proportional to the switching speed. Almost all the current consumption is by transistors
passing through the linear region and charging and discharging of internal capacitances. If
a pin is configured as an input or three-state, then the input can oscillate because of power
supply noise or it can float to the mid-supply region, which can result in higher current
consumption. Current design techniques have made latch-up due to floating input unlikely,
but it is good design practice to terminate unused I/O pins that are not configured (high
impedance) or are configured as inputs.
Figure 52. CMOS Inverter
The best method to terminate unused I/O pins is with an individual pull-up or pull-down
resistor for each unused pin. Other, less desirable, methods include:
•
Connecting unused input pins to each other and then to a common termination point.
This cost- and space-effective method has the disadvantage of not allowing individual
pin configuration later and has the possibility of contention if the pins are later
declared as outputs.
142
Handling and Manufacturing Guidelines
