Control network, Server redundancy, Server notifications – Rockwell Automation 1757-SWKIT3200 ProcessLogix R320.0 Installation and Upgrade Guide User Manual
Page 250
Publication 1757-IN032B-EN-P - April 2001
7-10 Performance and Capacity Specifications
Control Network
Server Redundancy
Server Notifications
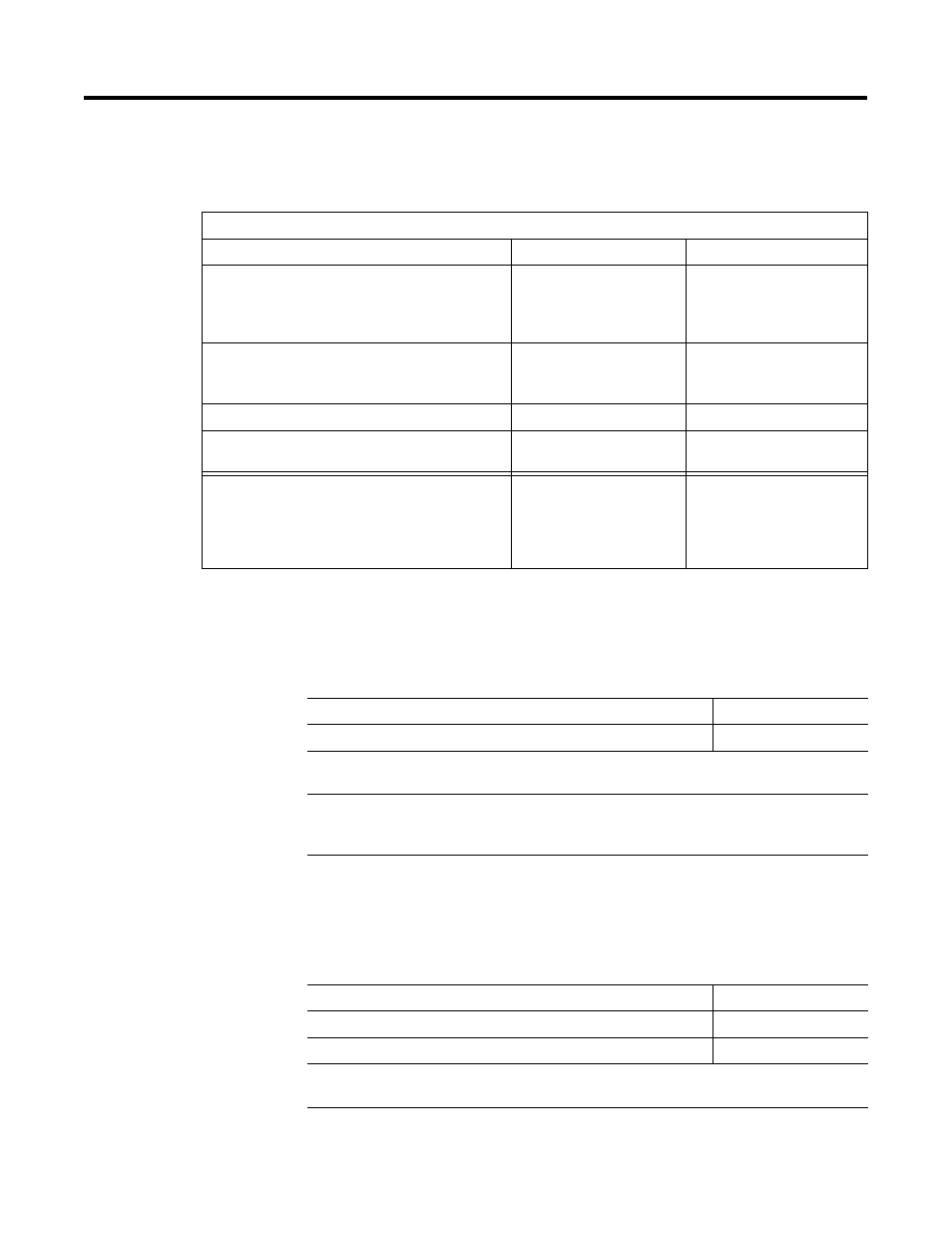
Table 7.I Process Control Network Specifications
Supervisory Process Control Network
Network Media
Ethernet
ControlNet
Supervisory Networks per ProcessLogix Server
- 1 1784-PCIC Card per NT
Mixed Supervisory ControlNet & Ethernet on the
same Server is not supported.
1 non-redundant network
serviced by 1 redundant or
non-redundant Server
1 redundant or non-redundant
network serviced by 1
redundant or non-redundant
Server
Allowable Combinations of Controllers * per Server
Up to 10 Non-Redundant
only
Up to 10 Redundant or
Non-Redundant in any
combination
Data Rate
10 Mbits/sec
5 Mbit/sec
Media Redundancy
Non-redundant only
Single cable or redundant
media operation supported.
*Controller Definitions including PLCs
Multiple 1757-PLX52s per chassis are NOT
supported. However, a non-redundant 1757-PLX52
can reside in the same chassis as a Logix 5550.
Non-Redundant:
•
1 1757-PLX52
•
1 Logix5550
•
1 PLC5/C or E
•
1 SLC (Ethernet only)
Redundant:
•
2 1757-PLX52s in a
Chassis Pair with 2
1757-SRMs
Table 7.J Server redundancy specifications
Server Switchover Time – Default
30-40 sec
Server Switchover Time – Fastest Configurable Time
10 sec
On Server switchover, the 1757-PLX52 performs an event recovery. This causes the controller to
report all current alarm conditions. The Server will report all current process alarms and events.
Database synchronization is performed as a background activity and is performed online without
affecting the operation of the Servers. Time to perform synchronization will depend on the system
configuration (e.g., database size, history, processor speed).
Table 7.K Server notification specifications
Maximum number of events (burst condition)
500 events
Maximum number of events/second (sustained)
40/sec
Maximum number of alarms/second (sustained)
20/sec
Note: Up to two events are also generated for every alarm, including one event for entering the
alarm condition and one for return to normal.
