Path/pspl commands, Cir/arc commands, Cir /arc /arcd/arcc commands – IAI America ASEL User Manual
Page 262: Cir2/arc2/arcd/arcc commands
Part 2 Programs
Chapter 4 Key Characteristics of
Actuator
Control Commands and Points to Note
240
Part 2 Programs
2. PATH/PSPL Commands
When executing a PATH or PSPL command, pay attention to the locus because it will change if the
acceleration/deceleration is different between points.
The locus can be fine-tuned by changing the acceleration/deceleration, but different
acceleration/deceleration settings between points will prevent smooth transition of speeds when
moving from one position to another.
If there is a large difference in deceleration/acceleration between points and the positioning distance is
small, the speed may drop. Exercise caution.
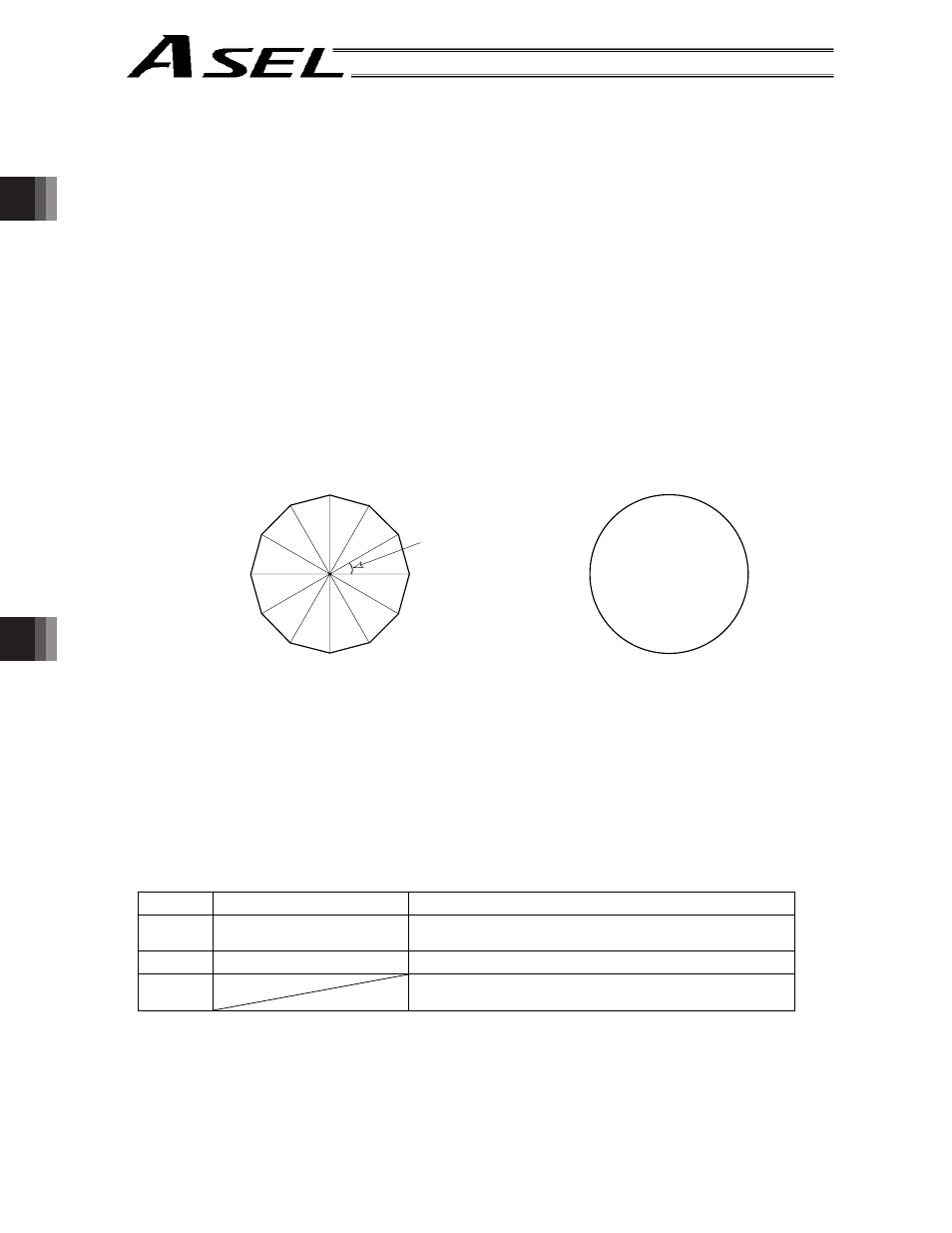
3. CIR/ARC Commands
The processing by a CIR or ARC command resembles moving along a polygon with a PATH
command.
A small division angle may cause the speed to drop.
CIR2, ARC2, ARCD and ARCC commands actually perform arc interpolation.
4. CIR2/ARC2/ARCD/ARCC Commands
With a CIR2, ARC2, ARCD or ARCC command, the speed can be changed (only in the arc
interpolation section) by inputting a speed for the point specified in operand 1. These commands are
effective when you must lower the speed partially because the radius is small and the arc locus
cannot be maintained inside the allowable range.
The speed and acceleration will take valid values based on the following priorities:
Priority
Speed
Acceleration (deceleration)
1
Setting in the position data
specified in operand 1
Setting in the position data specified in operand 1
2
Setting by VEL command Setting by ACC (DCL) command
3
Default acceleration in all-axis parameter No. 11
(Default deceleration in all-axis parameter No. 12)
Division angle set by a
DEG command
CIR
CIR2
