Frame relay ip routing, Frame relay ip routing -15, Rwsx – Alcatel Carrier Internetworking Solutions Omni Switch/Router User Manual
Page 887
Frame Relay IP Routing
Page 29-15
Frame Relay IP Routing
Frame Relay routing is different than standard
LAN
IP
Routing. In normal
LAN IP
Routing
MAC
addresses are used as source and destination addresses. In Frame Relay IP Routing, no
MAC
addresses are included in a routed frame. In fact, the only address in a routed Frame Relay
frame is the
DLCI
, or virtual circuit identifier. The
DLCI
is the main indentifier for source and
destination addresses.
Because Frame Relay uses 10-bit
DLCIs
as the main addressing units, routed Frame Relay
frames require less overhead than
LAN
IP
frames, which use
LAN
standard 48-bit addresses.
However, due to the nature of
DLCIs
on a
WAN
, Frame Relay routing requires a special
version of the IP protocol. The
DLCI
for a single VC may or may not be different on both
sides of a Frame Relay connection. That’s why Frame Relay uses the Inverse Address Resolu-
tion Protocol (InARP) to resolve
DLCI
issues and to automatically learn the IP addresses of
remote routers.
The InARP protocol ensures that before any data passes between two Frame Relay routers,
those routers notify each other of their IP addresses and associated
DLCIs
. So, the first
communication over a routed Frame Relay network is normally initiated by InARP.
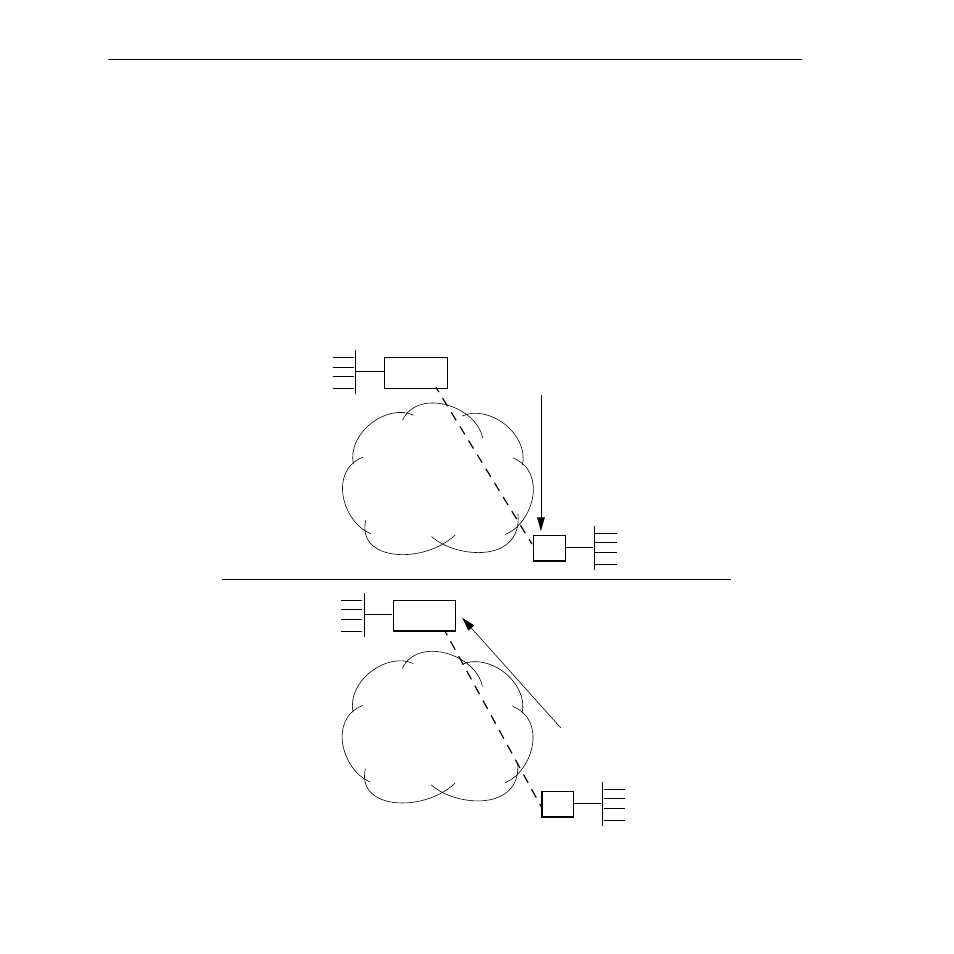
Frame Relay InARP Protocol
R
WSX
WSX
sends Router a message inform-
ing of its IP address and
DLCI
(“IP
111.22.33.44 on
DLCI
24”).
Router returns a message to
WSX
with its IP address and
DLCI
(“IP
222.33.44.55 on
DLCI
32”).
➊
➋
DLCI 24
R
WSX
DLCI 32
Frame Relay
Network
