Ip routing, Introduction, 25 ip routing – Alcatel Carrier Internetworking Solutions Omni Switch/Router User Manual
Page 723: Introduction -1
Page 25-1
25
IP Routing
Introduction
This chapter gives an overview of IP routing and includes information about configuring static
routes and viewing/configuring TCP/IP protocols such as Telnet and the Routing Information
Protocol (
RIP
). IP routing requires at least one virtual router port to be configured on the
switch. For information about configuring virtual router ports, see Chapter 19, “Managing
Groups and Ports.”
When IP routing is enabled on the switch, the switch exchanges routing information with
external IP routers in the network, and stations connected to groups and
VLANs
with virtual
router ports can communicate. Groups or
VLANs
that do not have router ports with routing
enabled are essentially firewalled from each other.
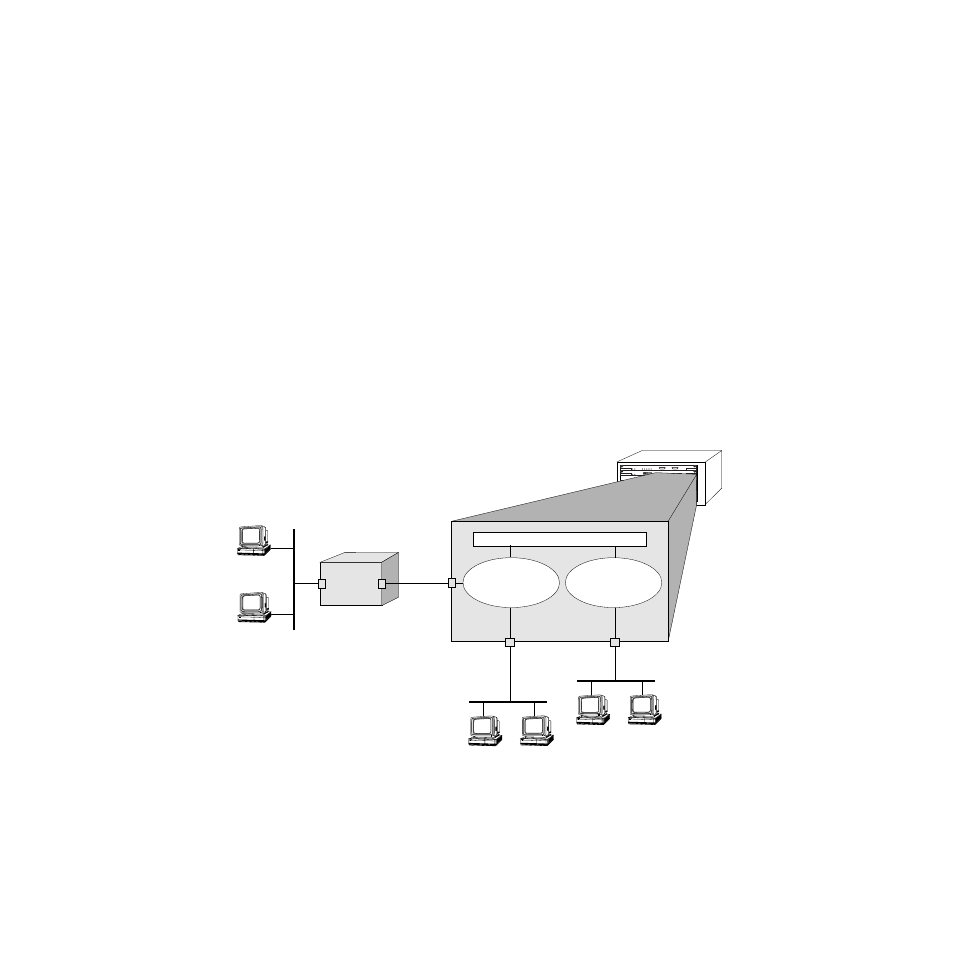
In the example shown here, stations connected to each group can communicate if a virtual
router port is created for each group and each router port on the switch has IP routing
enabled. Stations in group 2 and group 3 communicate with stations attached to the external
IP router if a default route to that router is configured on the switch or the switch learns
about the external router through
RIP
or some other routing protocol.
Omni Switch/Router
12345678
123456
Group 2
130.0.0.11
130.0.0.12
140.0.0.14 140.0.0.15
125.0.0.1
125.0.0.2
External
IP
Router
Group 3
130.0.0.0
140.0.0.0
Internal IP Router
