4 er osion cy cles – HEIDENHAIN TNC 406 User Manual
Page 161
140
8 Programming: Cycles
8.4 Er
osion Cy
cles
Expansion mode PAT
The expansion mode PAT determines the movement of the electrode
during erosion.
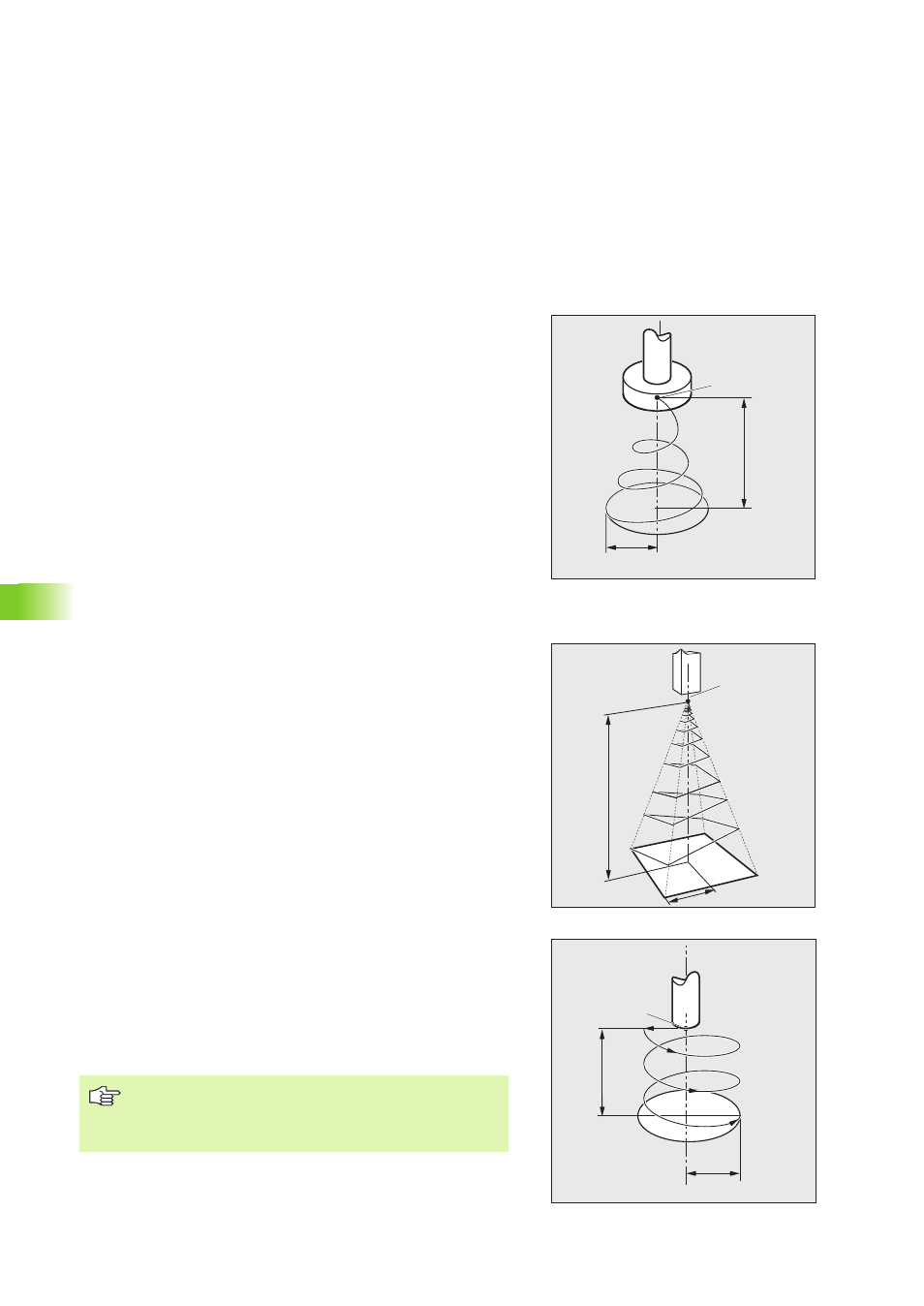
PAT = 0: Circular expansion (top illustration)
From the starting depth S the electrode moves along the surface of
a circular cone until it reaches the programmed eroding depth T and
the expansion radius RAD. The gap is controlled along an angular
vector. The electrode is retracted to the starting point along a
diagonal path.
PAT = 1: Quadratic expansion (center illustration)
Same as PAT = 0, but with quadratic expansion instead of circular
expansion.
PAT = 2: Circular orbital sinking (bottom illustration)
The electrode moves from the starting point S by the expansion
radius RAD in radial direction. It then follows a circular path until
reaching the eroding depth. The gap is controlled only in the eroding
axis. The electrode is retracted to the starting point along a diagonal
path.
PAT = 3: Quadratic orbital sinking
Same as PAT = 2, but with quadratic sinking instead of circular
sinking.
PAT = 4: Circular expansion in two phases
1.) From the starting depth S the electrode moves along the surface
of a circular cone (0° direction) until it reaches the programmed
eroding depth T and the expansion radius RAD. The gap is controlled
along an angular vector.
2.) At the eroding depth T, expansion is carried out in a circular path
with radius = entered end radius. The gap is controlled along the
circular path. The electrode is retracted first along the erosion path
and then diagonally back to the starting point.
PAT = 5: Quadratic expansion in two phases
Same as PAT = 4, but with quadratic expansion instead of circular
expansion.
PAT = 6: Circular expansion in two phases
1.) From the starting depth S the electrode moves along the surface
of a circular cone (0° direction) until it reaches the programmed
eroding depth T and the expansion radius RAD. The gap is controlled
along an angular vector.
2.) At the eroding depth T, expansion is carried out in a circular path
with radius = entered end radius. The gap is controlled along the
circular path. The electrode is retracted to the starting point along a
diagonal path.
PAT = 7: Quadratic expansion in two phases
Same as PAT = 6, but with quadratic expansion instead of circular
expansion.
There is the danger of collision if retraction to the starting
point follows a diagonal vector.
Select an electrode radius Re greater than the expansion
radius RAD for the corresponding expansion modes.
S
RAD
T
S
RAD
T
S
RAD
T
