5 path contours - polar coordinates, Overview, Polar coordinate origin: pole cc – HEIDENHAIN TNC 406 User Manual
Page 130: 5 path contours — polar coordinates
HEIDENHAIN TNC 406, TNC 416
109
6.5 P
a
th Cont
ours — P
o
lar Coor
dinat
e
s
6.5 Path Contours — Polar
Coordinates
Overview
With polar coordinates you can define a position in terms of its angle
PA and its distance PR relative to a previously defined pole CC (see
”Polar coordinates” on page 45).
Polar coordinates are useful with:
Positions on circular arcs
Workpiece drawing dimensions in degrees, e.g. bolt hole circles
Polar coordinates are identified with a P.
Overview of path functions with polar coordinates
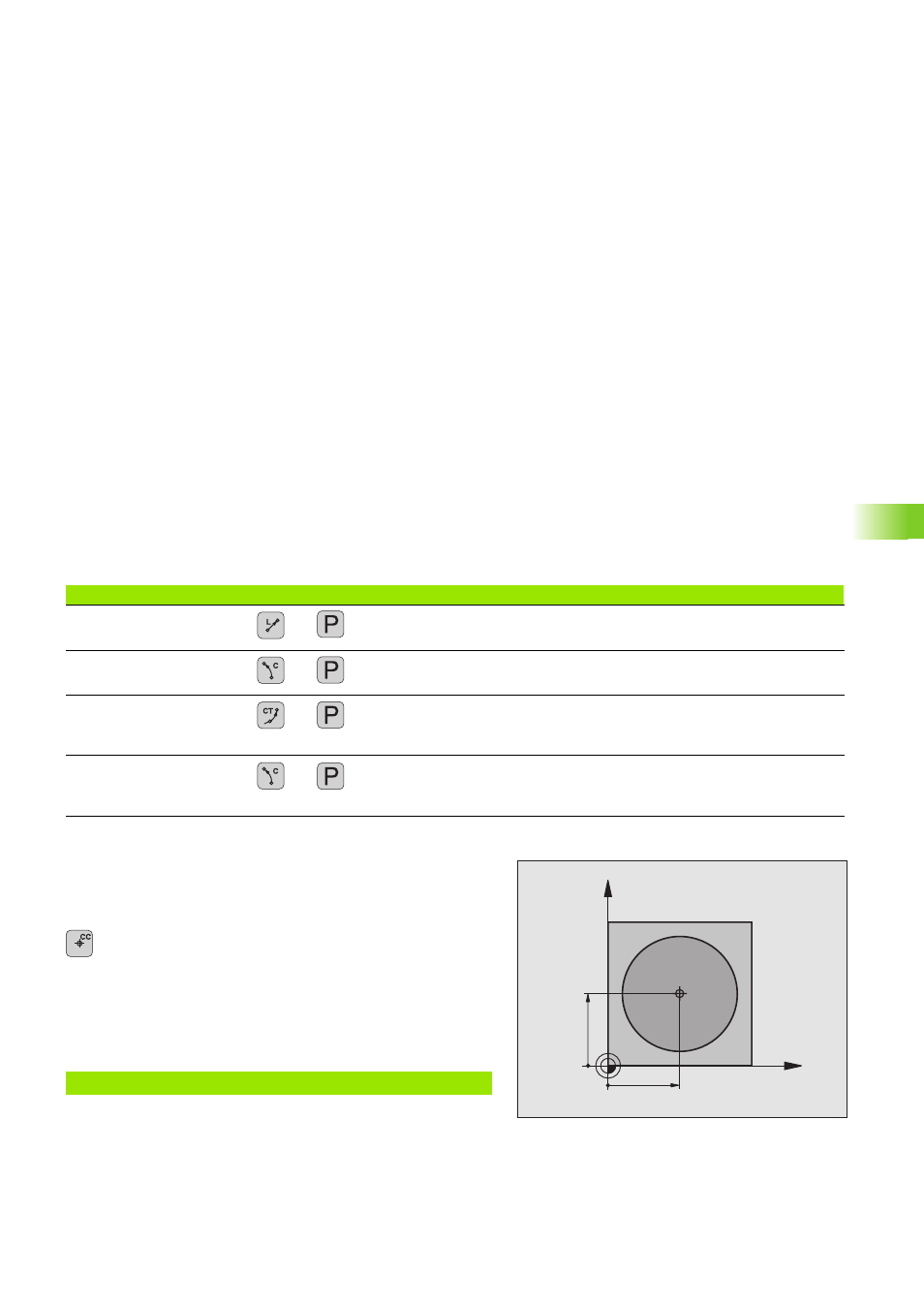
Polar coordinate origin: Pole CC
You can define the pole CC anywhere in the part program before
blocks containing polar coordinates. Enter the pole in Cartesian
coordinates as a circle center in a CC block.
8
Coordinates
CC: Enter Cartesian coordinates for the
pole, or
If you want to use the last programmed position, do
not enter any coordinates. Before programming polar
coordinates, define the pole CC. You can only define
the pole CC in Cartesian coordinates. The pole CC
remains in effect until you define a new pole CC.
Example NC blocks
Function
Path function key
Tool movement
Required input
Line LP
+
Straight line
Polar radius, polar angle of the
straight-line end point
Circular arc CP
+
Circular path around circle center/
pole CC to arc end point
Polar angle of the arc end point,
direction of rotation
Circular arc CTP
+
Circular arc with tangential
connection to the preceding
contour element
Polar radius, polar angle of the arc
end point
Helical interpolation
+
Combination of a circular and a
linear movement
Polar radius, polar angle of the arc
end point, coordinate of the end
point in the tool axis
12 CC X+45 Y+25
X
Y
CC
X
CC
Y
CC
