4 p ath cont ours — car tesian coor dinat es – HEIDENHAIN TNC 406 User Manual
Page 128
HEIDENHAIN TNC 406, TNC 416
107
6.4 P
ath Cont
ours — Car
tesian Coor
dinat
es
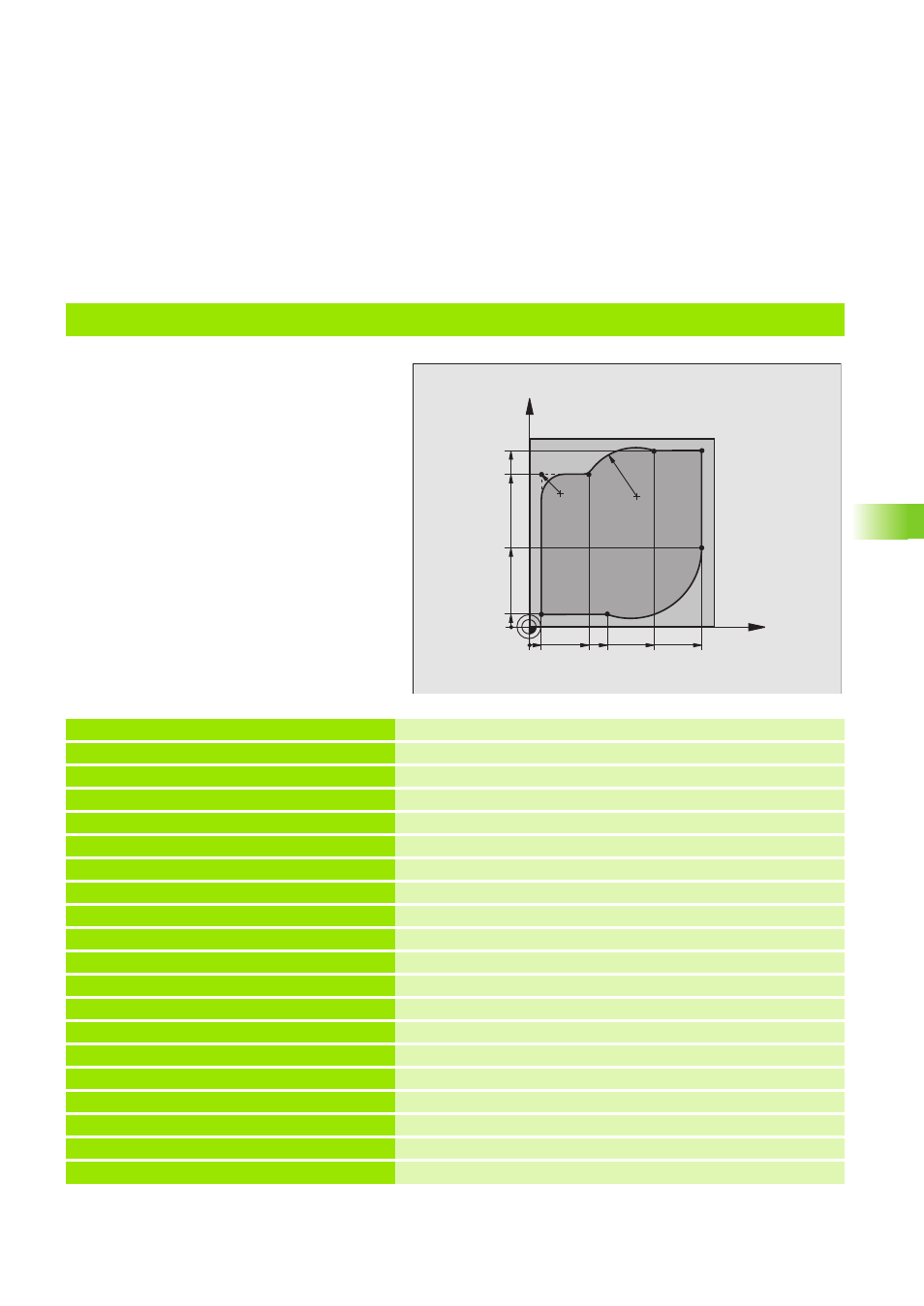
Example: Circular movements with Cartesian coordinates
0 BEGIN PGM CIRCULAR MM
1 BLK FORM 0.1 Z X+0 Y+0 Z-20
Define blank form for graphic workpiece simulation
2 BLK FORM 0.2 X+100 Y+100 Z+0
3 CYCL DEF 1.0 GENERATOR
Cycle GENERATOR (see ”Cycle 1 GENERATOR” on page 133)
4 CYCL DEF 1.1 P-TAB CUST1
Select erosion table (here, table CUST1)
5 CYCL DEF 1.2 MAX=6 MIN=6
Set power stage (here, to stage 6)
6 TOOL DEF 6 L+0 R+10
Define electrode in the program
7 TOOL CALL 6 Z U+1.5
Call electrode in the infeed axis Z, undersize 1.5 mm
8 L Z+100 C+0 R0 F MAX M37
Retract in the infeed axis; orient electrode; eroding OFF
9 L X-10 Y-10 R F MAX
Pre-position in X and Y; rapid traverse
10 L Z-5 R0 F MAX M
Move to working depth
11 L X+5 Y+5 RL F M36
Approach the contour at point 1 with radius compensation; eroding ON
12 L X+5 Y+85 R F M
Point 2: first straight line for corner 2
13 RND R10 F
Insert radius with R = 10 mm
14 L X+30 Y+85 R F M
Move to point 3: Starting point of the arc with CR
15 CR X+70 Y+95 R+30 DR-
Move to point 4: End point of the arc with CR, radius 30 mm
16 L X+95 R F M
Move to point 5
17 L X+95 Y+40 R F M
Move to point 6
18 CT X+40 Y+5 R F M
Move to point 7: End point of the arc, radius with tangential
connection to point 6, TNC automatically calculates the radius
X
Y
95
5
95
5
85
40
40
30
70
R10
R30
