Circular path ct with tangential connection, 4 p ath cont ours — car tesian coor dinat es – HEIDENHAIN TNC 406 User Manual
Page 124
HEIDENHAIN TNC 406, TNC 416
103
6.4 P
ath Cont
ours — Car
tesian Coor
dinat
es
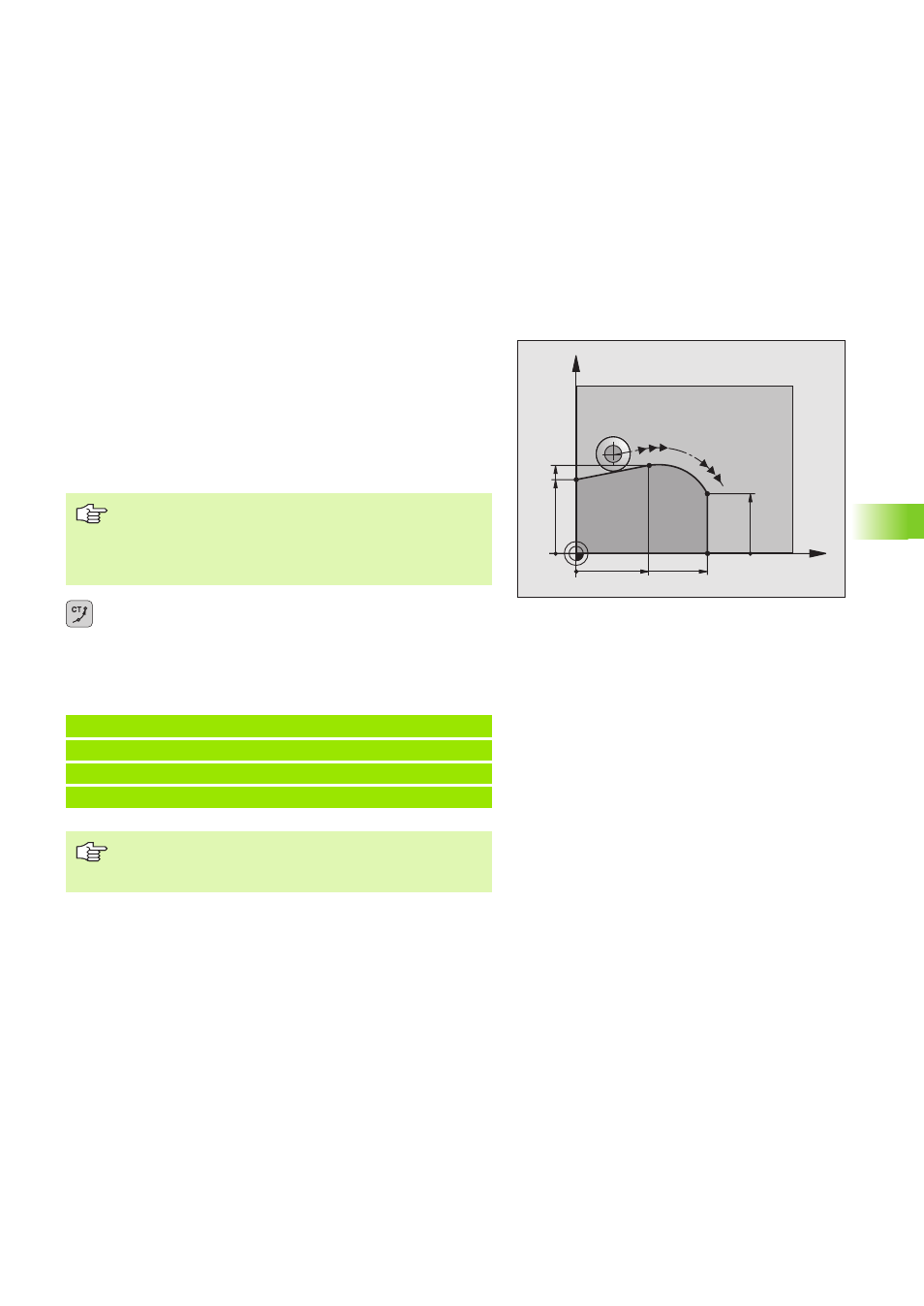
Circular path CT with tangential connection
The electrode moves on an arc that starts at a tangent with the
previously programmed contour element.
A transition between two contour elements is called tangential when
there is no kink or corner at the intersection between the two
contours—the transition is smooth.
The contour element to which the tangential arc connects must be
programmed immediately before the CT block. This requires at least
two positioning blocks.
8
Coordinates
of the arc end point
Further entries, if necessary:
8
Feed rate F
8
Miscellaneous function M
Example NC blocks
If you are using an electrode with tool compensation in
the XY plane, you must rotate the electrode in synchrony
with the angle on circular arcs. For example, for a
semicircle you must rotate the C axis by 180°
(incremental).
7 L X+0 Y+25 RL F M36
8 L X+25 Y+30 R F M
9 CT X+45 Y+20 R F M
10 L Y+0 R F M
A tangential arc is a two-dimensional operation: the
coordinates in the CT block and in the contour element
preceding it must be in the same plane of the arc.
X
Y
25
45
25
30
20
