Circular path cp around pole cc, 5 p a th cont ours — p o lar coor dinat e s – HEIDENHAIN TNC 406 User Manual
Page 132
HEIDENHAIN TNC 406, TNC 416
111
6.5 P
a
th Cont
ours — P
o
lar Coor
dinat
e
s
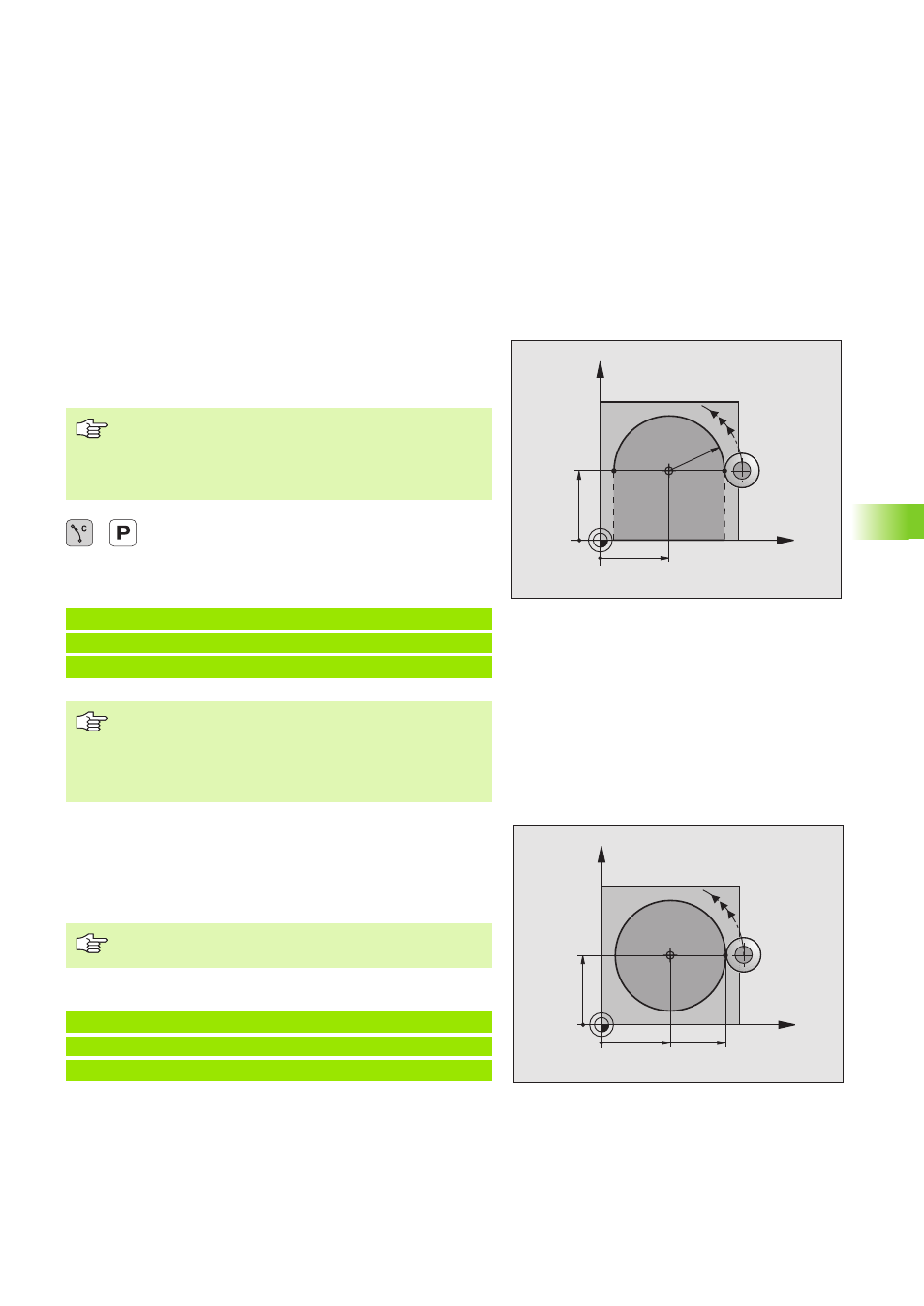
Circular path CP around pole CC
The polar coordinate radius PR is also the radius of the arc. It is defined
by the distance from the starting point to the pole CC. The last
programmed electrode position before the CP block is the starting
point of the arc.
8
Polar coordinates angle PA:
Angular position of the
arc end point
8
Direction of rotation DR
Example NC blocks
Full circle
For a full circle you must program the incremental polar coordinate
angle IPA with 360°. The electrode moves from the starting point
around the circle center CC.
The linear coordinate IC +360 rotates the electrode in synchrony with
the angle on the circular path.
Example NC blocks
If you are using an electrode with tool compensation in
the XY plane, you must rotate the electrode in synchrony
with the angle on circular arcs. For example, for a
semicircle you must rotate the C axis by 180°
(incremental).
18 CC X+25 Y+25
19 LP PR+20 PA+0 RR F M
20 CP PA+180 DR+ R F M
For incremental coordinates, enter the same sign for
DR and PA.
For PA you may enter values from –5400 to +5400.
The end point of the circle may not be identical with the
starting point of the circle.
You can only program a full circle with the incremental
polar coordinate angle IPA.
5 CC X+25 Y+25
6 L X+45 Y+25 RR F M
7 CP IPA +360 IC+360 DR+ R F M
X
Y
25
25
R20
CC
X
Y
25
45
25
CC
