Circular path cr with defined radius, 4 p ath cont ours — car tesian coor dinat es – HEIDENHAIN TNC 406 User Manual
Page 122
HEIDENHAIN TNC 406, TNC 416
101
6.4 P
ath Cont
ours — Car
tesian Coor
dinat
es
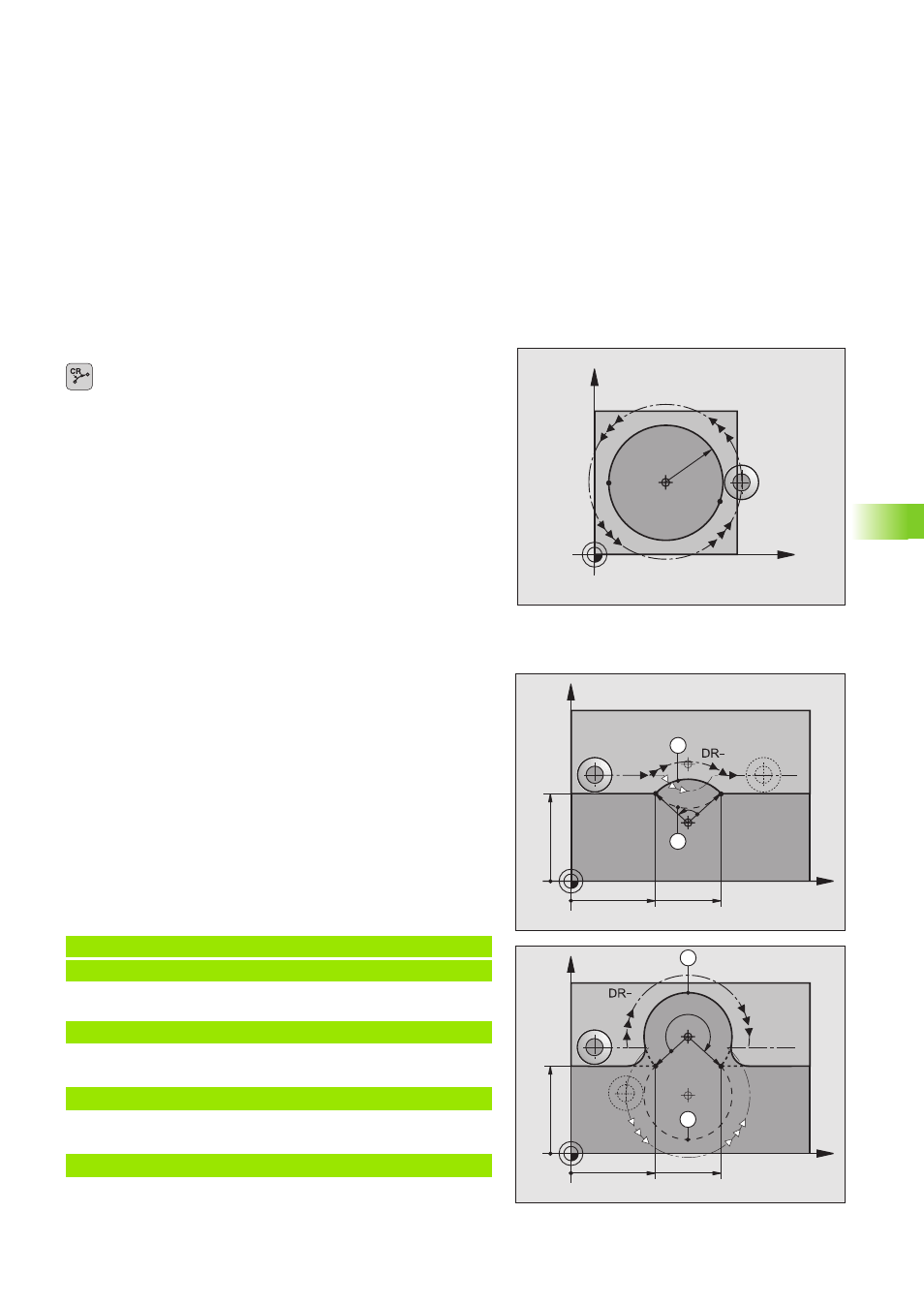
Circular path CR with defined radius
The electrode moves on a circular path with the radius R.
8
Coordinates
of the arc end point
8
Radius R
Note: The algebraic sign determines the size of the arc!
8
Direction of rotation DR
Note: The algebraic sign determines whether the arc
is concave or convex!
Further entries, if necessary:
8
Miscellaneous function M
8
Feed rate F
Full circle
To program a full circle you must enter two CR blocks in succession: The
end point of the first semicircle is the starting point of the second circle.
The end point of the second semicircle is the starting point of the first.
The easiest method of programming a full circle is described on
page 111.
Central angle CCA and arc radius R
The starting and end points on the contour can be connected with four
arcs of the same radius:
Smaller arc: CCA<180°
Enter the radius with a positive sign R>0
Larger arc: CCA>180°
Enter the radius with a negative sign R<0
The direction of rotation determines whether the arc is curving
outward (convex) or curving inward (concave):
Convex: Direction of rotation DR– (with radius compensation RL)
Concave: Direction of rotation DR+ (with radius compensation RL)
Example NC blocks
or
or
or
10 L X+40 Y+40 RL F M36
11 CR X+70 Y+40 R+20 DR- (ARC 1)
11 CR X+70 Y+40 R+20 DR+ (ARC 2)
11 CR X+70 Y+40 R-20 DR- (ARC 3)
11 CR X+70 Y+40 R-20 DR+ (ARC 4)
X
Y
CC
S
1
=E
2
E
1
=S
2
R
X
Y
40
40
70
DR+
4
ZW
3
R
R
X
Y
ZW
R
R
40
40
70
1
2
DR+
