Cycle 16 orbit, 4 er osion cy cles – HEIDENHAIN TNC 406 User Manual
Page 160
HEIDENHAIN TNC 406, TNC 416
139
8.4 Er
osion Cy
cles
Cycle 16 ORBIT
The ORBIT cycle is a machining cycle which facilitates programming
of spark-out behavior and movement of the electrode.
In Cycle 16 ORBIT you enter the
Eroding axis
Eroding depth
Miscellaneous function M
Expansion radius RAD
Rotational direction DIR
Expansion mode PAT
Spark-out mode SPO
If necessary, you may also use Q parameters for the cycle definition.
Eroding axis and depth
The eroding axis determines the coordinate axis parallel to which
eroding takes place in the ”depth.”
The sign of the eroding depth determines whether the working
direction is the direction of the positive coordinate axis (depth +) or of
the negative coordinate axis (depth –).
You can enter the eroding depth in absolute or incremental
dimensions.
Miscellaneous function M
You can enter a miscellaneous function in Cycle 16 ORBIT, such as
M36 (eroding ON).
Expansion radius RAD
The TNC feeds the electrode in radial direction (perpendicular to the
eroding depth) by the value of the expansion radius.
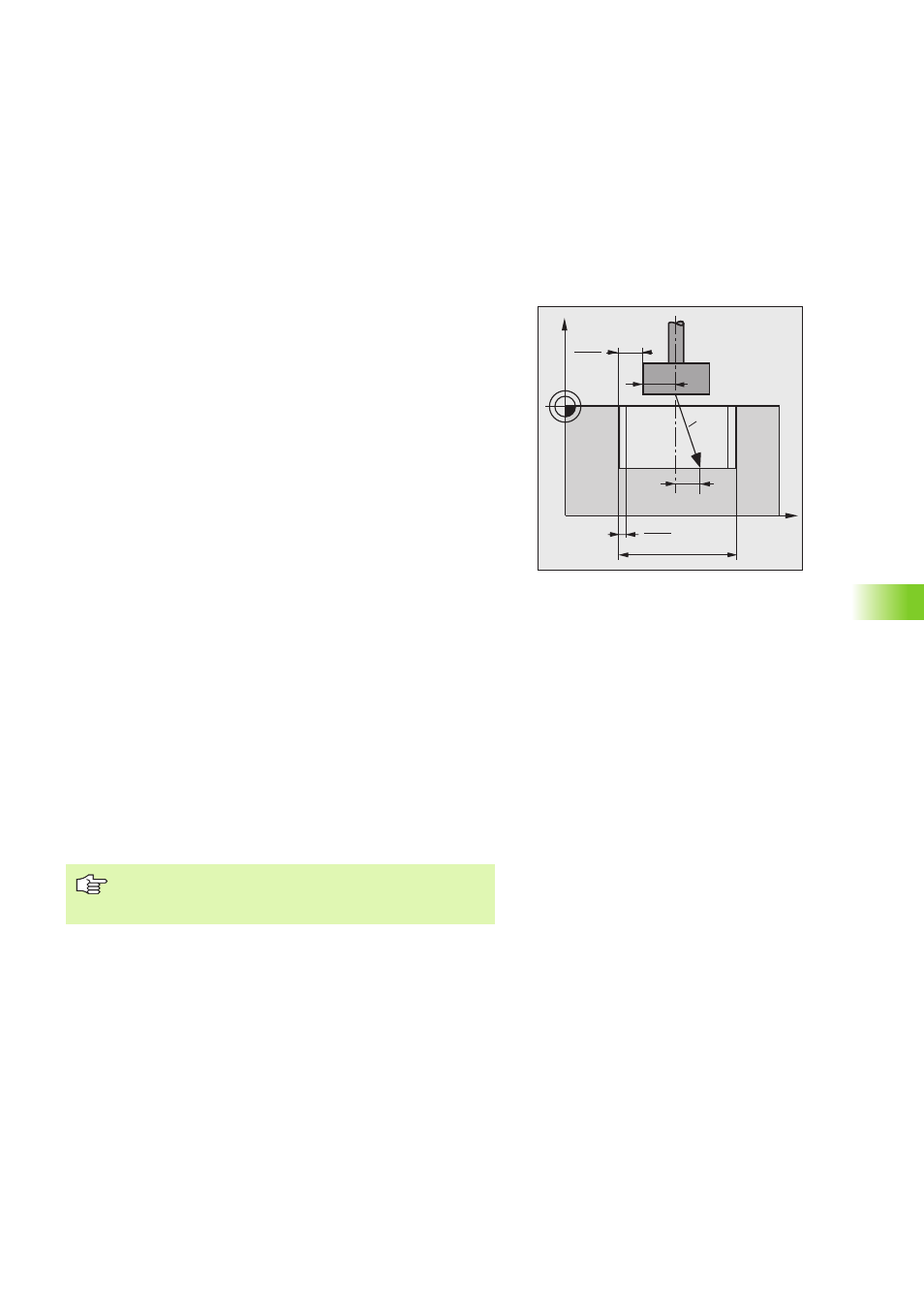
Calculating the expansion radius RAD
If the diameter D of the disk is known, you can calculate the expansion
radius RAD from the following data:
Diameter D of the disk
Electrode undersize UM
Electrode minimum undersize UNS
Electrode radius Re
RAD = 0.5 • (UM – UNS) = 0.5 • D – Re – 0.5 • UNS
Rotational direction DIR
Counterclockwise erosion movement: DIR = 0
Clockwise erosion movement: DIR = 1
X
Z
RAD
UM
2
D
Re
UNS
2
V
The electrode radius Re must be larger than the expansion
radius RAD. Otherwise the pocket (disk) will not be
completely eroded.
