Executing the ping operation at the cli, Tracert – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 17
6
Executing the ping operation at the CLI
Task Command
Remarks
Test the network
connectivity to an IP
address.
•
For IPv4 networks:
ping [ ip ] [ -a source-ip | -c count | -f | -h ttl | -i
interface-type interface-number | -m interval | -n | -p
pad | -q | -r | -s packet-size | -t timeout | -tos tos | -v
| -vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] * host
•
For IPv6 networks:
ping ipv6 [ -a source-ipv6 | -c count | -m interval | -s
packet-size | -t timeout | -vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name] * host [ -i interface-type
interface-number ]
Required.
Available in any view.
NOTE:
•
Set a larger value for the timeout timer (indicated by the -t keyword in the command) for a low-speed
network.
•
Only the directly connected segment address can be pinged if the outgoing interface is specified with
the -i keyword.
•
The destination firewall whose ping response function is disabled cannot be pinged.
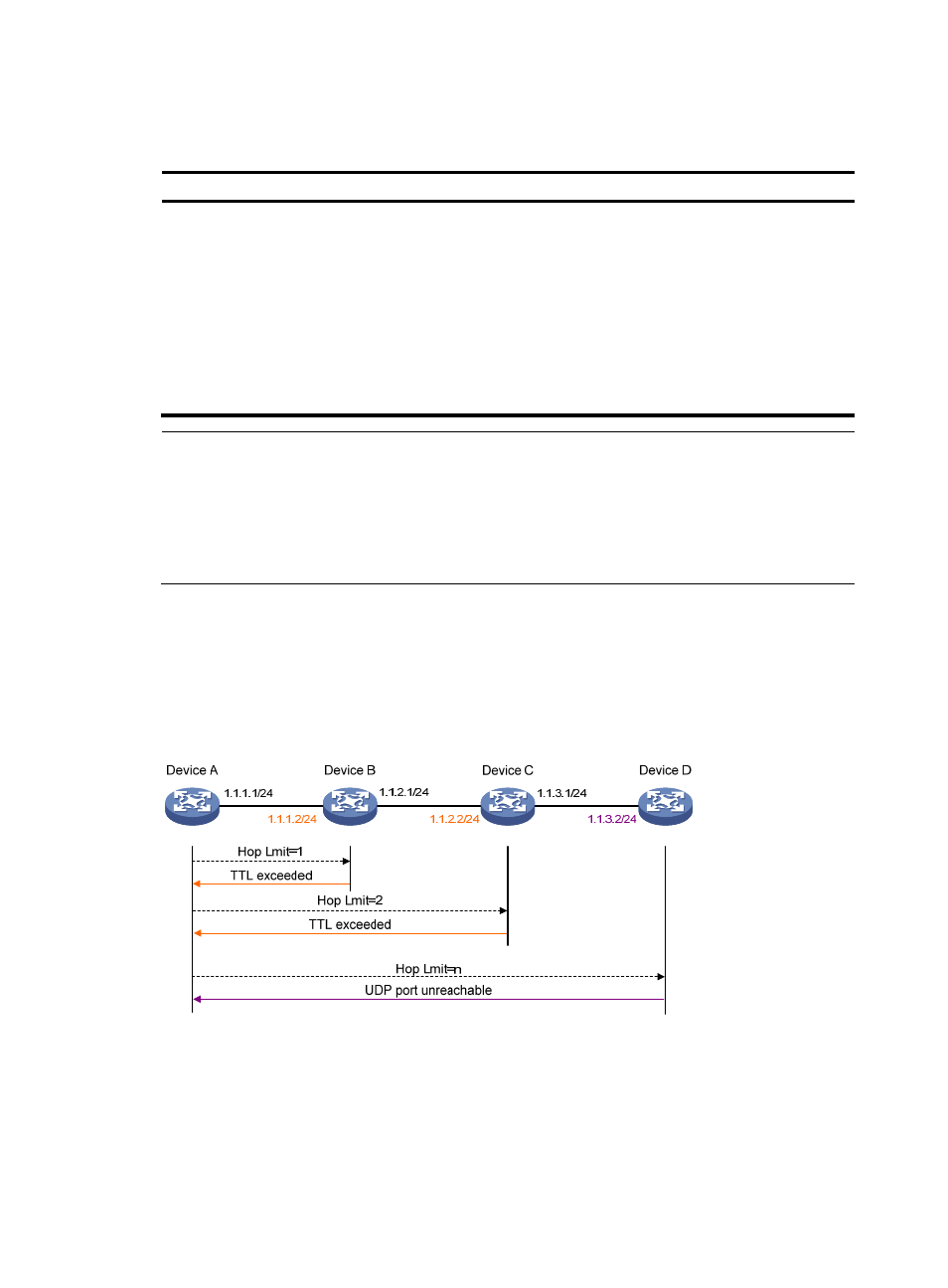
Tracert
Tracert (also called "Traceroute") enables you to get the IP addresses of Layer 3 devices in the path to a
specific destination. You can use tracert to test network connectivity and identify failed nodes.
Figure 4 Tracert diagram
Tracert uses received ICMP error messages to get the IP addresses of devices. As shown in
,
tracert works as follows:
1.
The source device (Device A) sends a UDP packet with a TTL value of 1 to the destination device
(Device D). The destination UDP port of the packet is not used by any application of the
destination.
- H3C SecPath F5000-A5 Firewall H3C SecPath F1000-A-EI H3C SecPath F1000-E-SI H3C SecPath F1000-S-AI H3C SecPath F5000-S Firewall H3C SecPath F5000-C Firewall H3C SecPath F100-C-SI H3C SecPath F1000-C-SI H3C SecPath F100-A-SI H3C SecBlade FW Cards H3C SecBlade FW Enhanced Cards H3C SecPath U200-A U200-M U200-S H3C SecPath U200-CA U200-CM U200-CS
