Private alarm group, Configuring the rmon statistics function – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 136
125
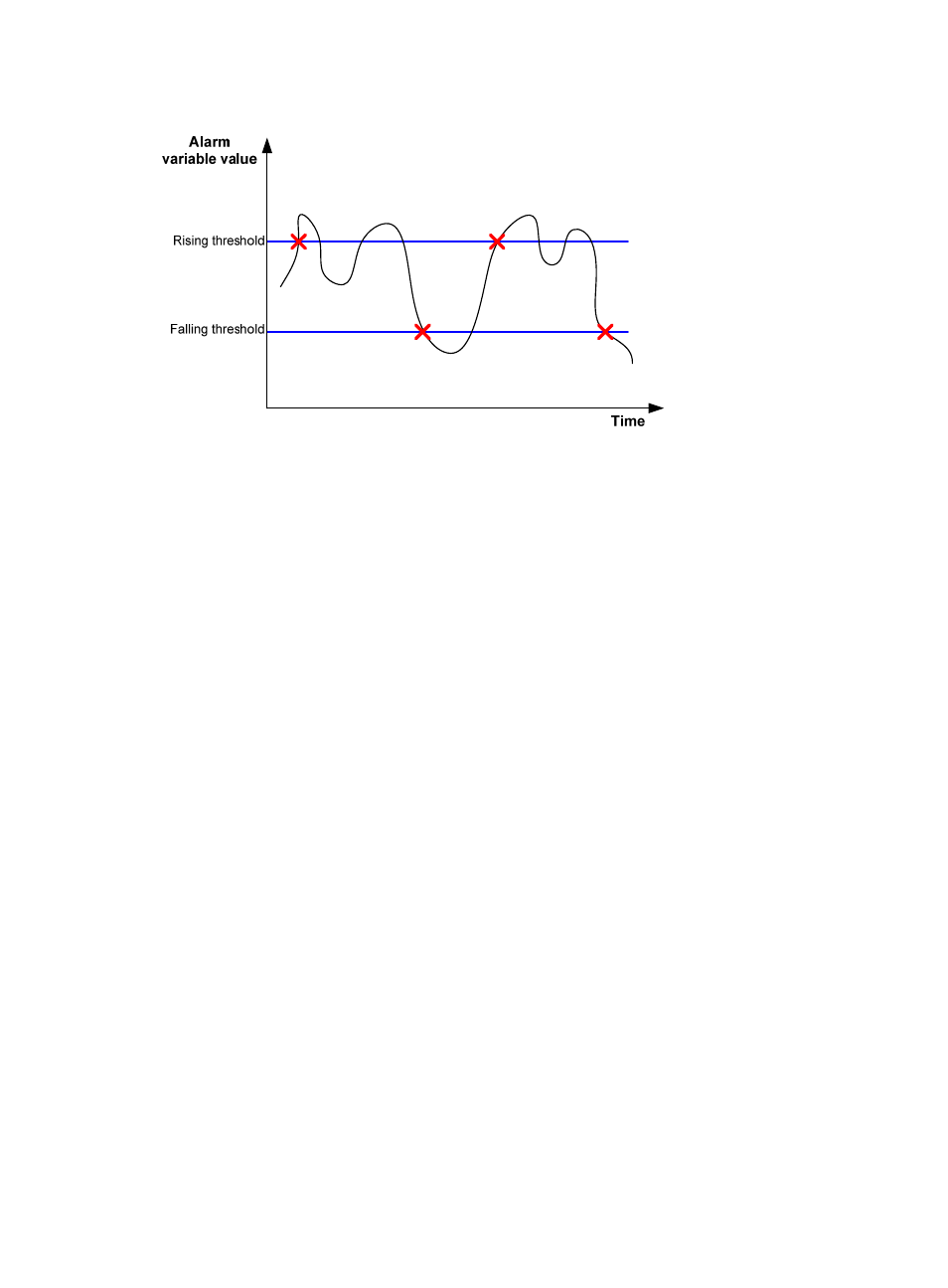
Figure 56 Rising and falling alarm events
Private alarm group
The private alarm group calculates the values of alarm variables and compares the results with the
defined threshold for a more comprehensive alarming function.
The system handles the prialarm table entry (as defined by the user) in the following ways:
•
Periodically samples the prialarm variables defined in the prialarm formula.
•
Calculates the sampled values based on the prialarm formula.
•
Compares the result with the defined threshold and generates an appropriate event.
If a private alarm entry crosses a threshold multiple times in succession, the RMON agent generates an
alarm event only for the first crossing. For example, if the value of a sampled alarm variable crosses the
rising threshold multiple times before it crosses the falling threshold, only the first crossing triggers a rising
alarm event. If the count result of the private alarm group overpasses the same threshold multiple times,
only the first one can cause an alarm event. In other words, the rising alarm and falling alarm are
alternate.
Configuring the RMON statistics function
The RMON statistics function can be implemented by either the Ethernet statistics group or the history
group, but the objects of the statistics are different, as follows:
•
A statistics object of the Ethernet statistics group is a variable defined in the Ethernet statistics table,
and the recorded content is a cumulative sum of the variable from the time the statistics entry is
created to the current time. For more information, see "
Configuring the RMON Ethernet statistics
."
•
A statistics object of the history group is the variable defined in the history record table, and the
recorded content is a cumulative sum of the variable in each period. For more information, see
- H3C SecPath F5000-A5 Firewall H3C SecPath F1000-A-EI H3C SecPath F1000-E-SI H3C SecPath F1000-S-AI H3C SecPath F5000-S Firewall H3C SecPath F5000-C Firewall H3C SecPath F100-C-SI H3C SecPath F1000-C-SI H3C SecPath F100-A-SI H3C SecBlade FW Cards H3C SecBlade FW Enhanced Cards H3C SecPath U200-A U200-M U200-S H3C SecPath U200-CA U200-CM U200-CS
