3 alarms, 3 alarms -7, App index – Yokogawa µR20000 User Manual
Page 23: Alarm types
1-7
IM 04P02B01-01E
Functional Explanation and Setup Guide
For the procedure to set the functions, see section 1.10, “Function Setup Guide.”
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
App
Index
1.3 Alarms
This function generates an alarm when the measured data meets a certain condition.
The alarm occurrence/release can be recorded on the chart paper. The alarm status can
be displayed on the screen.
Also, alarm output relays can be used to output contact signals when alarms occur (/A1,
/A2, /A3, /A4, and /A5 options).
Alarm Types
Number of Alarm Point Marks
Up to four alarms can be set for each channel. The 4 alarm settings are called Level 1,
Level 2, Level 3, and Level 4. The numbers do not indicate a difference in importance.
Alarm Conditions
The eight conditions below are available. The character inside the parentheses is the
symbol used to denote each alarm on the recorder.
• High Limit Alarm (H)
An alarm occurs when the input value exceeds the alarm value.
• Low Limit Alarm (L)
An alarm occurs when the input value falls below the alarm value.
Alarm
value
Alarm release
Measured value
Alarm occurrence
High limit alarm
Low limit alarm
Measured
value
Alarm release
Alarm value
Alarm occurrence
• Difference High Limit Alarm (h)*
An alarm occurs when the difference in the input values of two channels is greater
than or equal to the specified value.
• Difference Low Limit Alarm (l)*
An alarm occurs when the difference in the input values of two channels is less than
or equal to the specified value.
* Can be specified on channels set to delta computation.
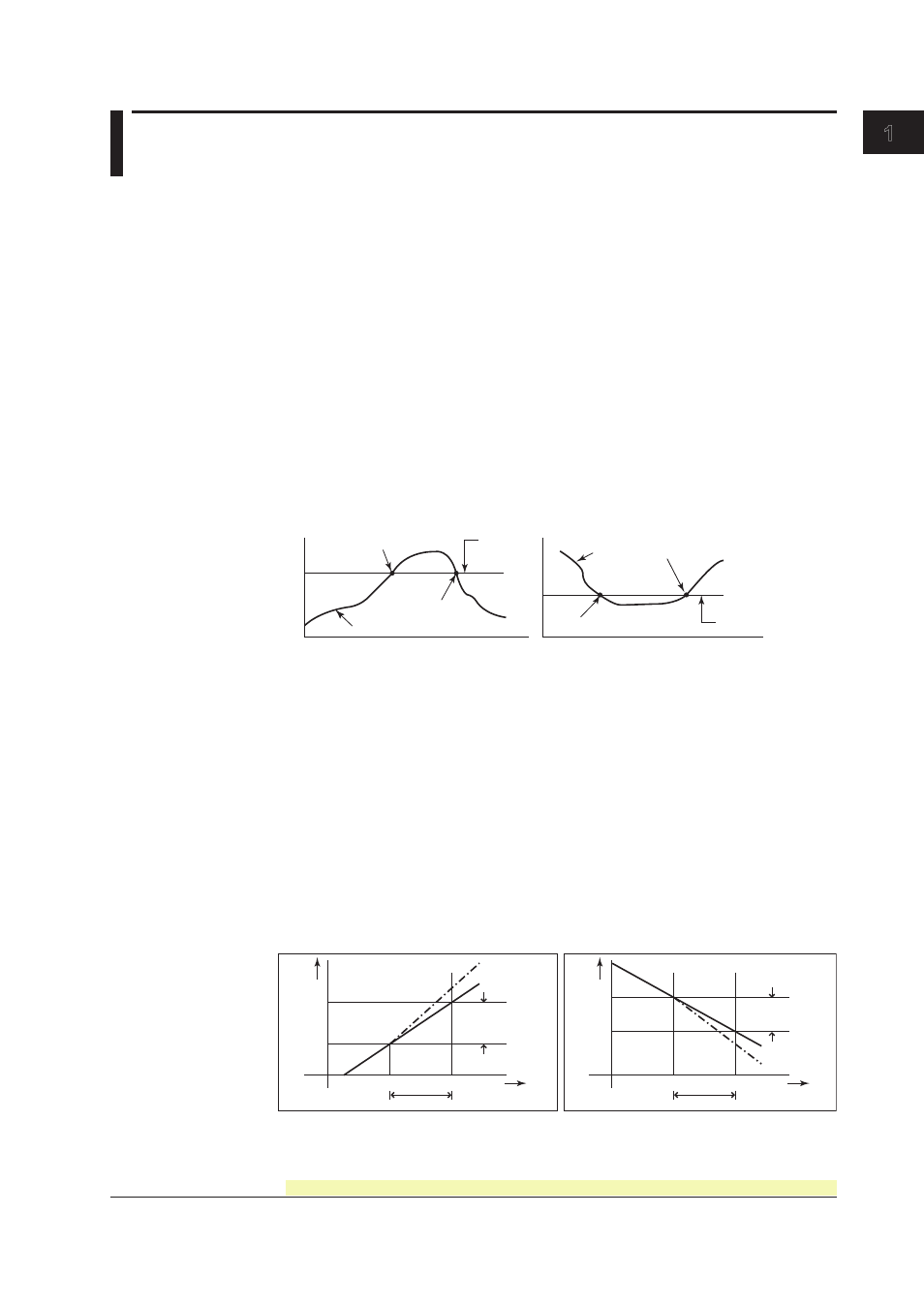
• High Limit on Rate-of-Change Alarm (R)
The rate-of-change of the measured values is checked over a certain time (interval).
An alarm occurs if the rate-of-change of the measured value in the rising direction is
greater than or equal to the specified value.
• Low Limit on Rate-of-Change Alarm (r)
The rate-of-change of the measured values is checked over a certain time (interval).
An alarm occurs if the rate-of-change of the measured value in the falling direction is
greater than or equal to the specified value.
Measured
value
Change in the
measured value
T1
Time
Interval
T2
t1
t2
Amount of change
in the setting
T2
Time
T1
t1
t2
Measured
value
Change in the
measured value
Amount of change
in the setting
|
|
High limit on rate-of-change alarm
Low limit on rate-of-change alarm
t2-t1
Interval
t2-t1
T2-T1
|
|
T2-T1
The alarm value of the rate-of-change alarm is set using an absolute value. The
interval is derived using the following equation and set using the number of samples.
Interval = the scan interval × the number of samples
