Yaskawa G5HHP Drive User Manual
Page 208
Advanced Operation
7.5.1 Application Constants: b
7 - 44
Table 7.6 PID Control Applications
Application
Control contents
Sensors used
(example)
Speed con-
trol
S
Speeds are matched to target values as speed information in a mechani-
cal system.
S
Speed information for another mechanical system is input as target val-
ues, and synchronized control is executed by feeding back actual
speeds.
Tachogenerator
Pressure
control
Pressure information is returned as feedback for stable pressure control.
Pressure sensor
Flow control Flow information is returned as feedback for accurate flow control.
Flow sensor
Tempera-
ture control
Temperature information is returned as feedback to control temperature
by turning a fan.
S
Thermocouple
S
Thermistor
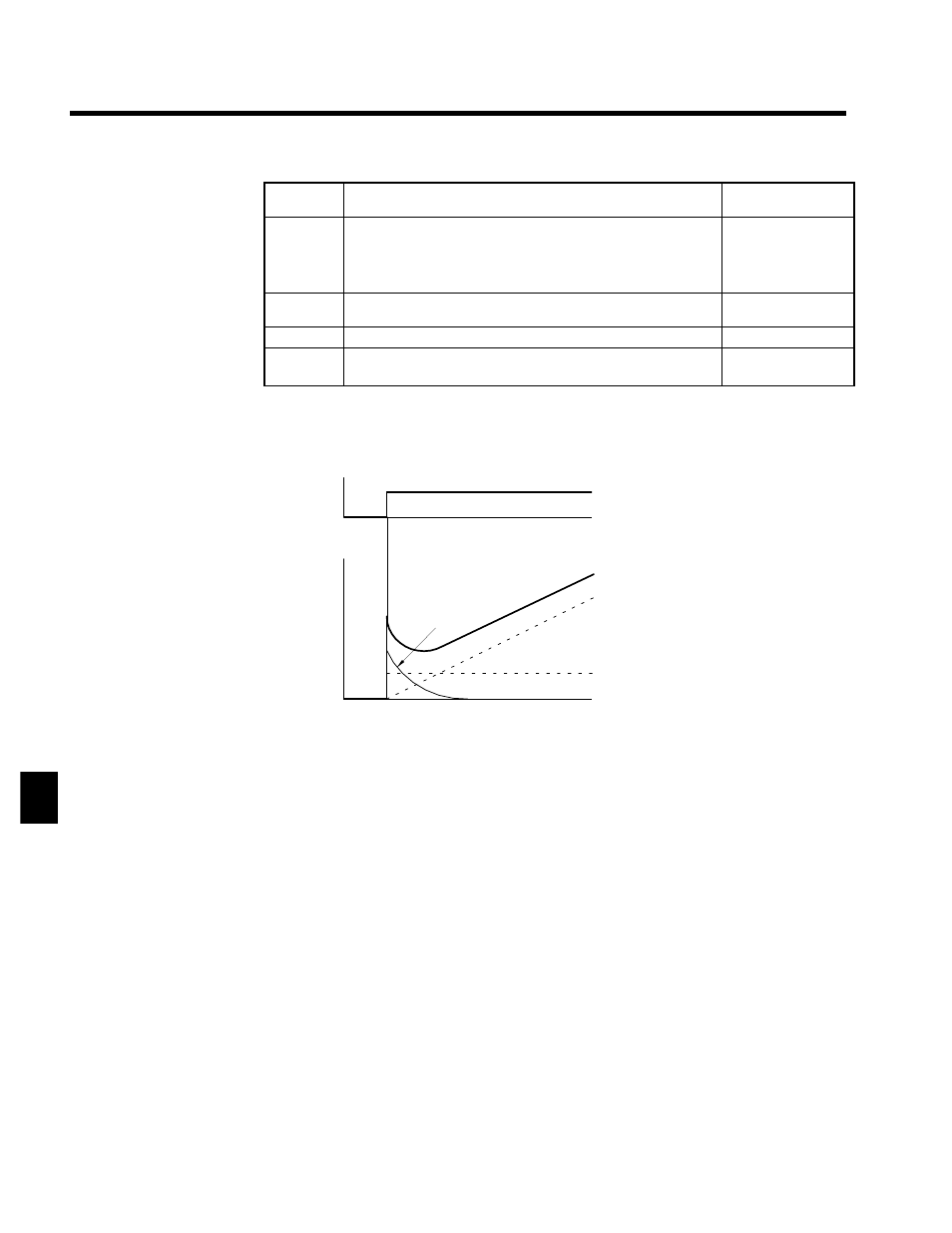
PID Control Operations
In order to distinguish the separate PID control operations (i.e., proportional, integral, and derivative), Fig-
ure 7.21 shows the changes in the control input (i.e., the output frequency) when the deviation between the
target value and the feedback is held constant.
Deviation
Time
Control input
D control
PID control
I control
P control
Time
Fig 7.21
PID Control Operations
D
P Control:
A control input proportional to the deviation is output. The deviation cannot be zeroed
by P control alone.
D
I Control:
A control input which is an integral of the deviation is output. This is effective for
matching the feedback to the target value. Sudden changes, however, cannot be fol-
lowed.
D
D Control:
A control input which is an integral of the deviation is output. Quick response to sudden
changes is possible.
D
PID Control: Optimum control is achieved by combining the best features of P, I, and D control.
Types of PID Control
Two types of PID control are possible with the Inverter: Measured-value derivative PID control and basic
PID control. The type that is normally used is measured-value derivative PID control.
D
Measured-value Derivative PID Control:
With measured-value derivative PID control, the feedback value is differentiated for PID control. Re-
sponse is possible with respect to changes both in target values and the control object.
7
