'sqcx)' 3: ■h' 2: 23, Q qo @ x (i, Ie) cd – HP 48g Graphing Calculator User Manual
Page 206
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
5. Enter the step size of the increment. The number of elements
generated is the integer portion of
(final —initial)
step
+
1
.
17
6
. Execute SEQ .
Example: Generate a list of squares from 23 to 27.
Step 1:
Enter the function, the variable name, the initial value, and
the final value.
Q QO @ X (I
nt
IE) CD
@
X ( E N T E R
1
23
( E N T E R )
27
( E N T E R )
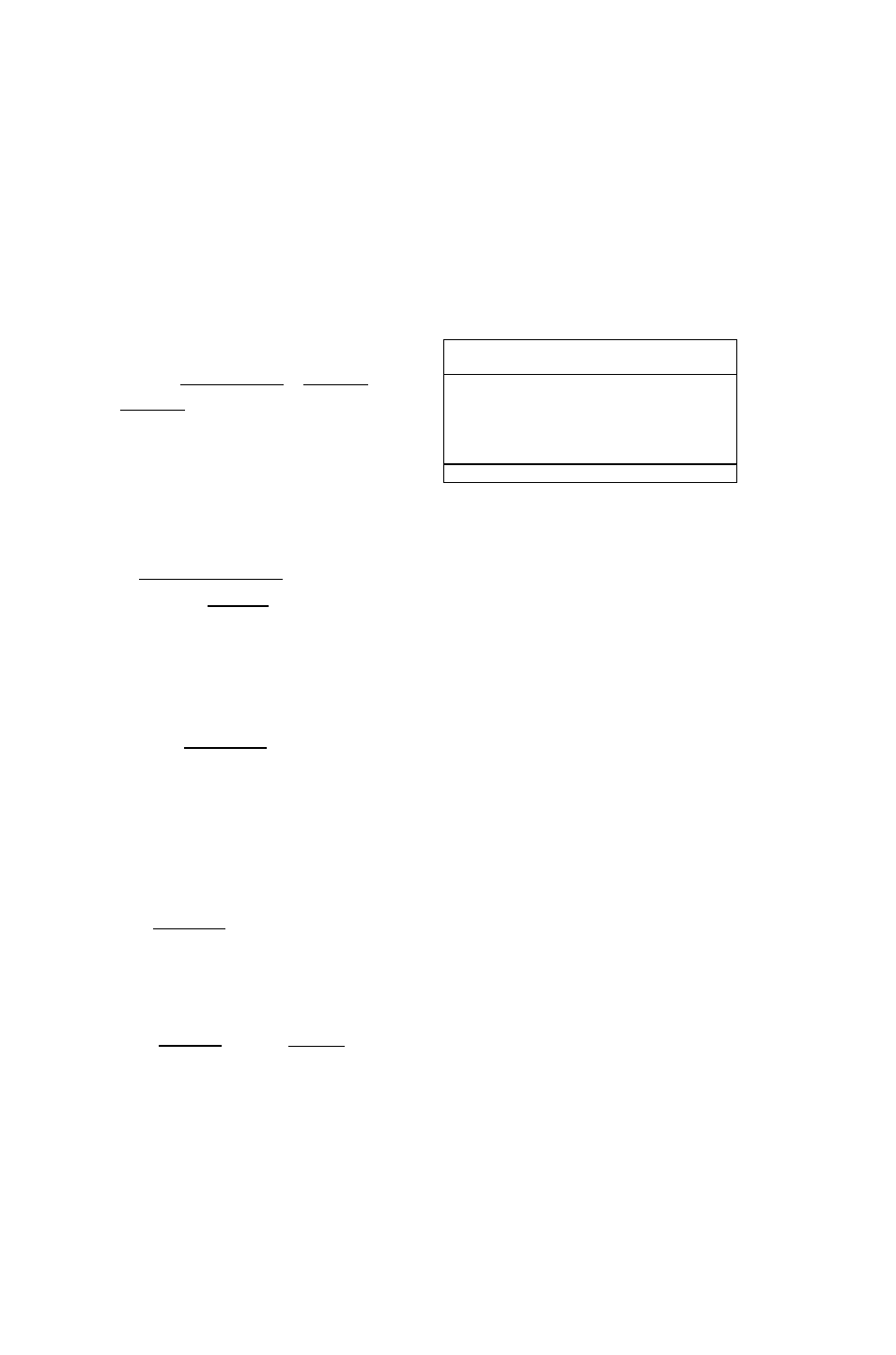
r HDME >
4:
'SQCX)'
3:
■H'
2:
23
1:
27
■QiiiBiiQiHii3izRniaii:i;tcMiBnajnia4Ami
Step 2:
Enter the step size, and generate the sequence.
1 (ENTER )(
p
M1
l i s t
P R O C (NXT) S E i J
1: £ 529 576 625 676
729 }
To find the sum
of a
finite sequence expressed as a list:
1. Enter the list.
2. Execute ( M T H )
. I S
1
.
You can also find the sum of a finite sequence using the X function in
an algebraic expression—see page 7-5.
To find the product of a finite sequence expressed as a list;
1. Enter the list.
2. Press (MTH ) L I S !
ti
’.L I S !'.
To find the set of
fires
t'ifierences of a finite sequence:
1. Enter the sequence as a list.
2. Press (MT
h
I L I ST fN)an i L 1 S T .
The first differences for the list C x\ x-i ... T is defined as
C X2-XX . . . x n - x ^ _ i >.
17-8 Lists and Sequences
