Using boolean operators, Manipulating bits and bytes – HP 48g Graphing Calculator User Manual
Page 190
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
Using Boolean Operators
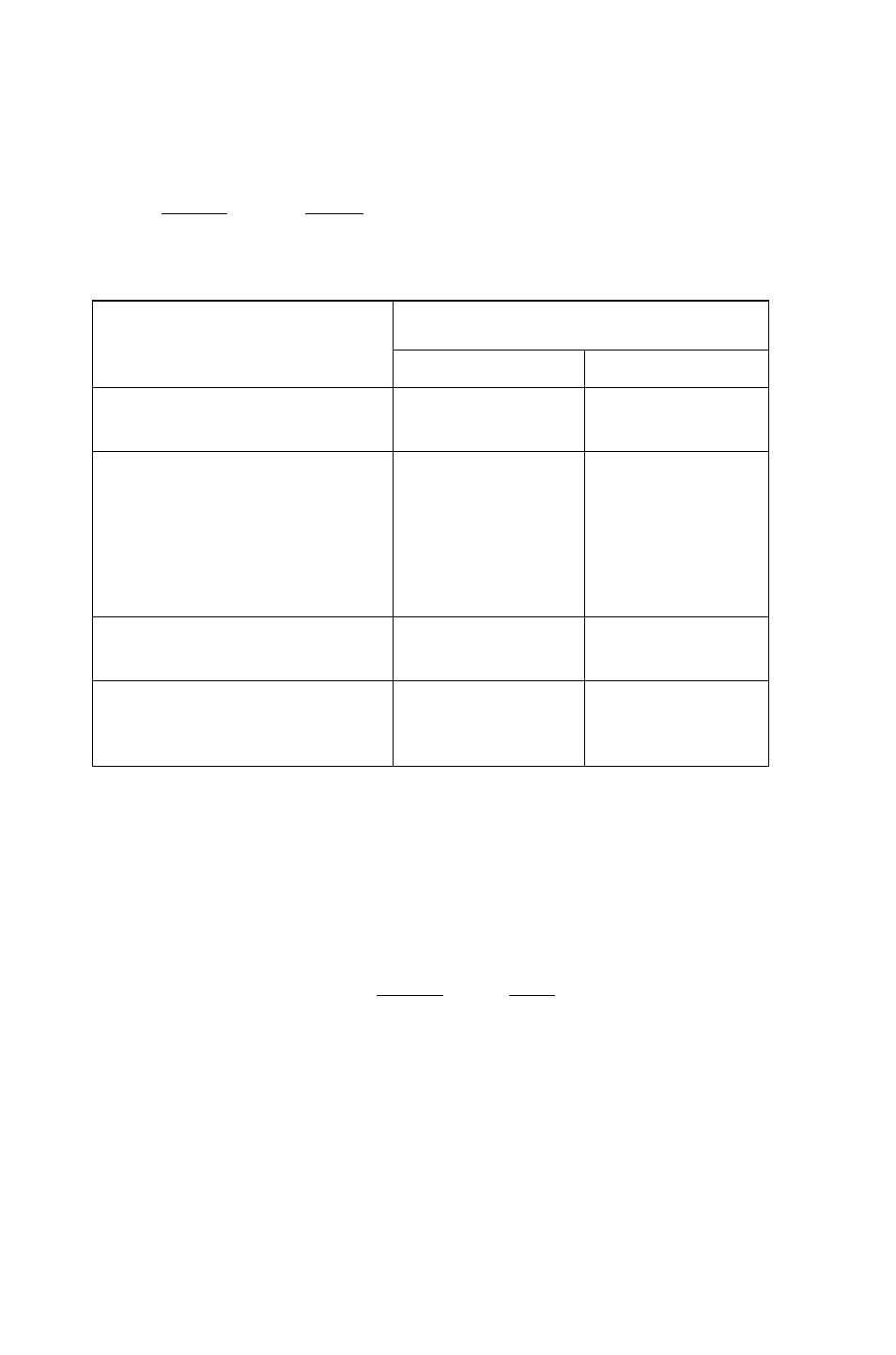
The following table contains commands from the MTH BASE LOGIC
menu
(fMTH
)
i3i-lSE (NX
t
I LOGIC)
that perform Boolean operations
on binary integers. Unless otherwise stated, each example assumes the
wordsize is set to 24.
Command
/
Description
Example
Input
Output
AND Logical bit-by-bit
AND of two arguments.
L“ w 11BBb
1; # 1 0 0 0 b
NOT Returns the
one’s complement of the
argument. Each bit in the
result is the complement of
the corresponding bit in the
argument.
I s # FF00FFh
1s # FF00h
OR Logical bit-by-bit OR,
of two arguments.
1
i!
il:
1
i”i
i
i!-i
j-":
is # 1110b
XOR Logical bit-by-bit
exclusive OR of two
arguments.
Is # 1 0 1 1 b
I s # 110b
15
Manipulating Bits and Bytes
The following table contains commands from the MTH BASE BIT
and MTH BASE BYTE menus
(fMTlTl BASE
|WT|
B I
T and .,
B Y
T
E
) that are useful for manipulating binary integers either one
bit or one byte at a time. Unless otherwise stated, each example
assumes the wordsize is set to 24.
15-4 Binary Arithmetic and Number Bases
