For details on performing failovers, see, Performing failovers and failbacks, For details on performing failbacks, see – HP XP P9500 Storage User Manual
Page 37: Performing failovers and
The paths are simply selected in order from among all the connected
paths.
¢
Extended Least I/Os
The path that has the least number of I/Os being processed is
selected from among all the connected paths.
¢
Extended Least Blocks
The path that has the least number of I/O blocks being processed is
selected from among all the connected paths.
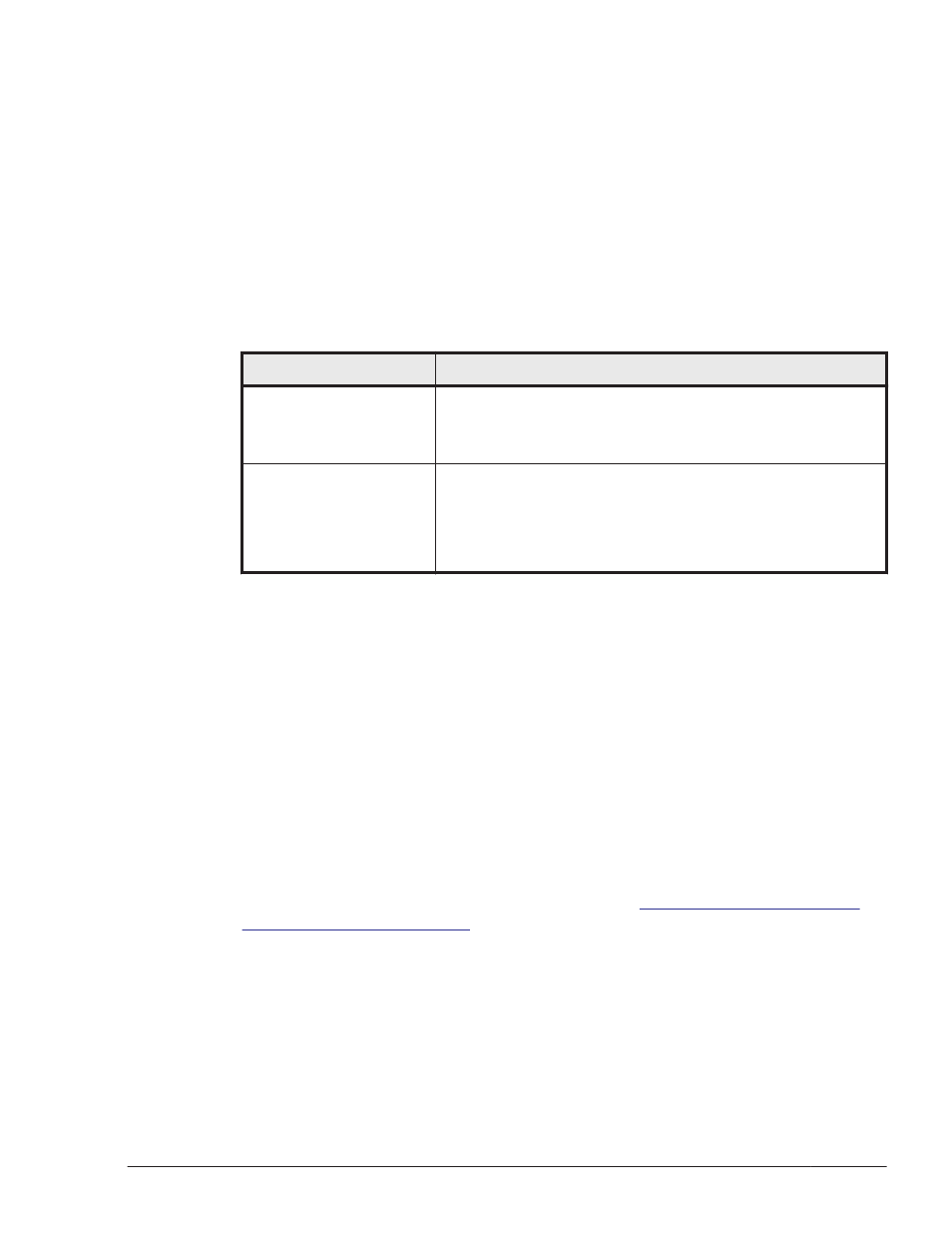
The following table lists and describes the features of the load balancing
algorithms.
Table 2-4 Features of the Load Balancing Algorithms
Algorithm type
Algorithm features
•
Round Robin
#
•
Least I/Os
•
Least Blocks
These types of algorithms are most effective when a lot of
discontinuous, non-sequential I/Os are issued.
•
Extended Round
Robin
•
Extended Least I/Os
•
Extended Least
Blocks
If the I/O data is from something like a read request and is
generally sequential with the previous I/Os, an improvement
in reading speed can be expected due to the storage system
cache functionality. These types of algorithms are most
effective when a lot of continuous, sequential I/Os are issued.
#
Some I/O operations managed by HDLM can be distributed across all,
available paths, and some cannot. Thus, you should be aware that even if
you specify the Round Robin algorithm, some of the I/O operations will
never be issued uniformly across all the given paths.
The default algorithm is the Extended Least I/Os algorithm, which is set when
HDLM is first installed. When an upgrade installation of HDLM is performed,
the algorithm that is currently being used is inherited.
Select the load balancing algorithm most suitable for the data access patterns
of your system environment. However, if there are no recognizable data
access patterns, we recommend using the default algorithm, the Extended
Least I/Os algorithm.
You can specify the load balancing function by the dlnkmgr command's set
operation. For details on the set operation, see
Performing Failovers and Failbacks Using Path Switching
When the system contains multiple paths to an LU and an error occurs on the
path that is currently being used, HDLM can switch to another functional
path, so that the system can continue operating. This is called a failover.
HDLM Functions
2-15
Hitachi Dynamic Link Manager User Guide for Solaris
®
