About clustered-host storage – HP XP Array Manager Software User Manual
Page 152
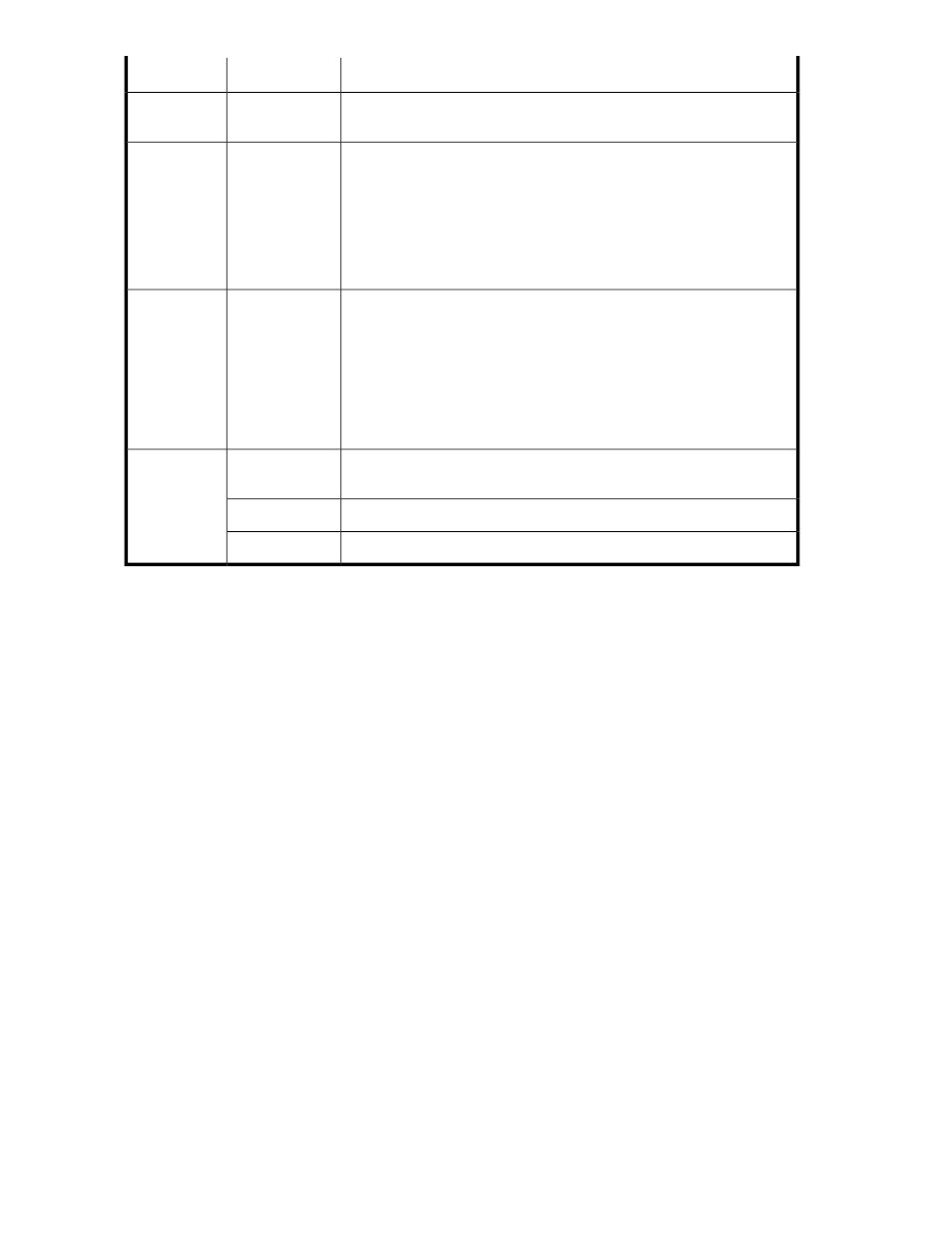
Description
Subfield
Field
Select one or more host mode options for supporting special requirements
for specific applications.
Host mode op-
tions
Logical unit (LU) numbers can be assigned automatically or manually for
the volumes being allocated.
To automatically assign LU numbers to the allocated volumes, select auto
and enter a start from number (or use the default). LU numbers are set in
ascending order while avoiding existing numbers.
To manually assign LU numbers to the allocated volumes, select manual
and click Select LU Number to choose a starting LU number.
auto or manual
selection buttons
LU Number
An option for manually specifying the starting virtual LDEV ID to use for
allocated volumes. Volumes for which virtual IDs have not been specified
are assigned a new virtual LDEV ID when they are allocated to a host that
belongs to resource groups used in data migrations that use virtual IDs.
Virtual LDEV IDs are assigned automatically by default, with unused IDs
assigned to volumes in ascending order. If a user manually specifies an
ID, volumes receive the lowest available ID that is equal to or greater than
the specified value.
(See the follow-
ing field for de-
tails)
>> Virtual ID
Settings
Logical disk controller (LDKC) number that forms part of the starting virtual
LDEV ID.
LDKC
Starting virtu-
al LDEV ID
Targets
Control unit (CU) number that forms part of the starting virtual LDEV ID.
CU
Device (DEV) number that forms part of the starting virtual LDEV ID.
DEV
Related topics
• Allocating volumes from general tasks
• Allocating volumes to selected hosts
• Allocating selected volumes to hosts
• Allocating volumes to clustered hosts
• Allocating volumes by using a keyword search
• Allocating volumes by using a criteria search
• Allocating volumes by using existing volume settings
• Notes on performing quick formats
About clustered-host storage
Clustered-host storage is a storage configuration that is created when volumes are allocated to a new
host that is added to a host group (also known as a host cluster).
When creating clustered-host storage, you add the WWN of the newly added host to the host group
to which the WWN of an existing host belongs, and you set LUN paths from the newly added host
to the same volumes as those for an existing host.
For example, to better manage and distribute the load on your applications and resources, update
the existing host group by creating clustered-host storage using existing volumes by allocating them
to a new host in the host group.
Provisioning storage
152
