1 general timer/counter control register - gtccr – Rainbow Electronics ATmega64C1 User Manual
Page 87
87
7647A–AVR–02/08
ATmega32/64/M1/C1
Each half period of the external clock applied must be longer than one system clock cycle to
ensure correct sampling. The external clock must be guaranteed to have less than half the sys-
tem clock frequency (f
ExtClk
< f
clk_I/O
/2) given a 50/50% duty cycle. Since the edge detector uses
sampling, the maximum frequency of an external clock it can detect is half the sampling fre-
quency (Nyquist sampling theorem). However, due to variation of the system clock frequency
and duty cycle caused by Oscillator source (crystal, resonator, and capacitors) tolerances, it is
recommended that maximum frequency of an external clock source is less than f
clk_I/O
/2.5.
An external clock source can not be prescaled.
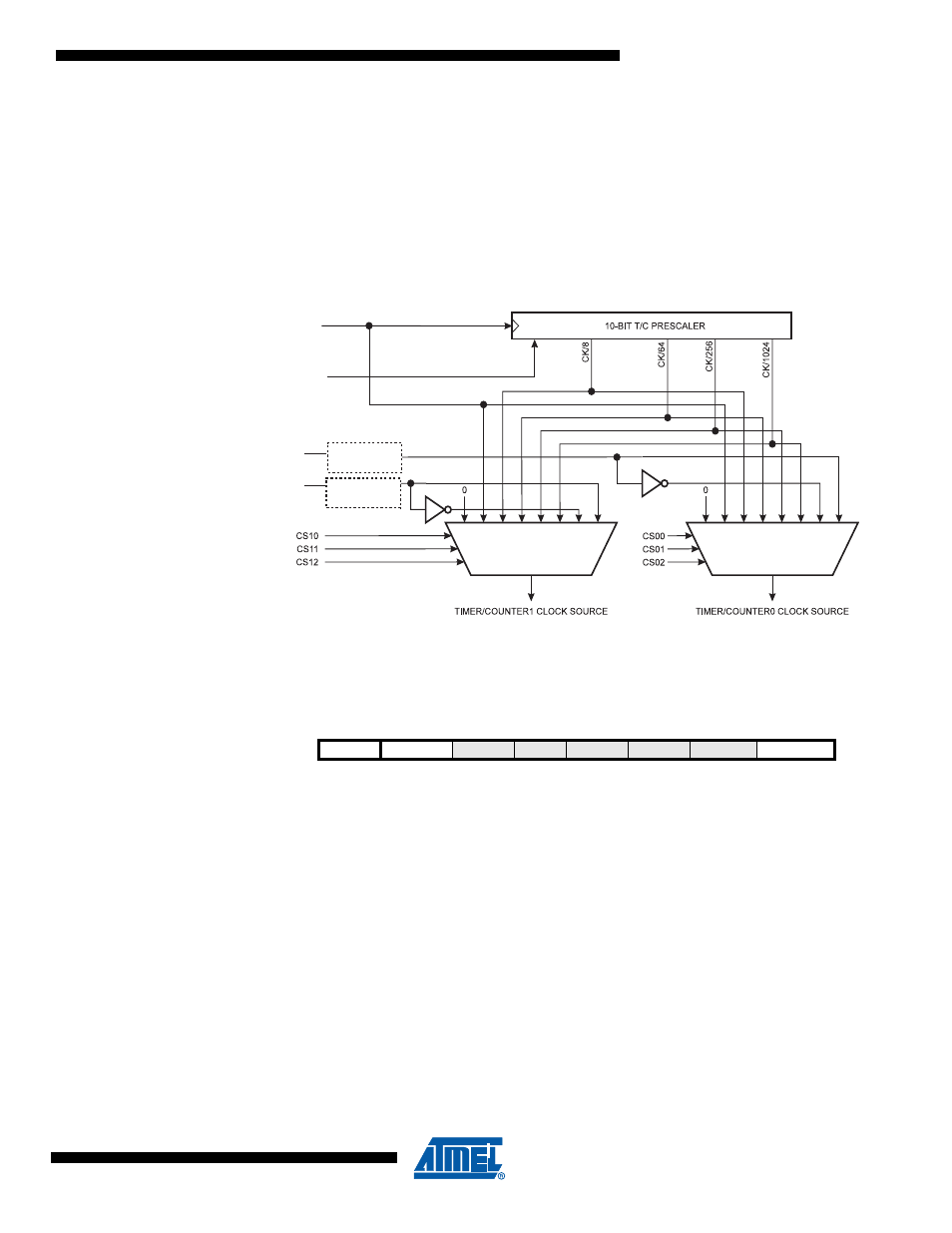
Figure 11-2. Prescaler for Timer/Counter0 and Timer/Counter1
Note:
1. The synchronization logic on the input pins (
Tn)
is shown in
11.3.1
General Timer/Counter Control Register – GTCCR
• Bit 7 – TSM: Timer/Counter Synchronization Mode
Writing the TSM bit to one activates the Timer/Counter Synchronization mode. In this mode, the
value that is written to the PSRSYNC bit is kept, hence keeping the corresponding prescaler
reset signals asserted. This ensures that the corresponding Timer/Counters are halted and can
be configured to the same value without the risk of one of them advancing during configuration.
When the TSM bit is written to zero, the PSRSYNC bit is cleared by hardware, and the
Timer/Counters start counting simultaneously.
• Bit6 – ICPSEL1:
Timer 1 Input Capture selection
PSRSYNC
Clear
clk
T1
clk
T0
T1
T0
clk
I/O
Synchronization
Synchronization
Bit
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
TSM
ICPSEL1
–
–
–
–
–
PSRSYNC
GTCCR
Read/Write
R/W
R/W
R
R
R
R
R
R/W
Initial Value
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
