Rainbow Electronics W90N745CDG User Manual
Page 384
W90N745CD/W90N745CDG
- 380 -
6.18 PS2 Host Interface Controller
W90N745 PS2 host controller interface is an APB slave consisted of PS2 protocol. It is used to
connect to your IBM keyboard or other device through PS2 interface. For example, the IBM keyboard
will sends scan codes to the host controller, and the scan codes will tell your Keyboard Bios what
keys you have pressed or released. Besides Scan codes, commands can also be sent to the
keyboard from host. The most common commands would be the setting/resetting of the status
indicators (i.e. the Num lock, Caps Lock & Scroll Lock LEDs).
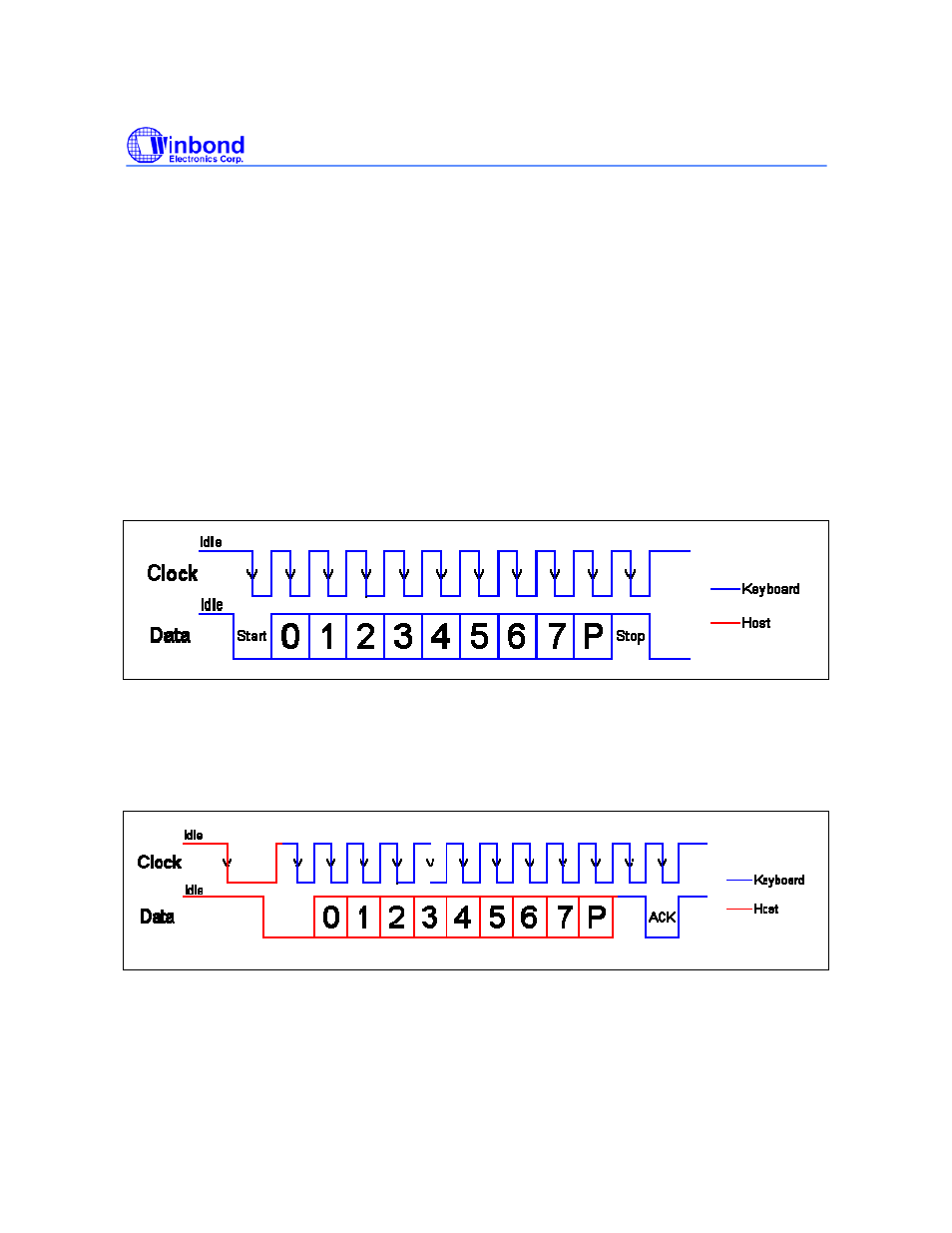
The PS2 interface implements a bi-directional protocol. The keyboard can send data to the Host and
the Host can send data to the Keyboard using two PS2 Clock and PS2 Data lines. Both the PS2
Clock and Data lines are Open Collector bi-directional I/O lines. The Host has the ultimate priority
over direction. The keyboard is free to send data to the host when both the PS2 Data and PS2 Clock
lines are high (Idle). If the host takes the PS2 Clock line low, the keyboard will buffer any data until
the PS2 Clock is released, ie goes high. The transmission of data in the forward direction, ie
Keyboard to Host is done with a frame of 11 bits. The first bit is a Start Bit (Logic 0) followed by 8 data
bits (LSB First), one Parity Bit (Odd Parity) and a Stop Bit (Logic 1). Each bit should be read on the
falling edge of the clock. The Keyboard will generate the clock. The frequency of the clock signal
typically ranges from 20 to 30 KHz.
The Host to Keyboard Protocol is initiated by taking the PS2 data line low. It is common to take the
PS2 Clock line low for more than 60us and then the KBD data line is taken low, while the KBD clock
line is released. After that, the keyboard will start generating a clock signal on its PS2 clock line. After
the first falling edge has been detected, host will load the first data bit on the PS2 Data line. This bit
will be read into the keyboard on the next falling edge, after which host place the next bit of data. This
process is repeated for the 8 data bits. It will follow an Odd Parity Bit after the data byte.
