3 slave mode, 4 interrupt generation, Slave mode – National CP3BT26 User Manual
Page 178: Interrupt generation, Cp3bt26
www.national.com
178
CP3BT26
23.3
SLAVE MODE
In Slave mode, the MSK pin is an input for the shift clock
MSK. MDIDO is placed in TRI-STATE mode when MWCS is
inactive. Data transfer is enabled when MWCS is active.
The slave starts driving MDIDO when MWCS is active. The
most significant bit (lower byte in 8-bit mode or upper byte
in 16-bit mode) is output onto the MDIDO pin first. After
eight or sixteen clocks (depending on the selected mode),
the data transfer is completed.
If a new shift process starts before MWDAT was written, i.e.,
while MWDAT does not contain any valid data, and the
ECHO bit is set, the data received from MDODI is transmit-
ted on MDIDO in addition to being shifted to MWDAT. If the
ECHO bit is clear, the data transmitted on MDIDO is the
data held in the MWDAT register, regardless of its validity.
The master may negate the MWCS signal to synchronize
the bit count between the master and the slave. In the case
that the slave is the only slave in the system, MWCS can be
tied to ground.
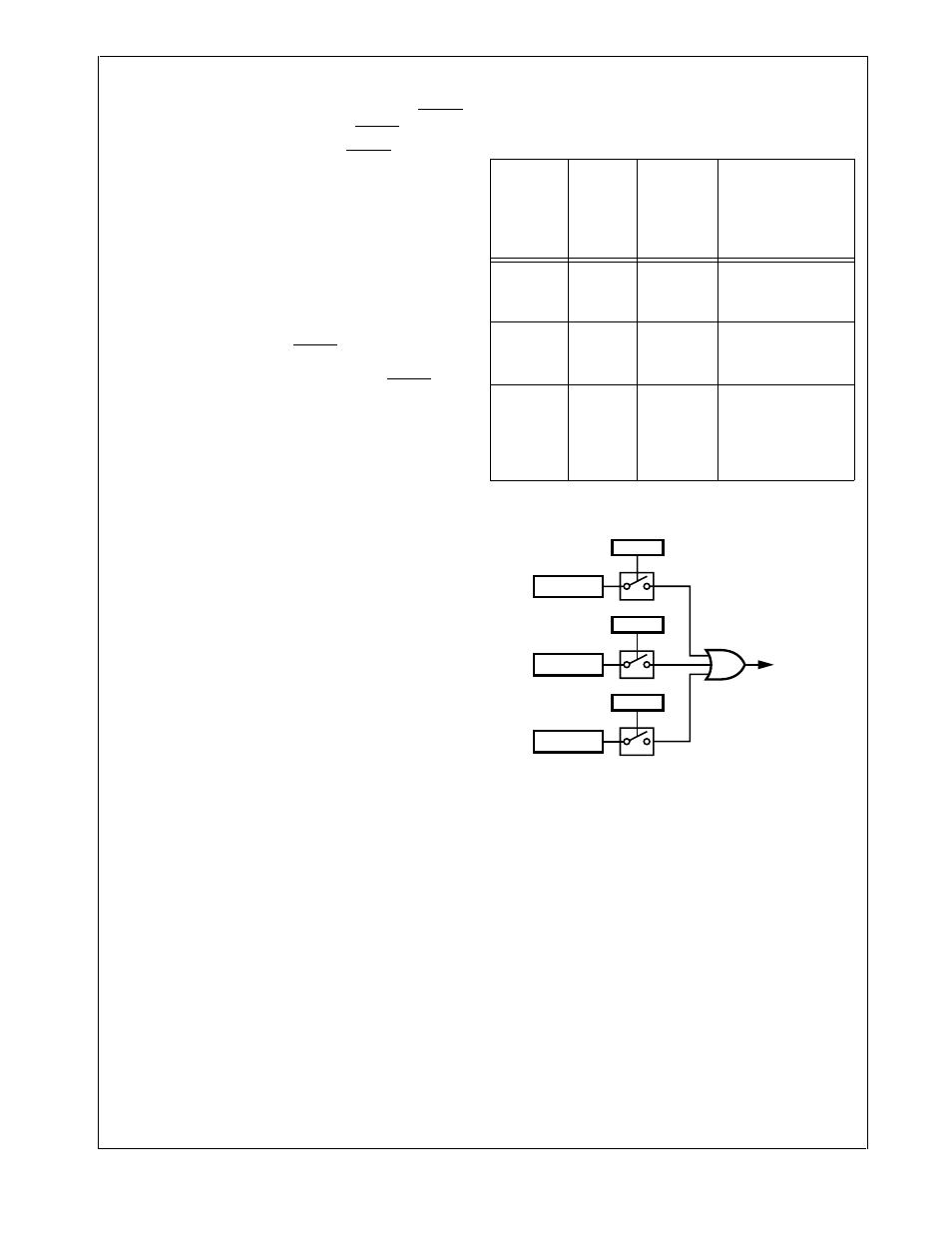
23.4
INTERRUPT GENERATION
Interrupts may be enabled for any of the conditions shown
in Table 73.
Figure 89 illustrates the interrupt generation logic of this
module.
Figure 89.
MWSPI Interrupts
Table 73
Microwire Interrupt Trigger Condition
Condition
Status
Bit in the
MWSTAT
Register
Interrupt
Enable Bit
in the
MWCTRL1
Register
Description
Not Busy
BSY
EIW
The shifter is ready
for the next data
transfer sequence.
Read
Buffer Full
RBF
EIR
The read buffer is
full and waiting to be
unloaded.
Overrun
OVF
EIO
A new data transfer
sequence started
while both the shifter
and the read buffer
were full.
MWSPI
Interrupt
OVR = 1
EIO
RBF = 1
EIR
BSY = 0
EIW
DS073
