Queue scheduler, Spq (strict priority queuing), Spq scheduler – ATL Telecom R1-SW Ethernet Switch User Manual
Page 177
Configuring QoS
9-9
Queue Scheduler
The output port is generally slower than the input port because the output port transmits
packets that are received from the several input ports. In the output port, at least one queue is
assigned, and packets that have to be processed by the output port are saved. When saved
packets in a queue are more than bandwidth that can transmit packets - it means congestion,
what packets are transmitted first should be defined in the output port. This is called queue
scheduling.
There are various queues scheduling method, and the following methods are generally used.
y
Strict Priority Queuing
y
WRR (Weight Round Robin)
y
WFQ (Weight Fair Queuing)
y
DWRR (Deficit Weight Round Robin)
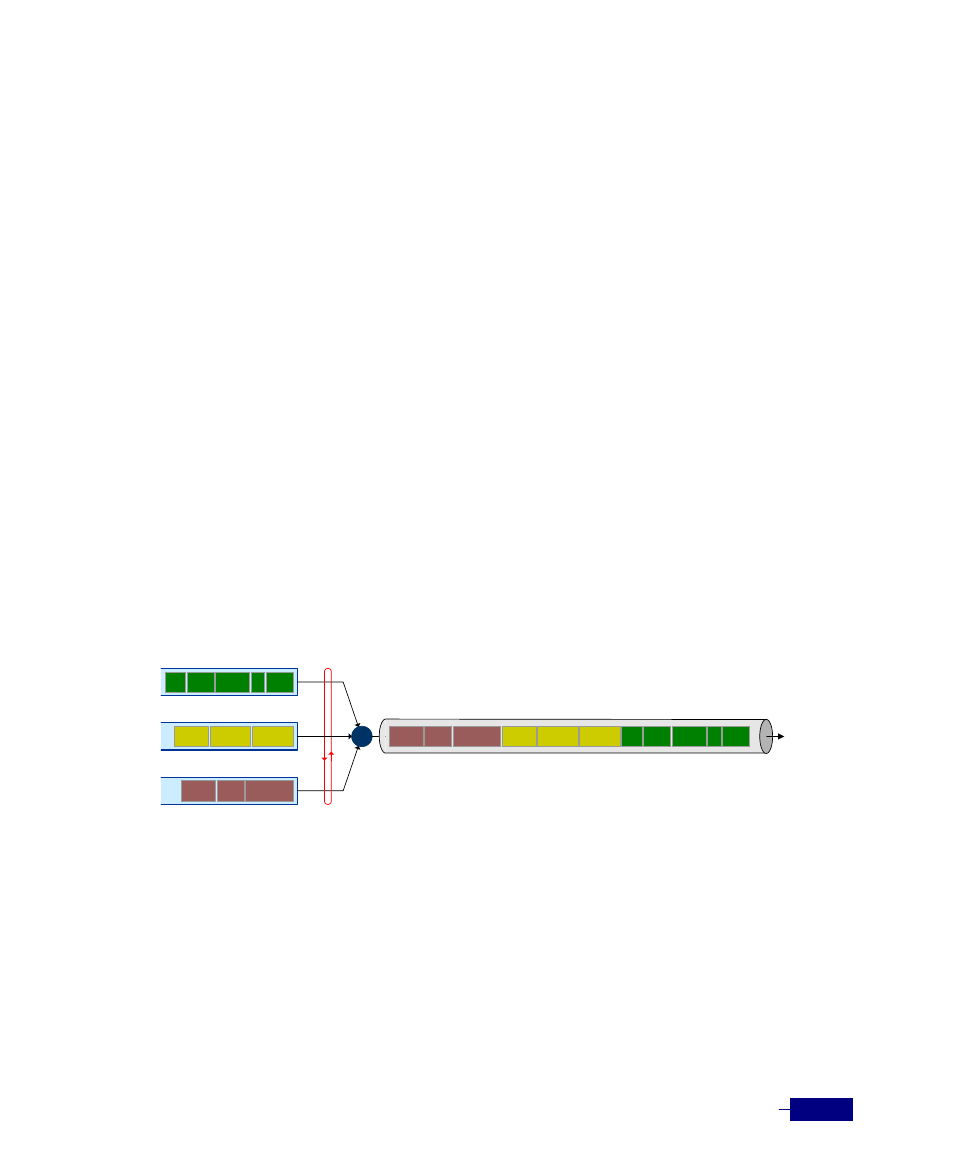
SPQ (Strict Priority Queuing)
In this method, each queue has assigned priorities (high, medium, low), and packets in the high
priority queue are transmitted first. After packets in the high priority are transmitted
completely, packets in the next priority queue are transmitted.
This method is easy to implement, but if there are plenty of packets that flows into the high
priority queue, packets in the low priority queue can not be transmitted at all. This is called
starvation
.
[Q1] Priority: High
[Q2] Priority: Medium
[Q3] Priority: Low
300B
200B
400B
300B
100B
600B
300B
400B
Output Port
600B
300B
400B
300B
200B
400B
300B
100B
SPQ Scheduler
400B
500B
500B
400B
500B
500B
