Supported mibs – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches User Manual
Page 406
41-2
SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c adopt community name authentication. The SNMP packets containing invalid
community names are discarded. SNMP community name is used to define the relationship between
SNMP NMS and SNMP agent. Community name functions as password. It can limit accesses made by
SNMP NMS to SNMP agent. You can perform the following community name-related configuration.
z
Specifying MIB view that a community can access.
z
Set the permission for a community to access an MIB object to be read-only or read-write.
Communities with read-only permissions can only query the device information, while those with
read-write permission can configure the device as well.
z
Set the basic ACL specified by the community name.
Supported MIBs
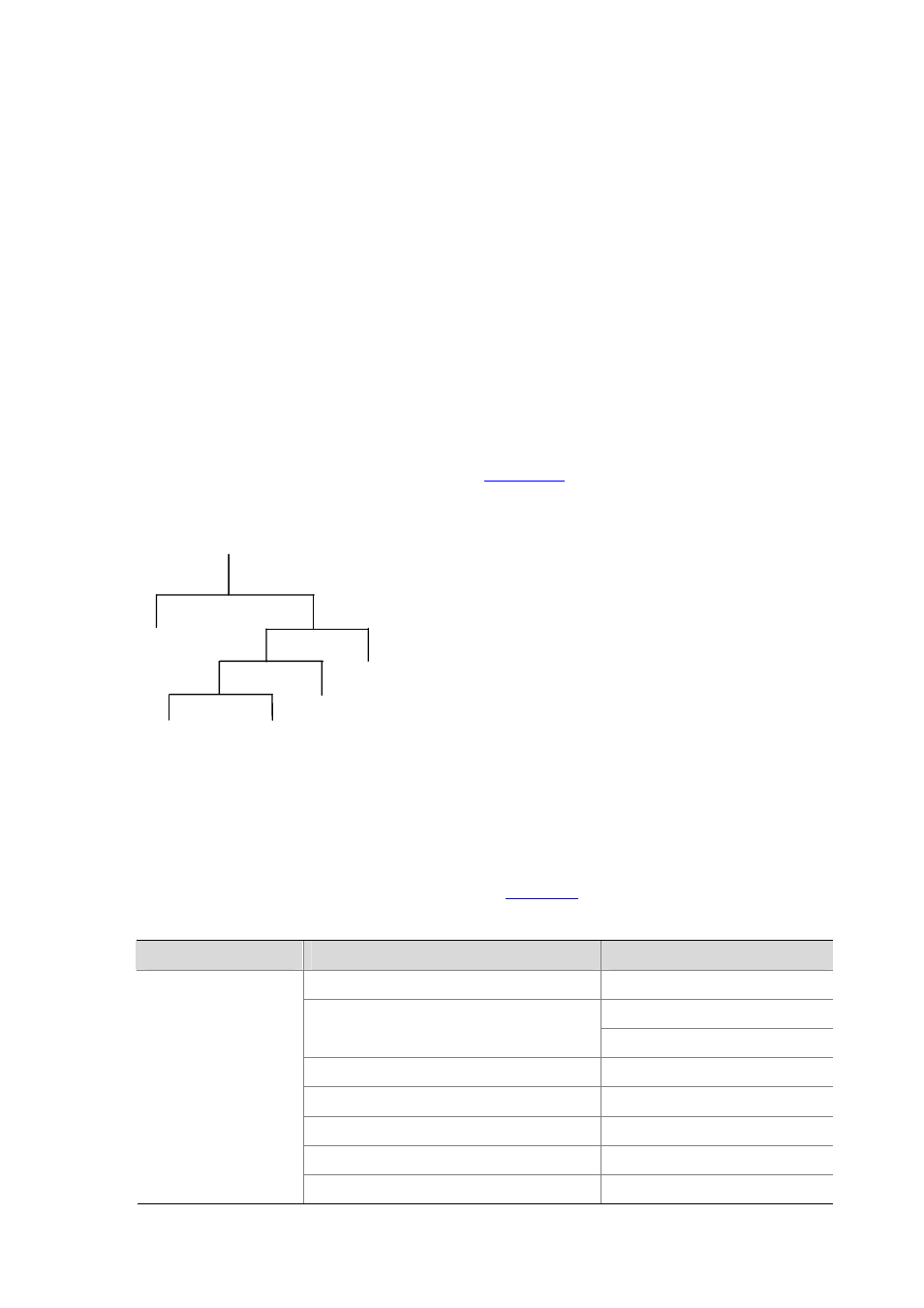
An SNMP packet carries management variables with it. Management variable is used to describe the
management objects of the device. To uniquely identify the management objects of the device, SNMP
adopts a hierarchical naming scheme to organize the managed objects. It is like a tree, with each tree
node representing a managed object, as shown in
. Each node in this tree can be uniquely
identified by a path starting from the root.
Figure 41-1
Architecture of the MIB tree
A
2
6
1
5
2
1
1
2
1
B
The management information base (MIB) describes the hierarchical architecture of the tree and it is the
set defined by the standard variables of the monitored network devices. In the above figure, the
managed object B can be uniquely identified by a string of numbers {1.2.1.1}. The number string is the
object identifier (OID) of the managed object.
The common MIBs supported by devices are listed in
.
Table 41-1
Common MIBs
MIB attribute
MIB content
Related RFC
MIB II based on TCP/IP network device
RFC 1213
RFC 1493
BRIDGE MIB
RFC 2675
RIP MIB
RFC 1724
RMON MIB
RFC 2819
Ethernet MIB
RFC 2665
OSPF MIB
RFC 1253
Public MIB
IF MIB
RFC 1573
