Local port mirroring, Remote port mirroring, 2 remote port mirroring – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches User Manual
Page 384
39-2
z
MAC-based mirroring: a device copies packets matching a specified MAC address to the
destination port.
z
VLAN-based mirroring: a device copies packets of a specified VLAN to the destination port.
Local Port Mirroring
In local port mirroring, packets passing through one or more source ports of a device are copied to the
destination port on the same device for packet analysis and monitoring. In this case, the source ports
and the destination port must be located on the same device.
Remote Port Mirroring
Remote port mirroring does not require the source and destination ports to be on the same device. The
source and destination ports can be located on multiple devices across the network. Therefore,
administrators can monitor the traffic on remote devices conveniently.
To implement remote port mirroring, a special VLAN, called remote-probe VLAN, is needed. All mirrored
packets are sent from the reflector port of the source switch to the monitor port (destination port) of the
destination switch through the remote-probe VLAN, so as to implement the monitoring of packets
received on and sent from the source switch on the destination switch.
illustrates the
implementation of remote port mirroring.
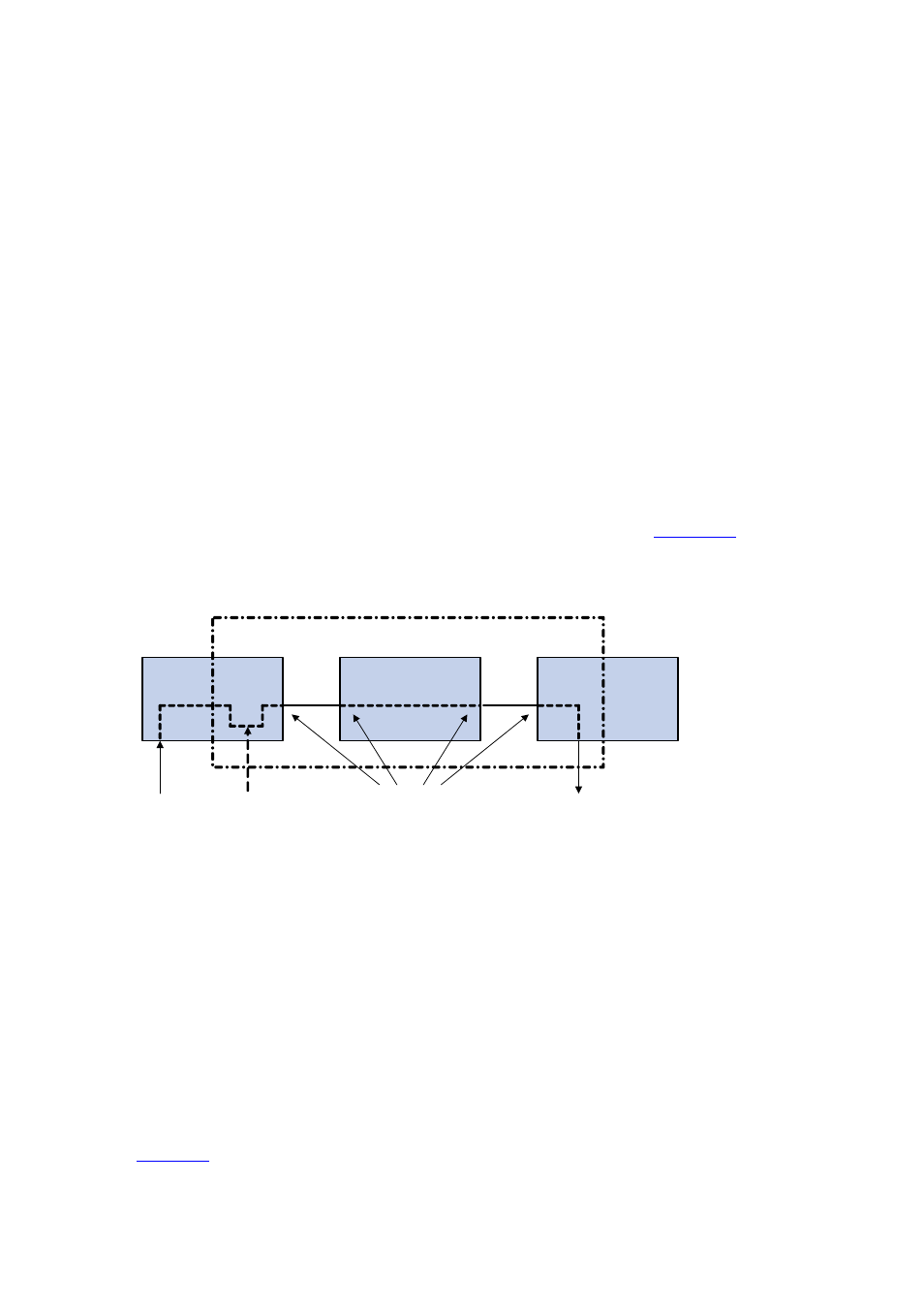
Figure 39-2
Remote port mirroring application
Reflector port
Source Port
Trunk port
Destination port
Remote-probe VLAN
Intermediate Switch
Source
Switch
Destination
Switch
The switches involved in the remote port mirroring implementation play the following three roles.
z
Source switch: The monitored port resident switch. It copies traffic to the reflector port, which then
transmits the traffic to an intermediate switch or destination switch through the remote-probe
VLAN.
z
Intermediate switch: Switches between the source switch and destination switch on the network.
An intermediate switch forwards mirrored traffic flows to the next intermediate switch or the
destination switch through the remote-probe VLAN. No intermediate switch is present if the source
and destination switches directly connect to each other.
z
Destination switch: The remote mirroring destination port resident switch. It forwards mirrored
traffic flows it received from the remote-probe VLAN to the monitoring device through the
destination port.
describes how the ports on various switches are involved in the mirroring operation.
