Edca parameters, Cac admission policies – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches User Manual
Page 165
153
devices have the same idle duration and contention window, and they are equal when contending for a
channel. In WMM, this equal contention mechanism is changed.
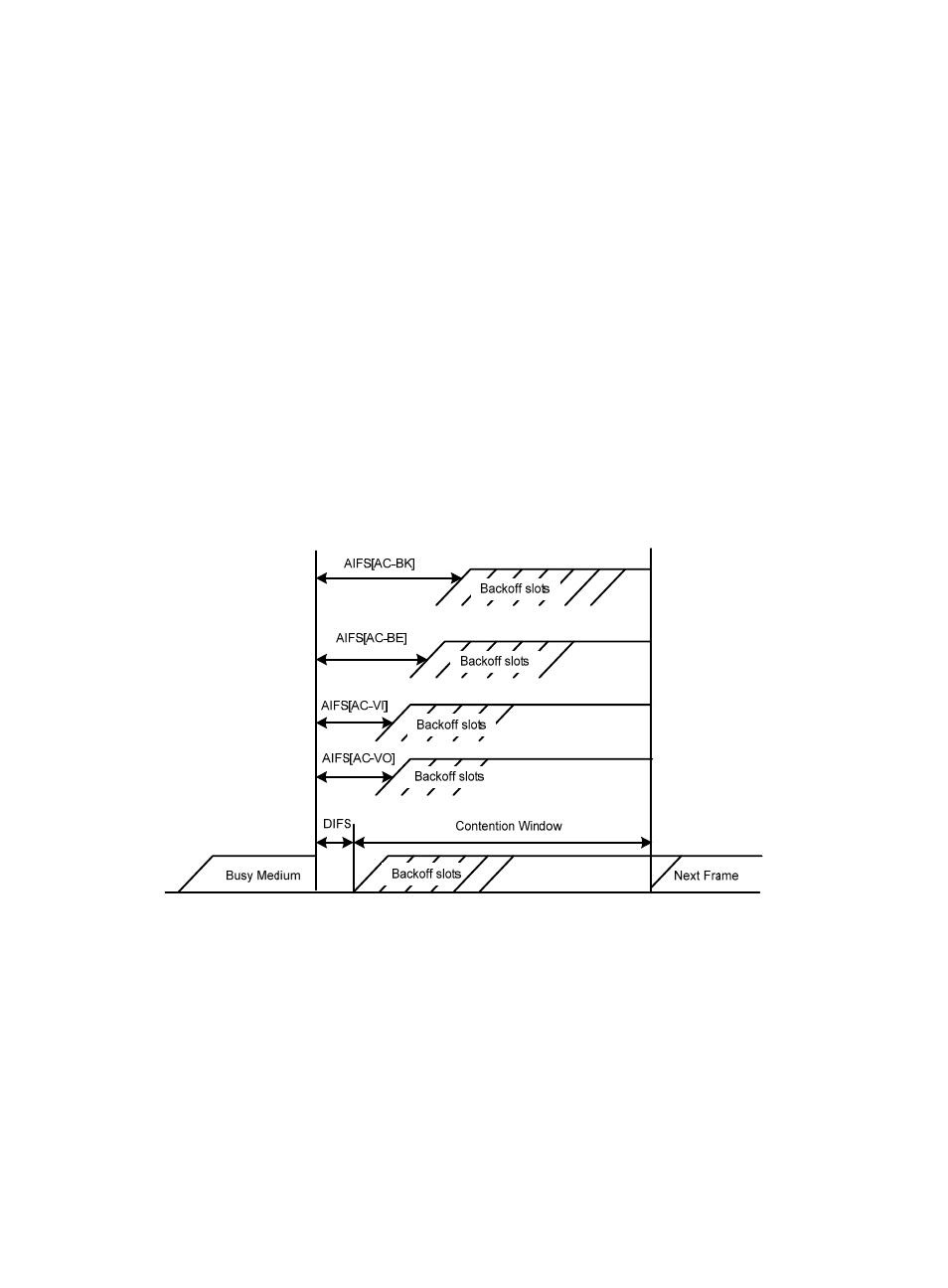
EDCA parameters
WMM assigns data packets in a basic service set (BSS) to four AC queues. By allowing a high-priority
AC queue to have more channel contention opportunities than a low-priority AC queue, WMM offers
different service levels for different AC queues.
WMM defines a set of EDCA parameters for each AC queue, as follows:
•
Arbitration inter-frame spacing number (AIFSN)—Different from the 802.11 protocol where the idle
duration (set using DIFS) is a constant value, WMM can define an idle duration per AC queue. The
idle duration increases as the AIFSN value increases (see
for the AIFS durations).
•
Exponent form of CWmin (ECWmin) and exponent form of CWmax (ECWmax)—Determine the
average backoff slots, which increases as the two values increase (see
for the backoff
slots).
•
Transmission opportunity limit (TXOPLimit)—Indicates the maximum time for which a user can hold
a channel after a successful contention. The greater the TXOPLimit is, the longer the user can hold
the channel. The value 0 indicates that the user can send only one packet each time it holds the
channel.
Figure 78 Per-AC channel contention parameters in WMM
CAC admission policies
CAC requires that a client obtain permission of the AP before it can use a high-priority AC queue for
transmission, thus guaranteeing bandwidth to the clients that have gained access. CAC controls real time
traffic (AC-VO and AC-VI traffic) but not common data traffic (AC-BE and AC-BK traffic).
If a client wants a high-priority AC queue, the client must send a request to the AP. The AP returns a
positive or negative response based on either of the following admission control policies:
•
Channel utilization-based admission policy—The AP calculates the total time that the existing
high-priority AC queues occupy the channel per second, and then calculates the time that the
requesting traffic will occupy the channel per second. If the sum of the two values is smaller than or
equal to the maximum hold time of the channel, the client can use the requested AC queue.
Otherwise, the request is rejected.
- H3C WX5500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX3500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX2500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM3WCMD0 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM1WCME0 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module H3C WA3600 Series Access Points H3C WA2600 Series WLAN Access Points
