Ieee thd and din – Rockwell Automation 1404-M4_M5_M6_M8 Powermonitor 3000 User Manual, PRIOR to Firmware rev. 3.0 User Manual
Page 157
Publication 1404-UM001D-EN-E - October 2004
Advanced Features 8-7
IEEE THD and DIN
Both of these total harmonic distortion calculation methods provide a
summary indication of the amount of distortion due to harmonics
present in a system. The standard IEEE definition of harmonic
distortion is “Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)” and is computed for
each channel as follows:
The standard IEC definition of harmonic distortion is the “Distortion
Index (DIN)” and is computed for each channel as follows:
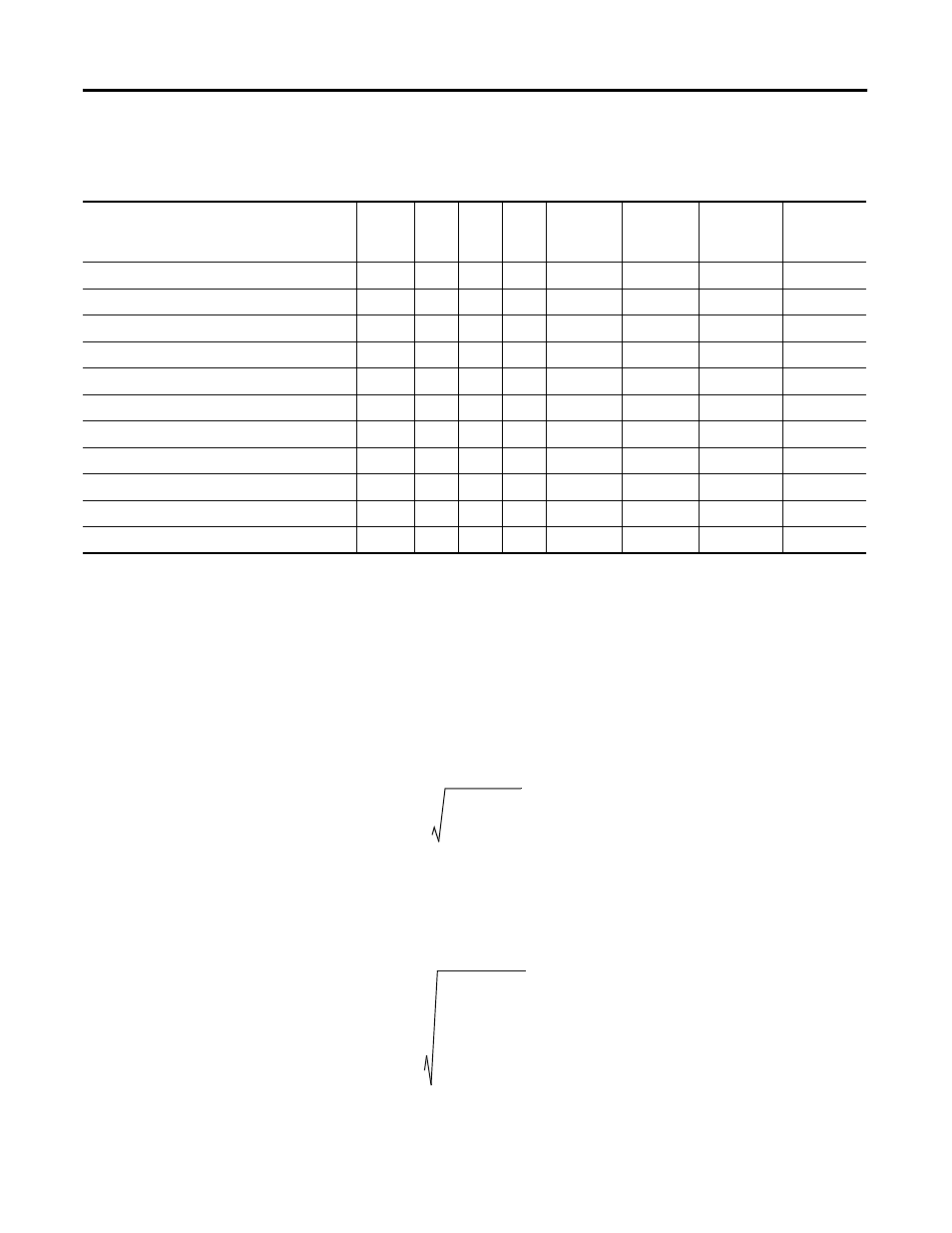
Table 8.2 Harmonic Analysis Functionality
Harmonic data
DM
(Avg.)
M4
M5
M6
M8
Per
current
channel
Per
voltage
channel
Avg. of
current
channels
Avg. of
voltage
channels
IEEE Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
IEC Distortion Index (DIN)
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Crest Factor
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Telephone Interference Factor (TIF)
•
•
•
•
•
•
K-factor
•
•
•
•
•
•
IEEE-519 Total Demand Distortion (TDD)
•
•
•
IEEE 519 Pass / Fail
•
•
•
•
Harmonic distortion, harmonics 1 to 41
•
•
•
•
Harmonic magnitude, harmonics 1 to 41
•
•
•
•
Harmonic distortion, harmonics 42 to 63
•
•
•
Harmonic magnitude, harmonics 42 to 63
•
•
•
THD
∞
Σ
n
2
=
H
n
(
)2
H
1
-------------------------
=
Where:
• H
n
= magnitude of the n
th
harmonic
(n
≤ 41 or 63)
• H
1
= magnitude of fundamental
DIN
∞
Σ
n
2
=
H
n
(
)2
∞
Σ
n
1
=
H
n
(
)2
---------------------
=
Where:
• H
n
= magnitude of the n
th
harmonic
(n
≤ 41 or 63)
• DIN is equivalent to IEC THD
