Bridge priority and the root bridge – Allied Telesis AT-S25 User Manual
Page 92
Section II: Local and Telnet Mangement
92
Bridge Priority
and the Root
Bridge
The first task that bridges perform when a spanning tree protocol is
activated on a network is the selection of a root bridge. A root bridge
distributes network topology information to the other network bridges
and is used by the other bridges to determine if there are redundant
paths in the network.
A root bridge is selected by a combination of a bridge priority number,
also referred to as the bridge identifier, and sometimes the bridge’s MAC
address. The bridge with the lowest bridge priority number in the
network is selected as the root bridge. If two or more bridges have the
same bridge priority number, of those bridges the one with the lowest
MAC address is designated as the root bridge.
The bridge priority number can be changed on an AT-8316F or an AT-
8324 Switch. You could designate which switch on your network you
wish as the root bridge by giving it the lowest bridge priority number.
You might also consider which bridge should function as the backup
root bridge in the event you need to take the primary root bridge off-
line, and assign that bridge the second lowest bridge identifier number.
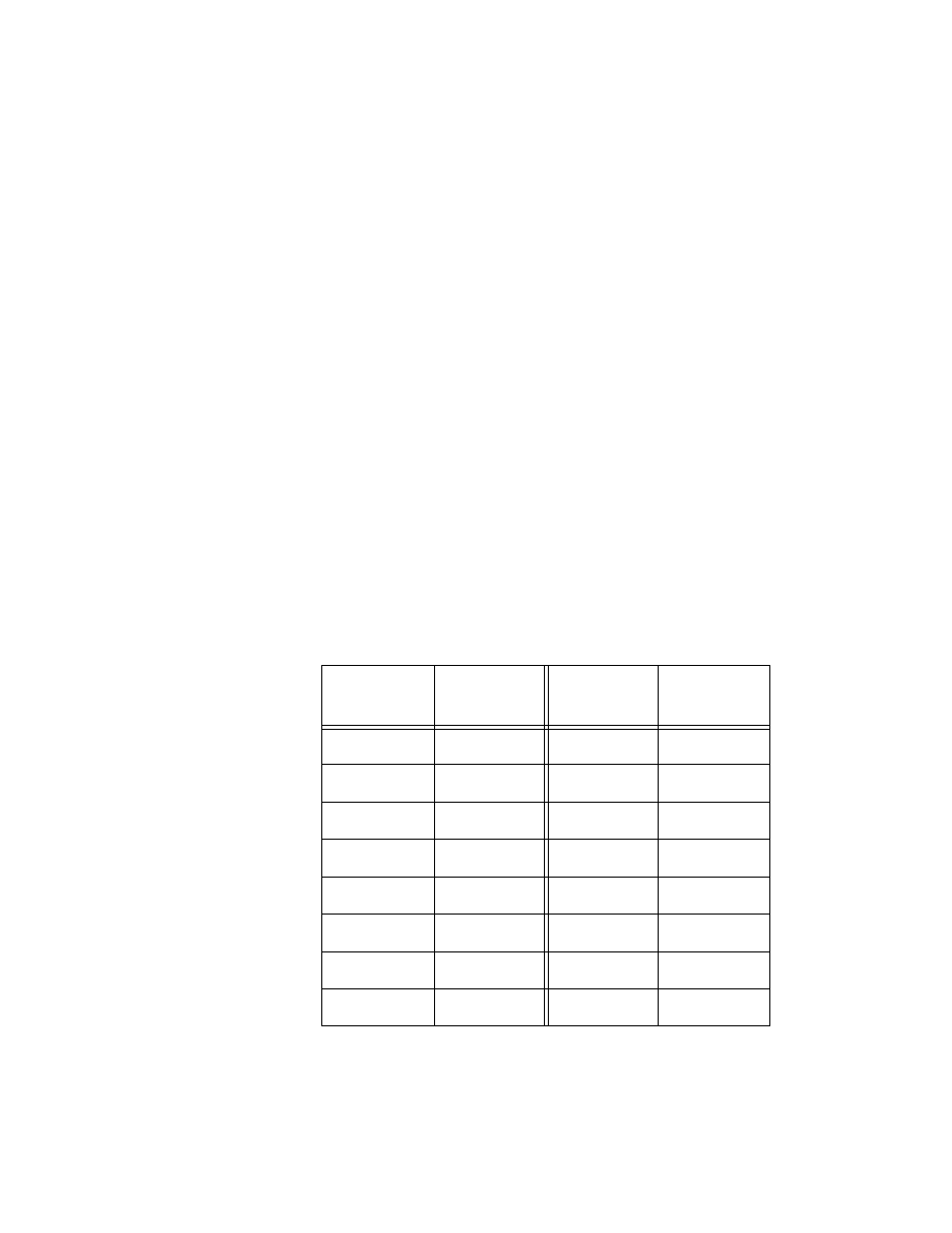
The bridge priority has a range of from 0 to 61440. You could only select
a value that is a multiple of 4096. To make this easier for you, the
management software divides the range into increments. You specify
the increment that represents the desired bridge priority value. The
range is divided into sixteen increments, as shown in the following table.
Table 2 Bridge Priority Value Increments
Increment
Bridge
Priority
Increment
Bridge
Priority
0
0
8
32768
1
4096
9
36864
2
8192
10
40960
3
12288
11
45056
4
16384
12
49152
5
20480
13
53248
6
24576
14
57344
7
28672
15
61440
